|
Melik
Мelik (, from ) was a hereditary Armenian noble title used in Eastern Armenia from the Late Middle Ages until the nineteenth century. The meliks represented some of the last remnants of the old Armenian nobility, as well as Persian nobility in Shirvan and other areas of the Persian Empire. The most prominent and powerful meliks were those of Karabagh ( Artsakh) and Syunik, which ruled autonomous or semi-autonomous principalities known as melikdoms () under Iranian suzerainty. Meliks also existed in Yerevan, Nakhichevan, Sevan, Lori, Northwestern Persia, and other areas, although outside of Karabagh and Syunik most were merely hereditary leaders of local Armenian communities, not rulers of principalities. The meliks of Karabagh each had their troops and military fortifications known as s. They ruled on legal disputes within their territory and collected tax. The meliks of Karabagh saw themselves as the last bastion of Armenian independence in the region. After the conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Hasan-Jalalyan
Hasan-Jalalyan ( is a medieval Armenian dynasty that ruled over parts of the South Caucasus. From the early thirteenth century, the family held sway in Khachen (Greater Artsakh) in what are now the regions of lower Karabakh, Nagorno-Karabakh, and Syunik in modern Armenia. Ulubabian, Bagrat. s.v. Hasan-Jalalyanner asan-Jalalyans Armenian Soviet Encyclopedia, vol. 6, p. 246. The family was founded by Hasan-Jalal Dawla, an Armenian feudal prince from Khachen. The Hasan-Jalalyans maintained their autonomy over the course of several centuries of nominal foreign domination by the Seljuk Turks, Persians and Mongols. They, along with the other Armenian princes and ''meliks'' of Khachen, saw themselves as holding the last bastion of Armenian independence in the region. Through their patronage of churches and monasteries, Armenian culture flourished in the region. By the late sixteenth century, the Hasan-Jalalyan family had branched out to establish principalities in nearby Gülüsta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syunik (historical Province)
Syunik () was a region of historical Armenia and the ninth province (') of the Kingdom of Armenia from 189 BC until 428 AD. From the 7th to 9th centuries, it fell under Arab control. In 821, it formed two Armenian principalities: Kingdom of Syunik and principality of Khachen, which around the year 1000 was proclaimed the Kingdom of Artsakh, becoming one of the last medieval eastern Armenian kingdoms and principalities to maintain its autonomy following the Turkic invasions of the 11th to 14th centuries.Hewsen. ''Armenia'', pp. 118-121. Name The name Syunik is ancient and appears in the earliest Armenian written sources. ', a later name for the province of Iranian origin, first appears in the 6th-century Syriac chronicle of Pseudo-Zacharias; it is first mentioned in Armenian sources in the history of Movses Khorenatsi, who explains this name as deriving from Sisak, the name of one of the descendants of the legendary Armenian progenitor Hayk. Strabo mentions a region of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Artsakh
The Kingdom of Artsakh () was a medieval dependent Armenian kingdom on the territory of Syunik and Artsakh provinces, Gardman canton of Utik province, Mazaz and Varazhnunik canton of Ayrarat province. Contemporary sources referred to it as the Khachen. However, because the domain of Khachen during the reign of Prince Hasan Jalal included the entire territory of the modern Nagorno Karabakh Republic plus many contiguous lands to its west, south and north, his principality was often called the Kingdom of Artsakh. The royal house of Khachen was a cadet branch of the ancient Syunid dynasty and was named Khachen, after its main stronghold. Hasan-Jalal traced his descent to the Armenian Aranshahik dynasty, a family that predated the establishment of the Parthian Arsacids in the region. Artsakh maintained its sovereign rulers, though in the early 13th century they accepted Georgian, then Mongol suzerainty A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik
Malik (; ; ; variously Romanized ''Mallik'', ''Melik'', ''Malka'', ''Malek'', ''Maleek'', ''Malick'', ''Mallick'', ''Melekh'') is the Semitic term translating to "king", recorded in East Semitic and Arabic, and as mlk in Northwest Semitic during the Late Bronze Age (e.g. Aramaic, Canaanite, Hebrew). Although the early forms of the name were to be found among the pre-Arab and pre-Islamic Semitic speakers of the Levant, Canaan, and Mesopotamia, it has since been adopted in various other, mainly but not exclusively Islamized or Arabized non-Semitic Asian languages for their ruling princes and to render kings elsewhere. It is also sometimes used in derived meanings. The female version of Malik is Malikah (; or its various spellings such as '' Malekeh'' or ''Melike''), meaning "queen". The name Malik was originally found among various pre-Arab and non-Muslim Semitic speakers such as the indigenous ethnic Assyrians of Iraq, Amorites, Jews, Arameans, Mandeans, other Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lori (historic Province)
Lori () is a historical geographical region of Armenia. In ancient times and the Middle Ages, it was also known as Tashir or Tashirk. After the construction of Lori Fortress by King David I Anhoghin in the 11th century, the region was also referred to as Lori. Name In ancient times, the region of Lori was known in Armenian as or (, in Georgian). Pliny the Elder, Pliny refers to the region as (Robert H. Hewsen, Robert Hewsen suggests the reading *). In the Middle Ages, Georgians also called the place Somkhiti, i.e., Armenia, along with the other nearest regions. The central part of the region was also referred to as , meaning 'Tashir plain' in Old Armenian (currently Lori Plateau). Until the 7th century, its center was Odzun; later, Lori (Lore) or Loriberd became the central town. It was in the 11th century that the region began to be called Lori after its principal settlement. Geography Lori was located in between the Javakheti (to the west), Virahayots (to the north), Bazu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
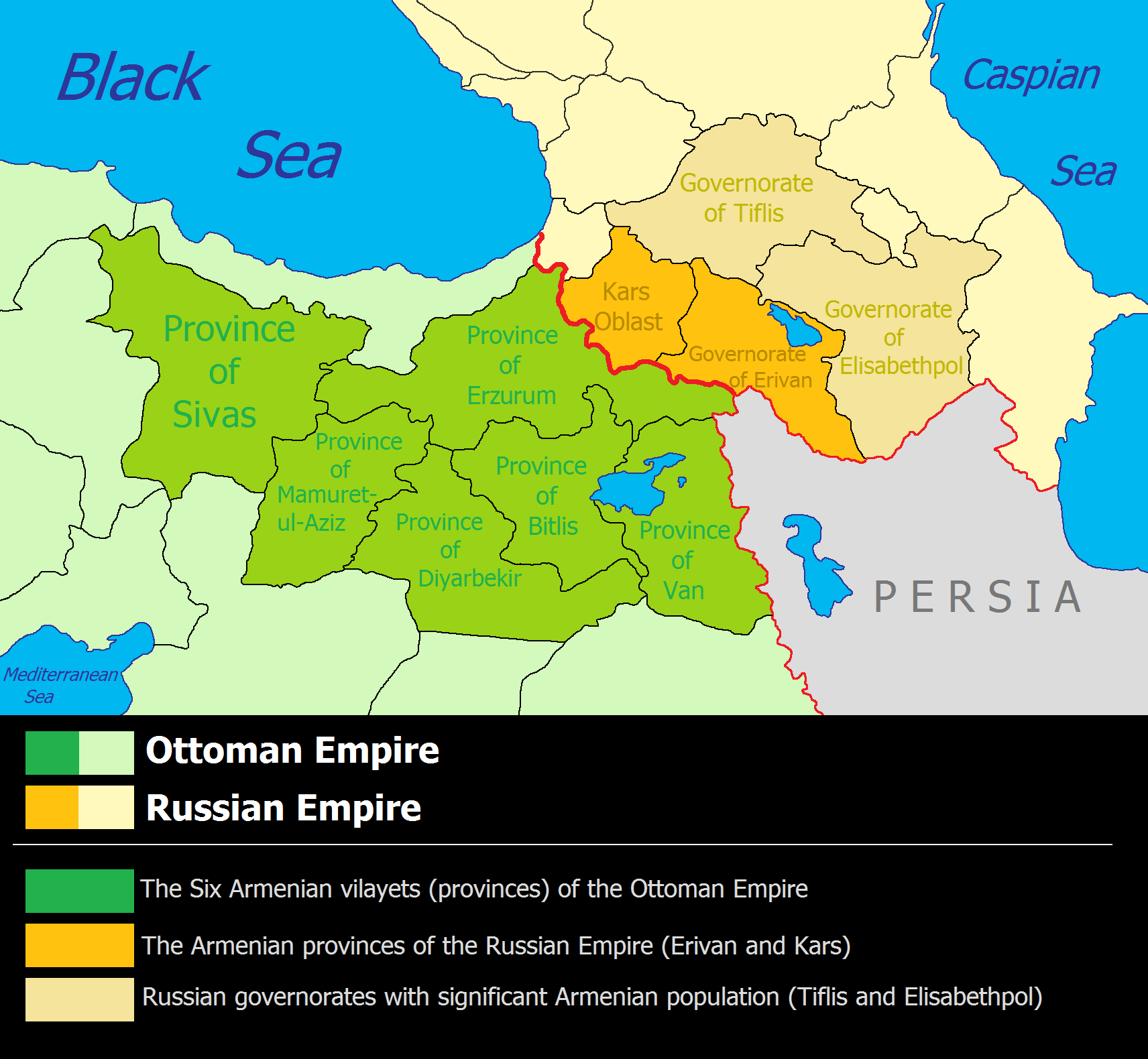
Eastern Armenia
Eastern Armenia (Armenian: Արևելյան Հայաստան, ''Arevelyan Hayastan'') refers to the eastern portion of the Armenian Highlands, historically inhabited by the Armenian people. Throughout history, Eastern Armenia has been contested and ruled by various empires, including the Sasanian, Arab Caliphates, Safavid and Qajar Persia, the Russian Empire, and the Soviet Union. Today, it forms the core of the independent Republic of Armenia. The term gained more precise meaning after the 17th century, particularly following the Treaty of Zuhab (1639), which formalized the division of Armenian territories between the Ottoman Empire (Western Armenia) and Persia (Eastern Armenia). This distinction was reinforced in the 19th century with the Russian Empire’s annexation of Persian-controlled Eastern Armenian lands. Historical Partitions of Armenia Armenia was divided four major times during the medieval and early modern periods: * First Partition (387): Peace of Acilise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Principalities Of Karabakh
5 (five) is a number, numeral (linguistics), numeral and numerical digit, digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. Humans, and many other animals, have 5 Digit (anatomy), digits on their Limb (anatomy), limbs. Mathematics 5 is a Fermat prime, a Mersenne prime exponent, as well as a Fibonacci number. 5 is the first congruent number, as well as the length of the hypotenuse of the smallest integer-sided right triangle, making part of the smallest Pythagorean triple (3, 4, 5). 5 is the first safe prime and the first good prime. 11 forms the first pair of sexy primes with 5. 5 is the second Fermat number, Fermat prime, of a total of five known Fermat primes. 5 is also the first of three known Wilson primes (5, 13, 563). Geometry A shape with five sides is called a pentagon. The pentagon is the first regular polygon that does not Tessellation, tile the Plane (geometry), plane with copies of itself. It is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somkhiti
Somkhiti ( ka, სომხითი, ) was an ambiguous geographic term used in medieval and early modern Georgian historical sources to refer to Armenia on one hand and to the Armeno-Georgian marchlands along the river valleys of Debed and Khrami on the other hand. In the 18th century, ''Somkhiti'' was largely replaced with Somkheti ( ka, სომხეთი, ) as a Georgian exonym for Armenia, but it continued, for some time, to denote the frontier region which is currently divided between Lori, Armenia, and Kvemo Kartli, Georgia. This patch of land was sometimes referred to as "Georgian Armenia" in the 19th-century European sources."Georgia", in ''Encyclopædia Metropolitana'', ed. by Edward Smedley, Hugh James Rose and Henry John Rose (1845), p. 538. Etymology The term "Somkhiti"/"Somkheti" is presumed by modern scholars to have been derived from "Sukhmi" or "Sokhmi", the name of an ancient land located by the Assyrian and Urartian records along the upper Euphrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Khachen
The Principality of Khachen ( Modern Armenian: ) was a medieval Armenian principality on the territory of historical Artsakh (present-day Karabakh).''Abū-Dulaf Misʻar Ibn Muhalhil's Travels in Iran (circa A.D. 950)'', ed. and trans. Vladimir Minorsky. Cairo: Cairo University Press, 1955, p. 74. "Khajin (Armenian Khachen) was an Armenian principality immediately south of Barda'a." The provinces of Artsakh and Utik were attached to the Kingdom of Armenia in antiquity, although they were later lost to Caucasian Albania. In the early medieval period, these provinces were under Sassanid and then Arab suzerainty until the establishment of the Bagratid Kingdom of Armenia in the 9th century. From the 12th century, the principality of Khachen dominated the region. The Byzantine emperor Constantine VII addressed his letters to the prince of Khachen with the inscription "To Prince of Khachen, Armenia." All of the contemporary sources refer to the ruler of the principality an Arme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jahan Shah
Muzaffar al-Din Jahan Shah ibn Yusuf (; ; 1397 in Khoy or 1405 in Mardin – 30 October or 11 November 1467 near Bingöl) or Abu al-Muzaffar Jahan Shah was the leader of the Qara Qoyunlu Oghuz Turkic tribal confederacy in Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan and Arran (Azerbaijan), Arran who reigned c. 1438 – 1467. During his reign he managed to expand the Qara Qoyunlu's territory to its largest extent, including Anatolia, Eastern Anatolia, most of present-day Iraq, central Iran, and even eventually Kerman. He also conquered neighbouring states. He was one of the greatest rulers of the Qara Qoyunlu. He was also allegedly fond of drinking and entertainment. During his reign Jahan Shah had the Gökmedrese and Muzafferiye theological schools constructed in his capital city Tabriz. Early life Jahan Shah was the son of Qara Yusuf. He had several brothers, some of whom ruled the Qara Qoyunlu before him: Pirbudag (r.1411–1414), Ispend bin Yusuf, Iskandar (Qara Qoyunlu), Iskander (r.1421� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qara Qoyunlu
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu (, ; ), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, English Black Sheep, Turkmen tribal federation that ruled Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Iraq from about 1375 to 1468." "Better known as Turkomans... the interim Ak-Koyunlu and Karakoyunlu dynasties..." monarchy that ruled over the territory comprising present-day Azerbaijan, Armenia, northwestern Iran, eastern Turkey, and northeastern Iraq from about 1374 to 1468. History Etymology The name Qara Qoyunlu literally means "hose withblack sheep". It has been suggested that this name refers to old totemic symbols, but according to Rashid al-Din Hamadani, the Turks were forbidden to eat the flesh of their totem-animals, and so this is unlikely given the importance of mutton in the diet of pastoral nomads. Another hypothesis is that the name refers to the predominant color of their flocks. Origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert H
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |