|
Makar
A makar () is a term from Scottish literature for a poet or bard, often thought of as a royal court poet. Since the 19th century, the term ''The Makars'' has been specifically used to refer to a number of poets of fifteenth and sixteenth century Scotland, in particular Robert Henryson, William Dunbar and Gavin Douglas, who wrote a diverse genre of works in Middle Scots in the period of the Northern Renaissance. The Makars have often been referred to by literary critics as ''Scots Chaucerians''. In modern usage, poets of the Scots revival in the 18th century, such as Allan Ramsay and Robert Fergusson are also makars. Since 2002, the term "makar" has been revived as the name for a publicly funded poet, first in Edinburgh, followed by the cities of Glasgow, Stirling and Dundee. In 2004 the position of Makar, was authorized by the Scottish Parliament. Etymology Middle Scots (plural ) is the equivalent of Middle English '' maker''. The word functions as a calque (literal t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makar (National Poet For Scotland)
The Makar is the national poet of Scotland which was established in February 2004 by the Scottish Executive and supported by Creative Scotland. The incumbent Makar serves a maximum term of three years which is non–renewable, and has overall responsibility for the promotion of literacy, poetry and writing across the country, as well as producing annual reports for both the Scottish Government and Scottish Parliament. The current Makar is Pàdraig MacAoidh, who was appointed in December 2024 by First Minister of Scotland, first minister John Swinney. Holders of the post are appointed by the Scottish Government and supported by the Scottish Poetry Library, which celebrated its 40th anniversary in 2024. History The position of Makar, also known in English as "National Poet for Scotland", was created in February 2004 by the Scottish Government under then first minister Jack McConnell. The government was supported by Creative Scotland in the establishment of the position. Speaking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dunbar
William Dunbar (1459 or 1460 – by 1530) was a Scottish makar, or court poet, active in the late fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries. He was closely associated with the court of King James IV and produced a large body of work in Scots distinguished by its great variation in themes and literary styles. He was probably a native of East Lothian, as assumed from a satirical reference in '' The Flyting of Dumbar and Kennedie''. W. Mackay Mackenzie, ''The Poems of William Dunbar'', The Mercat Press, Edinburgh,1990. His surname is also spelt ''Dumbar''. Biography Dunbar first appears in the historical record in 1474 as a new student or ''determinant'' of the Faculty of Arts at the University of St Andrews.J.M. Anderson, ''Early records of the University of St Andrews: the graduation roll 1413–1579 and the matriculation roll 1473–1579'', Scottish History Society, Edinburgh, 1926A.I. Dunlop, Acta facultatis artium Universitatis Sanctandree, 1413–1588, Oliver and Boyd, Edinb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Literature
Scottish literature is literature written in Scotland or by Scottish writers. It includes works in English, Scottish Gaelic, Scots, Brythonic, French, Latin, Norn or other languages written within the modern boundaries of Scotland. The earliest extant literature written in what is now Scotland, was composed in Brythonic speech in the sixth century and has survived as part of Welsh literature. In the following centuries there was literature in Latin, under the influence of the Catholic Church, and in Old English, brought by Anglian settlers. As the state of Alba developed into the kingdom of Scotland from the eighth century, there was a flourishing literary elite who regularly produced texts in both Gaelic and Latin, sharing a common literary culture with Ireland and elsewhere. After the Davidian Revolution of the thirteenth century a flourishing French language culture predominated, while Norse literature was produced from areas of Scandinavian settlement. The first survi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Fergusson
Robert Fergusson (5 September 1750 – 17 October 1774) was a Scottish poet. After formal education at the University of St Andrews, Fergusson led a Bohemianism, bohemian life in Edinburgh, the city of his birth, then at the height of intellectual and cultural ferment as part of the Scottish Enlightenment. Many of his extant poems were printed from 1771 onwards in Walter Ruddiman's ''Weekly Magazine'', and a collected works was first published early in 1773. Despite a short life, his career was highly influential, especially through its impact on Robert Burns. He wrote both Scottish English and the Scots language, and it is his vivid and masterly writing in the latter ''language, leid'' for which he is principally acclaimed. Life Robert Fergusson was born in a tenement between Cap and Feather Close and Halkerstons Wynd, both small vennels north of Edinburgh's Royal Mile, demolished in 1763 to make way for what is today the hidden southern arches of the North Bridge, Edinbur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Henryson
Robert Henryson (Middle Scots: Robert Henrysoun) was a poet who flourished in Scotland in the period c. 1460–1500. Counted among the Scots language, Scots ''makars'', he lived in the royal burgh of Dunfermline and is a distinctive voice in the Northern Renaissance at a time when the culture was on a cusp between Middle Ages, medieval and renaissance sensibilities. Little is known of his life, but evidence suggests that he was a teacher who had training in law and the Liberal arts, humanities, that he had a connection with Dunfermline Abbey and that he may also have been associated for a period with University of Glasgow, Glasgow University. His poetry was composed in Middle Scots at a time when this was the state language. His writing consists mainly of narrative poetry, narrative works. His surviving body of work amounts to almost 5000 lines. Works Henryson's surviving canon consists of three long poems and around twelve miscellaneous short works in various genres. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Ramsay (poet)
Allan Ramsay (15 October 16867 January 1758) was a Scottish poet (or ''makar''), playwright, publisher, librarian and impresario of early Scottish Enlightenment, Enlightenment Edinburgh. Ramsay's influence extended to England, foreshadowing the reaction that followed the publication of ''Percy's Reliques''. He was on close terms with the leading Intellectual#Man of Letters, men of letters in Scotland and England. He corresponded with William Hamilton (Jacobite poet), William Hamilton of Bangour, William Somervile, John Gay and Alexander Pope. He began writing poetry as a member of the Easy Club and in 1715 became Club Laureate. Ramsay published verses and turned bookseller in 1718, selling poetry collections like ''Wealth and the Woody'', a satire on the South Sea Company. In 1720, he collected and published his poems, establishing a circulating library in 1726. Ramsay edited ''The Tea-Table Miscellany'' and ''The Ever Green'' and is considered as a pastoral writer and editor who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Barbour (poet)
John Barbour (c.1320 – 13 March 1395) was a Scottish people, Scottish poet and the first major named literary figure to write in Scots language, Scots. His principal surviving work is the historical verse romance, ''The Brus'' (''The Robert I of Scotland, Bruce''), and his reputation from this poem is such that other long works in Scots which survive from the period are sometimes thought to be by him. He is known to have written a number of other works, but other titles definitely ascribed to his authorship, such as ''The Stewartis Oryginalle'' (''Genealogy of the House of Stuart, Stewarts'') and ''The Brut'' (''Brutus of Troy, Brutus''), are now lost. Barbour was latterly Archdeacon of the St Machar's Cathedral, Diocese of Aberdeen in Scotland. He also studied in University of Oxford, Oxford and University of Paris, Paris. Although he was a man of the church, his surviving writing is strongly secular in both tone and themes. His principal patron was Robert II of Scotla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
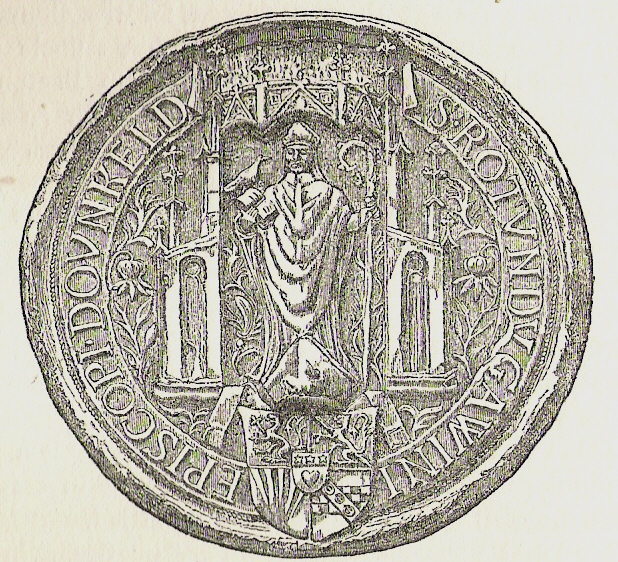
Gavin Douglas
Gavin Douglas (c. 1474 – September 1522) was a Scottish bishop, makar and translator. Although he had an important political career, he is chiefly remembered for his poetry. His main pioneering achievement was the '' Eneados'', a full and faithful vernacular translation of the ''Aeneid'' of Virgil into Scots, and the first successful example of its kind in any Anglic language. Other extant poetry of his includes ''Palice of Honour'', and possibly ''King Hart''. Life and career Early life Gavin (or Gawin, Gawane, Gawain) Douglas was born c. 1474–76, at Tantallon Castle, East Lothian, the third son of Archibald, 5th Earl of Angus by his second wife Elizabeth Boyd. A Vatican register records that Gavin Douglas was 13 in 1489, suggesting he was born in 1476. An application had been lodged to award Gavin the right to hold a Church canonry or prebend and enjoy its income. Another appeal to Rome concerning church appointments made in February 1495 states his age as 20. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Scots
Middle Scots was the Anglic language of Lowland Scotland in the period from 1450 to 1700. By the end of the 15th century, its phonology, orthography, accidence, syntax and vocabulary had diverged markedly from Early Scots, which was virtually indistinguishable from early Northumbrian Middle English. Subsequently, the orthography of Middle Scots differed from that of the emerging Early Modern English standard that was being used in England. Middle Scots was fairly uniform throughout its many texts, albeit with some variation due to the use of Romance forms in translations from Latin or French, turns of phrases and grammar in recensions of southern texts influenced by southern forms, misunderstandings and mistakes made by foreign printers. History The now established Stewart identification with the lowland language had finally secured the division of Scotland into two parts, the Gaelic Highlands and the Anglic Lowlands. The adherence of many Highlanders to the Catholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gower
John Gower (; c. 1330 – October 1408) was an English poet, a contemporary of William Langland and the Pearl Poet, and a personal friend of Geoffrey Chaucer. He is remembered primarily for three major works—the ''Mirour de l'Omme'', ''Vox Clamantis'', and ''Confessio Amantis—''three long poems written in French, Latin, and English respectively, which are united by common moral and political themes. Life Few details are known of Gower's early life. He was probably born into a family which held properties in Kent and Kentwell Hall, Suffolk.Lee, Sidney (1890). "wikisource:Dictionary of National Biography, 1885-1900/Gower, John, Gower, John". In ''Dictionary of National Biography''. 22. London. pp. 299-304. Stanley and Smith use a Confessio Amantis#Language, linguistic argument to conclude that "Gower’s formative years were spent partly in Kent and partly in Suffolk". Southern and Nicolas conclude that the Gower family of Kent and Suffolk cannot be related to the Yorkshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernacular
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken language, spoken form of language, particularly when perceptual dialectology, perceived as having lower social status or less Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige than standard language, which is more codification (linguistics), codified, institutionally promoted, literary language, literary, or formal. More narrowly, a particular language variety that does not hold a widespread high-status perception, and sometimes even carries social stigma, is also called a vernacular, vernacular dialect, nonstandard dialect, etc. and is typically its speakers' native language, native variety. Regardless of any such stigma, all nonstandard dialects are full-fledged varieties of language with their own consistent grammatical structure, phonology, sound system, body of vocabulary, etc. Overview Like any native language variety, a vernacular has an internally coherent system of grammar. It may be associated with a particular set of vocabulary, and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |