|
Magnetoelastic Filament
Magnetoelastic filaments are one-dimensional composite structures that exhibit both magnetic and elastic properties. Interest in these materials tends to focus on the ability to precisely control mechanical events using an external magnetic field. Like piezoelectricity materials, they can be used as actuators, but do not need to be physically connected to a power source. The conformations adopted by magnetoelastic filaments are dictated by the competition between its elastic and magnetic properties. Mechanical Behavior Magnetic nanochains Magnetic nanochains are a new class of magnetoresponsive and superparamagnetic nanostructures with highly anisotropic shapes which can be manipulated using magnetic field and magnetic field gradient. Such nanochains consist of self-assembled nanoparticle clusters which are magnetically assembled and fixated into a chain. Among the various linking methods used are silica coating, polyacrylic acid (PAA) coating, tetraethoxysilane condensation, biot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied stress (mechanics), mechanical stress. The piezoelectric effect results from the linear electromechanical interaction between the mechanical and electrical states in crystalline materials with no centrosymmetry, inversion symmetry. The piezoelectric effect is a reversible process (thermodynamics), reversible process: List of piezoelectric materials, materials exhibiting the piezoelectric effect also exhibit the reverse piezoelectric effect, the internal generation of a mechanical strain resulting from an applied electric field. For example, lead zirconate titanate crystals will generate measurable piezoelectricity when their static structure is Deformation (physics), deformed by about 0.1% of the original dimension. Conversely, those same crystals will change about 0.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larmor Precession
Sir Joseph Larmor (; 11 July 1857 – 19 May 1942) was an Irish mathematician and physicist who made breakthroughs in the understanding of electricity, dynamics, thermodynamics, and the electron theory of matter. His most influential work was ''Aether and Matter'', a theoretical physics book published in 1900. Biography He was born in Magheragall in County Antrim, the son of Hugh Larmor, a Belfast shopkeeper and his wife, Anna Wright. The family moved to Belfast circa 1860, and he was educated at the Royal Belfast Academical Institution, and then studied mathematics and experimental science at Queen's College, Belfast (BA 1874, MA 1875), where one of his teachers was John Purser. He subsequently studied at St John's College, Cambridge, where in 1880 he was Senior Wrangler ( J. J. Thomson was second wrangler that year) and Smith's Prizeman, getting his MA in 1883. After teaching physics for a few years at Queen's College, Galway, he accepted a lectureship in mathematics at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostriction
Magnetostriction is a property of magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron. Magnetostriction applies to magnetic fields, while electrostriction applies to electric fields. Magnetostriction causes energy loss due to frictional heating in susceptible ferromagnetic cores, and is also responsible for the low-pitched humming sound that can be heard coming from transformers, where alternating currents produce a changing magnetic field. Explanation Internally, ferromagnetic materials have a structure that is divided into '' domains'', each of which is a region of uniform magnetization. When a magnetic field is applied, the boundaries between the domains shift and the domains rota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Shape-memory Alloy
A magnetic shape-memory alloy (MSMA) is a type of smart material that can undergo significant and reversible changes in shape in response to a magnetic field. This behavior arises due to a combination of magnetic and shape-memory properties within the alloy, allowing it to produce mechanical motion or force under magnetic actuation. MSMAs are commonly made from ferromagnetic materials, particularly nickel-manganese-gallium (Ni-Mn-Ga), and are useful in applications requiring rapid, controllable, and repeatable movement. Introduction MSM alloys are ferromagnetic materials that can produce motion and forces under moderate magnetic fields. Typically, MSMAs are alloys of Nickel, Manganese and Gallium (Ni-Mn-Ga). A ''magnetically induced deformation'' of about 0.2% was presented in 1996 by Dr. Kari Ullakko and co-workers at MIT. Since then, improvements on the production process and on the subsequent treatment of the alloys have led to deformations of up to 6% for commercially availabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology, translating historic nanoscience insights and inventions into practical application. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials (materials whose structure is on the scale of nanometers, i.e. billionths of a meter). Functionalities can be added to nanomaterials by interfacing them with biological molecules or structures. The size of nanomaterials is similar to that of most biological molecules and structures; therefore, nanomaterials can be useful for both in vivo and in vitro biomedical research and applications. Thus far, the integration of nanomaterials with biology has led to the development of diagnostic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
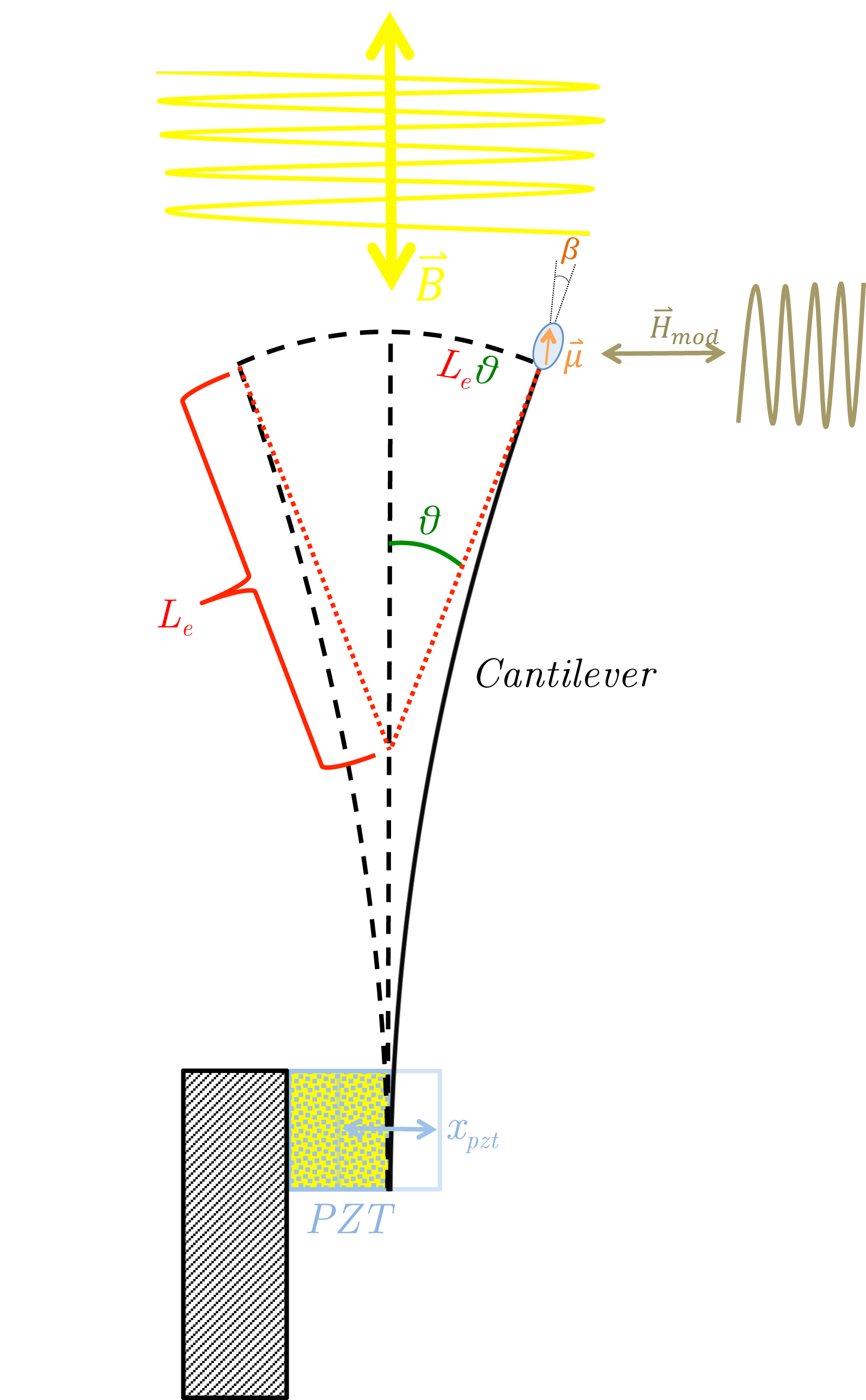
Cantilever Magnetometry
Cantilever magnetometry is the use of a cantilever to measure the magnetic moment of magnetic particles. On the end of cantilever is attached a small piece of magnetism, magnetic material, which interacts with external magnetic fields and exerts torque on the cantilever. These torques cause the cantilever to oscillate faster or slower, depending on the orientation of the particle's moment with respect to the external field, and the magnitude of the moment. The magnitude of the moment and magnetic anisotropy of the material can be deduced by measuring the cantilever's oscillation frequency versus external field. A useful, although limited analogy is that of a pendulum: on earth it oscillates with one frequency, while the same pendulum on, say, the moon, would oscillate with a slower frequency. This is because the mass on the end of the pendulum interacts with the external gravitational field, much as a magnetic moment interacts with an external magnetic field. Cantilever equation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focused Ion Beam
Focused ion beam, also known as FIB, is a technique used particularly in the semiconductor industry, materials science and increasingly in the biological field for site-specific analysis, deposition, and ablation of materials. A FIB setup is a scientific instrument that resembles a scanning electron microscope (SEM). However, while the SEM uses a focused beam of electrons to image the sample in the chamber, a FIB setup uses a focused beam of ions instead. FIB can also be incorporated in a system with both electron and ion beam columns, allowing the same feature to be investigated using either of the beams. FIB should not be confused with using a beam of focused ions for direct write lithography (such as in proton beam writing). These are generally quite different systems where the material is modified by other mechanisms. Ion beam source Most widespread instruments are using liquid metal ion sources (LMIS), especially gallium ion sources. Ion sources based on elemental gold an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Angle
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, , and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes at the magic angle. This property makes the magic angle of particular importance in magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy. In magnetic resonance imaging, structures with ordered collagen, such as tendons and ligaments, oriented at the magic angle may appear hyperintense in some sequences; this is called the magic angle artifact or effect. Mathematical definition The magic angle ''θ''m is \theta_\mathrm = \arccos \frac = \arctan \sqrt \approx 0.955\,32\ \text \approx 54.7^\circ \! , where arccos and arctan are the inverse cosine and tangent functions respectively. is the angle between the space diagonal of a cube and any of its three connecting edges, see image. Another representation of the magic angle is half of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
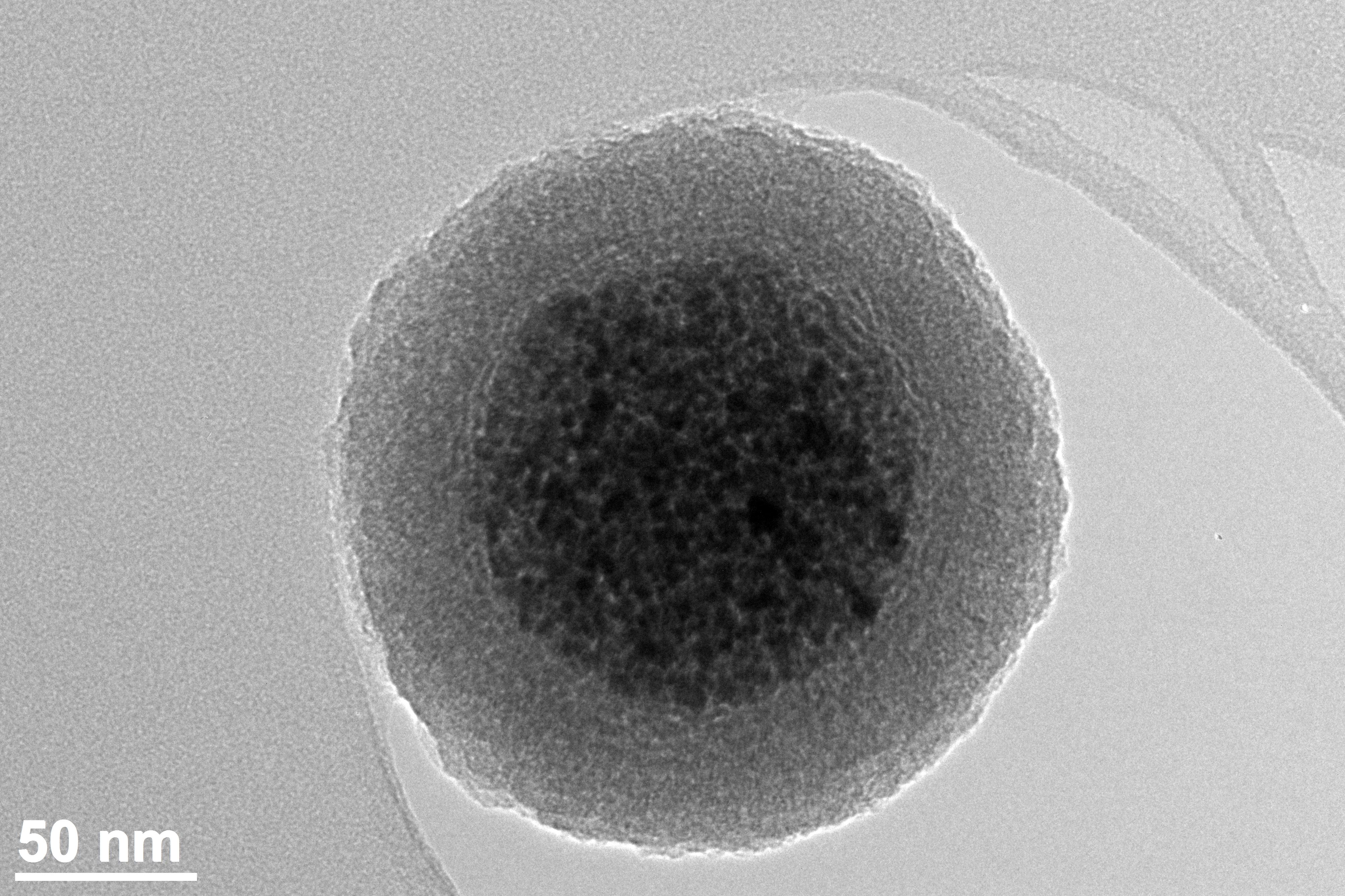
Magnetic Nanoparticles
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are a class of nanoparticle that can be manipulated using magnetic fields. Such particles commonly consist of two components, a magnetic material, often iron, nickel and cobalt, and a chemical component that has functionality. While nanoparticles are smaller than 1 micrometer in diameter (typically 1–100 nanometers), the larger microbeads are 0.5–500 micrometer in diameter. Magnetic nanoparticle clusters that are composed of a number of individual magnetic nanoparticles are known as magnetic nanobeads with a diameter of 50–200 nanometers. Magnetic nanoparticle clusters are a basis for their further magnetic assembly into magnetic nanochains. The magnetic nanoparticles have been the focus of much research recently because they possess attractive properties which could see potential use in catalysis including nanomaterial-based catalysts, biomedicine and tissue specific targeting, magnetically tunable colloidal photonic crystals, microfluidics, mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Nanochain
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, magnetism is one of two aspects of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminium and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Iron oxide nanoparticles are iron oxide particles with diameters between about 1 and 100 nanometers. The two main forms are composed of magnetite () and its oxidized form maghemite (γ-). They have attracted extensive interest due to their superparamagnetic properties and their potential applications in many fields (although cobalt and nickel are also highly magnetic materials, they are toxic and easily oxidized) including molecular imaging. Applications of iron oxide nanoparticles include terabit magnetic storage devices, catalysis, sensors, superparamagnetic relaxometry, high-sensitivity biomolecular magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic particle imaging, magnetic fluid hyperthermia, separation of biomolecules, and targeted drug and gene delivery for medical diagnosis and therapeutics. These applications require coating of the nanoparticles by agents such as long-chain fatty acids, alkyl-substituted amines, and diols. They have been used in formulations for supplementation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Decomposition
Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. It is used by plants to make cellulose, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world, for use in cell walls, and by all living organisms to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used by the cell as energy. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as amylose and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form is -glucose, while its stereoisomer -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |