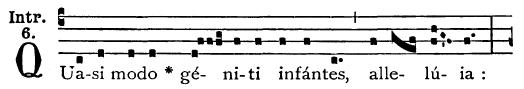|
Katabasia
Katabasia or Katavasia (Greek καταβασία, from καταβαίον, "descend") is a type of hymn, and the last troparion of an ode of a canon, chanted in the Eastern Orthodox Church and those Eastern Catholic Churches which follow the Byzantine Rite. Its name is derived from the Greek word ''katabasia'' for descent, so called because the cantors used to descend from their kliroses (choir stands) and unite in the middle of the church to sing them. The katabasia is an irmos that is sung at the end of an ode of the canon. The katabasia is chanted by the choir, who descend from their seats (''kathismata'') and stand on the floor of the church to sing it, whence its name. Katabasia are chanted at Matins and sometimes during other Divine Services such as Compline. They are also found at other occasional services such as the Mystery of Unction or funerals. At Matins, on ordinary weekdays, only Odes 3, 6, 8 and 9 have katabasia. On Sundays and higher-ranking feast days, there will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon (hymnography)
A canon () is a structured hymn used in a number of Eastern Orthodox services. It consists of nine ''odes'', based on the Biblical canticles. Most of these are found in the Old Testament, but the final ode is taken from the Magnificat and Song of Zechariah from the New Testament. The roots of this type of hymn go as far back as the 5th century, reaching maturity in the Greek language through the work of St. Andrew of Crete, whose penitential '' Great Canon'' is still used on certain occasions during Great Lent. It was further developed in the 8th century by Sts. John of Damascus and Cosmas of Jerusalem, and in the 9th century by Sts. Joseph the Hymnographer and Theophanes the Branded. Over time the canon came to replace the , a vestigial form of which is still used on several occasions and which has been incorporated into the performance of the canon. Each canon develops a specific theme, such as repentance or honouring a particular saint. Sometimes more than one canon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unction
Anointing is the ritual act of pouring aromatic oil over a person's head or entire body. By extension, the term is also applied to related acts of sprinkling, dousing, or smearing a person or object with any perfumed oil, milk, butter, or other fat. Scented oils are used as perfumes and sharing them is an act of hospitality. Their use to introduce a divine influence or presence is recorded from the earliest times; anointing was thus used as a form of medicine, thought to rid persons and things of dangerous spirits and demons which were believed to cause disease. In present usage, "anointing" is typically used for ceremonial blessings such as the coronation of European monarchs. This continues an earlier Hebrew practice most famously observed in the anointings of Aaron as high priest and both Saul and David by the prophet Samuel. The concept is important to the figure of the Messiah or the Christ (Hebrew and Greek for "The Anointed One") who appear prominently in Jewish a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Sunday
The Second Sunday of Easter is the eighth day of the Christian season of Eastertide, and the seventh after Easter Sunday. It is known by various names, including Divine Mercy Sunday, the Octave Day of Easter, White Sunday (), Quasimodo Sunday, Bright Sunday and Low Sunday. In Eastern Christianity, it is known as Antipascha, New Sunday, and Thomas Sunday. Biblical account The Second Sunday of Easter is the eighth day after Easter using the mode of inclusive counting, according to which Easter itself is the first day of the eight. Christian traditions which commemorate this day recall the Biblical account recorded to have happened on the same eighth day after the original Resurrection. It is because of this Scriptural episode that this day is called ''Thomas Sunday'' in the Eastern tradition. Western Christianity Names White Sunday In early Roman Rite liturgical books, Easter Week used to be known as "White Week" (), because of the white robes worn during that week ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bright Saturday
Easter Saturday, on the Christian calendar, is the seventh day of Eastertide, being the Saturday of Easter or Bright Week. In the kalendar of Western Christianity it is the last day of Easter Week, sometimes referred to as the Saturday of Easter Week or Saturday in Easter Week. It is the seventh day in the Octave of Easter too. In the liturgy of Eastern Christianity it is the last day of Bright Week, and called Bright Saturday, The Bright and Holy Septave Saturday of Easter Eve, or The Bright and Holy Septave Paschal Artos and Octoechoes Saturday of Iscariot's Byzantine Easter Eve. Easter Saturday is the day preceding the Second Sunday of Easter (also known as St. Thomas Sunday or Divine Mercy Sunday). Terminology The term "Easter Saturday" is also used colloquially to refer to Holy Saturday a.k.a. Easter Eve – a week before the religious holiday of Easter Saturday, probably because of references to the Easter weekend. Many people, especially religious authorities, rega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheesefare Sunday
Maslenitsa (; ; ; ), also known as Butter Lady, Butter Week, Crepe week, or Cheesefare Week, is an Eastern Slavic religious and folk holiday which has retained a number of elements of Slavic mythology in its ritual. It is celebrated during the last week before Great Lent; that is, the eighth week before Eastern Orthodox Pascha, equivalent to the West's Sexagesima. The date of Maslenitsa changes every year, depending on the date of the celebration of Easter. It corresponds to the Western Christian Carnival, except that Orthodox Lent begins on a Monday instead of a Wednesday, and the Orthodox date of Easter can differ greatly from the Western Christian date. The traditional attributes of the Maslenitsa celebration are the Maslenitsa effigy, sleigh rides, and festivities. Russians bake blini and flatbread, while Belarusians and Ukrainians cook pierogi and syrniki. Traditions According to archeological evidence from the 2nd century AD, Maslenitsa may be the oldest surviving Slavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triodion
The Triodion (, ; , ; , ), also called the Lenten Triodion (, ), is a liturgical book used by the Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic churches. The book contains the propers for the fasting period preceding Pascha (Easter) and for the weeks leading up to the fast. The canons for weekday Matins in the Triodion contain only three odes and so are known as "triodes", after which the Triodion takes its name. The period which the book covers extends from the Sunday of the Publican and Pharisee (the tenth week before Pascha: twenty-two days before the beginning of Great Lent), and concludes with the Midnight Office of Holy Saturday. The Triodion contains the propers for: * The Pre-Lenten period, begins with a week in which there is no fasting, including on Wednesdays and Fridays, which are normally kept as fast days throughout the year (with few exceptions). *The ''Apokreo'' marks the change of diet to the fasting practice of Lent: meat is no longer eaten after the "First ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meeting Of The Lord
The Presentation of Jesus is an early episode in the life of Jesus Christ, describing his presentation at the Temple in Jerusalem. It is celebrated by many churches 40 days after Christmas on Candlemas, or the "Feast of the Presentation of Jesus". The episode is described in chapter 2 of the Gospel of Luke in the New Testament. Within the account, "Luke's narration of the Presentation in the Temple combines the purification rite with the Jewish ceremony of the redemption of the firstborn (Luke 2, )." In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Presentation of Jesus at the temple is celebrated as one of the twelve Great Feasts, and is sometimes called ''Hypapante'' (, "meeting" in Greek). The Orthodox Churches which use the Julian Calendar celebrate it on 15 February, and the Armenian Church on 14 February. In Western Christianity, the ''Feast of the Presentation of the Lord'' is also known by its earlier name as the ''Feast of the Purification of the Virgin'' or the ''Meeting of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphany (holiday)
Epiphany ( ), also known as "Theophany" in Eastern Christian tradition, is a Christian feast day commemorating the visit of the Magi, the baptism of Jesus, and the wedding at Cana. In Western Christianity, the feast commemorates principally (but not solely) the visit of the Magi to the Christ Child, and thus Jesus Christ's physical manifestation to the Gentiles. It is sometimes called Three Kings' Day, and in some traditions celebrated as Little Christmas. Moreover, the feast of the Epiphany, in some denominations, also initiates the liturgical season of Epiphanytide. Eastern Christians, on the other hand, commemorate the baptism of Jesus in the River Jordan, seen as his manifestation to the world as the Son of God, and celebrate it as the Feast of the Epiphany or of the Theophany. The traditional site of the ministry of John the Baptist is in Al-Maghtas in Jordan, with the baptism of Jesus once marked in Byzantine times by a cross in the middle of the Jordan River, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Kronstadt
John of Kronstadt or John Iliytch Sergieff (Reforms of Russian orthography, pre-reform Russian: ; post-reform ; 1829 – ) was a Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox Archpriest#In Byzantine Christianity, archpriest and a member of the Most Holy Synod of the Russian Orthodox Church. He was known for his mass confessions, numerous miracles, and charitable work, as well as his monarchism, monarchistic, Chauvinism, chauvinistic and anti-communism, anti-communist views.Walter Laqueur. Black Hundreds: The Rise of the Extreme Right in Russia, New York : HarperCollins, 1993 John is a saint of the Eastern Orthodox Church and is known with the Epithet#Religion, epithet "Righteous". Early life The future Saint was born as Ivan Ilyich Sergiyev (Reforms of Russian orthography, pre-reform Russian: ; post-reform ) on in the northern village of Pinezhsky District, Sura, near the White Sea, in the Russian Empire. He came from a hereditary corporation of village clergymen, and his father w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theotokos
''Theotokos'' ( Greek: ) is a title of Mary, mother of Jesus, used especially in Eastern Christianity. The usual Latin translations are or (approximately "parent (fem.) of God"). Familiar English translations are "Mother of God" or "God-bearer" – but these both have different literal equivalents in , and Θεοφόρος respectively. The title has been in use since the 3rd century, in the Syriac tradition (as ) in the Liturgy of Mari and Addai (3rd century)''Addai and Mari, Liturgy of''. Cross, F. L., ed. ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church''. Oxford University Press. 2005. and the Liturgy of St James (4th century). The Council of Ephesus in AD 431 decreed that Mary is the ''Theotokos'' because her son Jesus is both God and man: one divine person from two natures (divine and human) intimately and hypostatically united. The title of Mother of God (Greek: ) or Mother of Incarnate God, abbreviated ΜΡ ΘΥ (the first and last letter of main two words in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterfeast
An Afterfeast, or Postfeast, is a period of celebration attached to one of the Great Feasts celebrated by the Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christian and Eastern Catholic Churches (somewhat analogous to what in Western Christianity would be called an Octave (liturgical), Octave). The celebration of the Great Feasts of the Orthodox Church, Great Feasts of the Church year#Eastern Orthodox Church, church year is extended for a number of days, depending upon the particular Feast. Each day of an Afterfeast will have particular hymns assigned to it, continuing the theme of the Feast being celebrated. At each of the divine services during an Afterfeast, the troparion and kontakion of the feast are read or chanted. The Canon (hymnography), canon of the feast will usually be chanted on every day of the Afterfeast (if two canons were chanted on the day of the feast, they will be alternated on the days of the afterfeast). Most of these Great Feasts also have a day or more of preparation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |