|
Islands Of Inversion
An island of inversion is a region of the chart of nuclides where isotopes have enhanced stability in a sea of mostly very unstable nuclei at the edge of the nuclear map. Each island contains isotopes with a non-standard ordering of single particle levels in the nuclear shell model. Such an area was first described in 1975 by French physicists carrying out spectroscopic mass measurements of exotic isotopes of lithium and sodium. Since then further studies have shown that at least five such regions exist. These are centered on five neutron-rich nuclides: Li, C, Na, Si, and Cr. Because there are five known islands of inversion, physicists have suggested renaming the phenomenon "archipelago of islands of shell breaking". Studies with the purpose of defining the edges of this region are still ongoing. See also * Table of nuclides * Periodic table and Extended periodic table * Island of stability References External links * * ''From Physical Review Letters: New neutron-rich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes And Half-life
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Sodium
There are 20 isotopes of sodium (11Na), ranging from to (except for the still-unknown 36Na and 38Na), and five isomers (two for , and one each for , , and ). is the only stable (and the only primordial) isotope. It is considered a monoisotopic element and it has a standard atomic weight of . Sodium has two radioactive cosmogenic isotopes (, with a half-life of ; and , with a half-life of ). With the exception of those two isotopes, all other isotopes have half-lives under a minute, most under a second. The shortest-lived is the unbound , with a half-life of seconds (although the half-life of the similarly unbound 17Na is not measured). Acute neutron radiation exposure (e.g., from a nuclear criticality accident) converts some of the stable (in the form of Na+ ion) in human blood plasma to . By measuring the concentration of this isotope, the neutron radiation dosage to the victim can be computed. is a positron-emitting isotope with a remarkably long half-life. It is used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Of Stability
In nuclear physics, the island of stability is a predicted set of isotopes of superheavy elements that may have considerably longer half-lives than known isotopes of these elements. It is predicted to appear as an "island" in the chart of nuclides, separated from known stable nuclide, stable and long-lived primordial radionuclides. Its theoretical existence is attributed to stabilizing effects of predicted "Magic number (physics), magic numbers" of protons and neutrons in the superheavy mass region. Several predictions have been made regarding the exact location of the island of stability, though it is generally thought to center near copernicium and flerovium isotopes in the vicinity of the predicted closed neutron nuclear shell model, shell at ''N'' = 184. These models strongly suggest that the closed shell will confer further stability towards nuclear fission, fission and alpha decay. While these effects are expected to be greatest near atomic number ''Z'' =&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Periodic Table
An extended periodic table theorizes about chemical elements beyond those currently known and proven. The element with the highest atomic number known is oganesson (''Z'' = 118), which completes the seventh period (row) in the periodic table. All elements in the eighth period and beyond thus remain purely hypothetical. Elements beyond 118 will be placed in additional periods when discovered, laid out (as with the existing periods) to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the properties of the elements. Any additional periods are expected to contain more elements than the seventh period, as they are calculated to have an additional so-called ''g-block'', containing at least 18 elements with partially filled g- orbitals in each period. An ''eight-period table'' containing this block was suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg in 1969. The first element of the g-block may have atomic number 121, and thus would have the systematic name unbiunium. Despite many searches, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
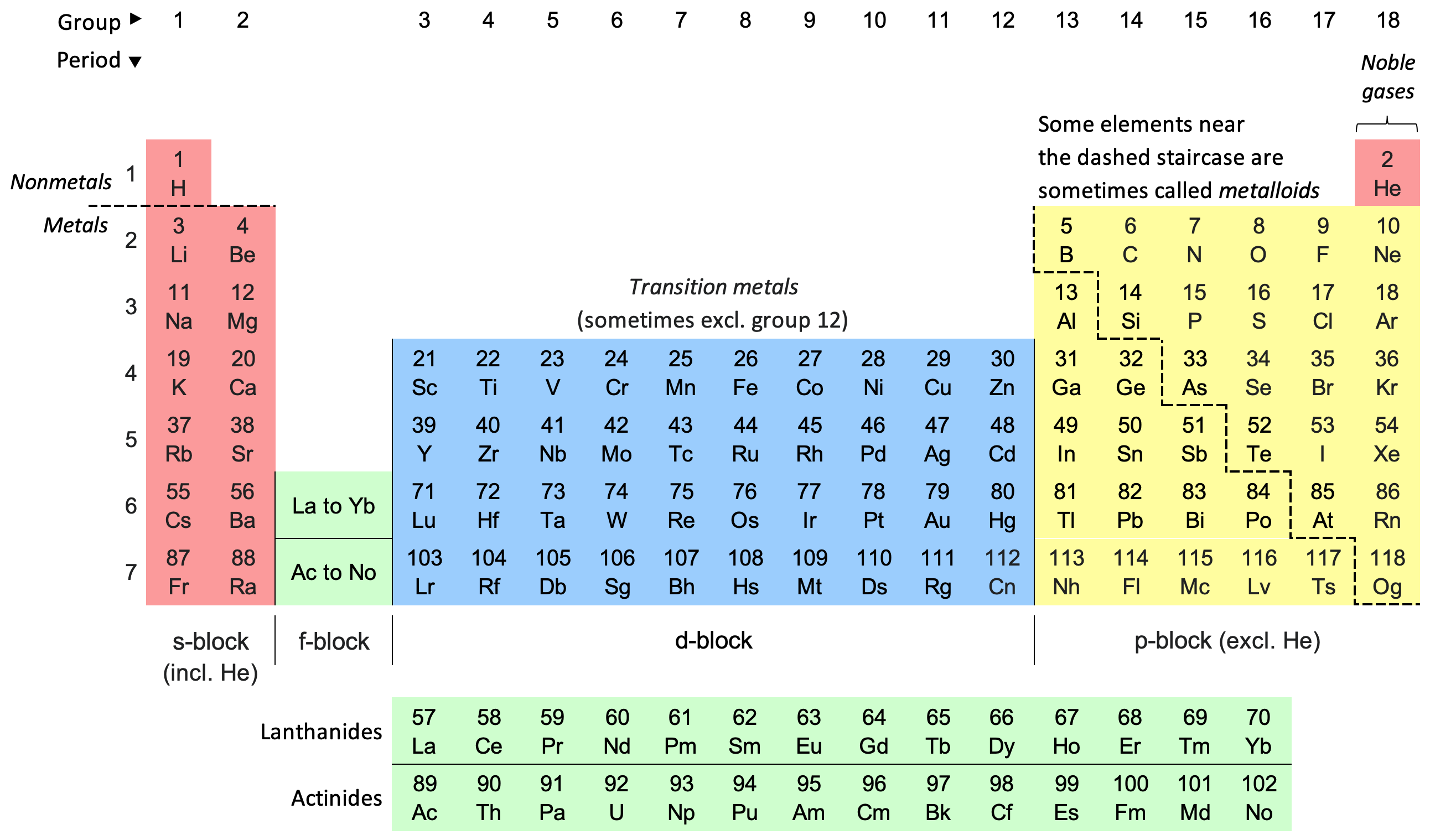
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Nuclides
A table or chart of nuclides is a two-dimensional graph of isotopes of the chemical elements, in which one axis represents the number of neutrons (symbol ''N'') and the other represents the number of protons (atomic number, symbol ''Z'') in the atomic nucleus. Each point plotted on the graph thus represents a nuclide of a known or hypothetical element. This system of ordering nuclides can offer a greater insight into the characteristics of isotopes than the better-known periodic table, which shows only elements and not their isotopes. The chart of the nuclides is also known as the Segrè chart, after Italian physicist Emilio Segrè. Description and utility A chart or table of nuclides maps the nuclear, or radioactive, behavior of nuclides, as it distinguishes the isotopes of an element. It contrasts with a periodic table, which only maps their chemical behavior, since isotopes (nuclides that are variants of the same element) do not differ chemically to any significant degr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Chromium
Naturally occurring chromium (24Cr) is composed of four stable isotopes; 50Cr, 52Cr, 53Cr, and 54Cr with 52Cr being the most abundant (83.789% natural abundance). 50Cr is suspected of decaying by β+β+ to 50Ti with a half-life of (more than) 1.8×1017 years. Twenty-two radioisotopes, all of which are entirely synthetic, have been characterized, the most stable being 51Cr with a half-life of 27.7 days. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 24 hours and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 1 minute. This element also has two meta states, 45mCr, the more stable one, and 59mCr, the least stable isotope or isomer. 53Cr is the radiogenic decay product of 53 Mn. Chromium isotopic contents are typically combined with manganese isotopic contents and have found application in isotope geology. Mn-Cr isotope ratios reinforce the evidence from 26Al and 107 Pd for the early history of the Solar System. Variations in 53Cr/52Cr and Mn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Silicon
Silicon (14Si) has 25 known isotopes, with mass numbers ranging from 22 to 46. 28Si (the most abundant isotope, at 92.23%), 29Si (4.67%), and 30Si (3.1%) are stable. The longest-lived radioisotope is 32Si, which is produced by cosmic ray spallation of argon. Its half-life has been determined to be approximately 150 years (with decay energy 0.21 MeV), and it decays by beta emission to 32 P (which has a 14.27-day half-life) and then to 32 S. After 32Si, 31Si has the second longest half-life at 157.3 minutes. All others have half-lives under 7 seconds. List of isotopes , -id=Silicon-22 , rowspan=3, 22Si , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 14 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 8 , rowspan=3, 22.03611(54)# , rowspan=3, 28.7(11) ms , β+, p (62%) , 21Mg , rowspan=3, 0+ , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , - , β+ (37%) , 22Al , - , β+, 2p (0.7%) , 20Na , -id=Silicon-23 , rowspan=3, 23Si , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 14 , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Carbon
Carbon (6C) has 14 known isotopes, from to as well as , of which only and are stable. The longest-lived radioisotope is , with a half-life of years. This is also the only carbon radioisotope found in nature, as trace quantities are formed cosmogenically by the reaction + → + . The most stable artificial radioisotope is , which has a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under 20 seconds, most less than 200 milliseconds. The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . Light isotopes tend to decay into isotopes of boron and heavy ones tend to decay into isotopes of nitrogen. List of isotopes , -id=Carbon-8 , , style="text-align:right" , 6 , style="text-align:right" , 2 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , Also immediately emits two protons for the net reaction of → + 4 , 0+ , , , -id=Carbon-9 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 6 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 3 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chart Of Nuclides
A table or chart of nuclides is a two-dimensional graph of isotopes of the chemical elements, in which one axis represents the number of neutrons (symbol ''N'') and the other represents the number of protons (atomic number, symbol ''Z'') in the atomic nucleus. Each point plotted on the graph thus represents a nuclide of a known or hypothetical element. This system of ordering nuclides can offer a greater insight into the characteristics of isotopes than the better-known periodic table, which shows only elements and not their isotopes. The chart of the nuclides is also known as the Segrè chart, after Italian physicist Emilio Segrè. Description and utility A chart or table of nuclides maps the nuclear, or radioactive, behavior of nuclides, as it distinguishes the isotopes of an element. It contrasts with a periodic table, which only maps their chemical behavior, since isotopes (nuclides that are variants of the same element) do not differ chemically to any significant degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Lithium
Naturally occurring lithium (3Li) is composed of two stable isotopes, lithium-6 (6Li) and lithium-7 (7Li), with the latter being far more abundant on Earth. Both of the natural isotopes have an unexpectedly low nuclear binding energy per nucleon ( for 6Li and for 7Li) when compared with the adjacent lighter and heavier elements, helium ( for helium-4) and beryllium ( for beryllium-9). The longest-lived radioisotope of lithium is 8Li, which has a half-life of just . 9Li has a half-life of , and 11Li has a half-life of . All of the remaining isotopes of lithium have half-lives that are shorter than 10 nanoseconds. The shortest-lived known isotope of lithium is 4Li, which decays by proton emission with a half-life of about (), although the half-life of 3Li is yet to be determined, and is likely to be much shorter, like 2He (helium-2, diproton) which undergoes proton emission within s. Both 7Li and 6Li are two of the primordial nuclides that were produced in the Big Bang, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |