|
Granulopoiesis
Granulopoiesis (or granulocytopoiesis) is a part of haematopoiesis, that leads to the production of granulocytes. A granulocyte, also referred to as a polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN), is a type of white blood cell that has multi lobed nuclei, usually containing three lobes, and has a significant amount of cytoplasmic granules within the cell. Granulopoiesis takes place in the bone marrow. It leads to the production of three types of mature granulocytes: neutrophils (most abundant, making up to 60% of all white blood cells), eosinophils (up to 4%) and basophils (up to 1%). Stages of granulocyte development Granulopoiesis is often divided into two parts; 1) Granulocyte lineage determination and 2) Committed granulopoiesis. Granulocyte lineage determination Granulopoiesis, as well as the rest of haematopoiesis, begins from a haematopoietic stem cell. These are multipotent cells that reside in the bone marrow niche and have the ability to give rise to all haematopoietic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocytes
Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear, that is, they have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus (segmented, irregular; often lobed into three segments); and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML, or PMNL). In common terms, ''polymorphonuclear granulocyte'' refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types ( eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells) have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Types There are four types of granulocytes (full name polymorphonuclear granulocytes): * Basophils * Eosinophils * Neutrophils * Mast cells Except for the mast cells, their names are derived from their staining characteristics; for example, the most abundant gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear, that is, they have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus (segmented, irregular; often lobed into three segments); and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML, or PMNL). In common terms, ''polymorphonuclear granulocyte'' refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types ( eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells) have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Types There are four types of granulocytes (full name polymorphonuclear granulocytes): * Basophils * Eosinophils * Neutrophils * Mast cells Except for the mast cells, their names are derived from their staining characteristics; for example, the most abundant granulocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
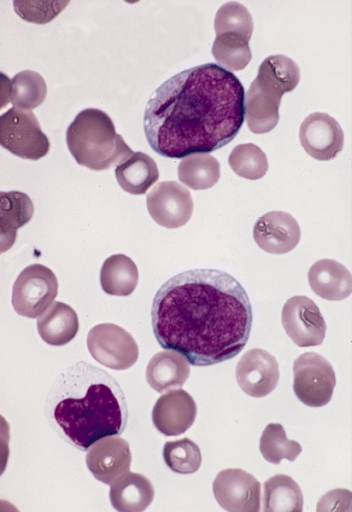
Metamyelocyte
A metamyelocyte is a cell undergoing granulopoiesis, derived from a myelocyte, and leading to a band cell. It is characterized by the appearance of a bent nucleus, cytoplasmic granules, and the absence of visible nucleoli. (If the nucleus is not yet bent, then it is likely a myelocyte.) Additional images File:Hematopoiesis (human) diagram en.svg, Hematopoiesis See also * Pluripotential hemopoietic stem cell Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the (m ... External links * - "Bone Marrow and Hemopoiesis: bone marrow smear, neutrophilic metamyelocyte and mature PMN" * * * Interactive diagram at lycos.es Histology Leukocytes {{developmental-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear, that is, they have varying shapes (morphology) of the nucleus (segmented, irregular; often lobed into three segments); and are referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN, PML, or PMNL). In common terms, ''polymorphonuclear granulocyte'' refers specifically to "neutrophil granulocytes", the most abundant of the granulocytes; the other types ( eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells) have varying morphology. Granulocytes are produced via granulopoiesis in the bone marrow. Types There are four types of granulocytes (full name polymorphonuclear granulocytes): * Basophils * Eosinophils * Neutrophils * Mast cells Except for the mast cells, their names are derived from their staining characteristics; for example, the most abundant granulocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoiesis (human) Diagram En
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten billion () to a hundred billion () new blood cells are produced per day, in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone (bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs (myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other differenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent white blood cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival. Structure Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords. Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Cell
A band cell (also called band neutrophil, band form or stab cell) is a cell undergoing granulopoiesis, derived from a metamyelocyte, and leading to a mature granulocyte. It is characterized by having a curved but not lobular nucleus. The term "band cell" implies a granulocytic lineage (e.g., neutrophils). Clinical significance Band neutrophils are an intermediary step prior to the complete maturation of segmented neutrophils. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils are initially released from the bone marrow as band cells. As the immature neutrophils become activated or exposed to pathogens, their nucleus will take on a segmented appearance. An increase in the number of these immature neutrophils in circulation can be indicative of an infection for which they are being called to fight against, or some inflammatory process. The increase of band cells in the circulation is called bandemia and is a "left shift" process. Blood reference ranges for neutrophilic band cells in adults ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten billion () to a hundred billion () new blood cells are produced per day, in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone ( bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/EBPε
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), epsilon, also known as CEBPE and CRP1, is a type of ccaat-enhancer-binding protein. CEBPE is its human gene and is pro-apoptotic. The protein encoded by this gene is a bZIP transcription factor which can bind as a homodimer to certain DNA regulatory regions. It can also form heterodimers with the related protein CEBP-δ. The encoded protein may be essential for terminal differentiation and functional maturation of committed granulocyte progenitor cell A progenitor cell is a biological cell that can differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor cells. Progenitor cells can only diffe ...s. Mutations in this gene have been associated with specific granule deficiency, a rare congenital disorder. Multiple variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of only one has been determined. References Furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unipotent
In mathematics, a unipotent element ''r'' of a ring ''R'' is one such that ''r'' − 1 is a nilpotent element; in other words, (''r'' − 1)''n'' is zero for some ''n''. In particular, a square matrix ''M'' is a unipotent matrix if and only if its characteristic polynomial ''P''(''t'') is a power of ''t'' − 1. Thus all the eigenvalues of a unipotent matrix are 1. The term quasi-unipotent means that some power is unipotent, for example for a diagonalizable matrix with eigenvalues that are all roots of unity. In the theory of algebraic groups, a group element is unipotent if it acts unipotently in a certain natural group representation. A unipotent affine algebraic group is then a group with all elements unipotent. Definition Definition with matrices Consider the group \mathbb_n of upper-triangular matrices with 1's along the diagonal, so they are the group of matrices :\mathbb_n = \left\. Then, a unipotent group can be define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Myeloid Progenitor
CFU-GEMM is a colony forming unit that generates myeloid cells. CFU-GEMM cells are the oligopotential progenitor cells for myeloid cells; they are thus also called common myeloid progenitor cells or myeloid stem cells. "GEMM" stands for granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte. The common myeloid progenitor (CMP) and the common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) are the first branch of cell differentiation in hematopoiesis after the hemocytoblast (hematopoietic stem cell). Structure In current terminology, CFU-S refers to the pluripotent stem cells that can differentiate into all types of blood cells. CFU-S divides into two lineages: the lymphoid precursor (CFU-LSC) and the myeloid precursor (CFU-GEMM). The CFU-GEMM cell is capable of differentiating into white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets, all of which are normally found in circulating blood. It has been suggested that eosinophils do not derive from the common myeloid progenitor in humans. In the adjacent image, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |