|
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis
Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM) is a disease that affects the central nervous system of horses. It is caused by a protozoal infection that is brought about by the apicomplexan parasites '' Sarcocystis neurona'' or '' Neospora hughesi''. Most cases are caused by ''S. neurona''. The lifecycle and transmission of ''N. hughesi'' is not well understood. The parasites create lesions in both the brain and spinal cord of the affected horses leading to neurological issues. Most horses infected with ''S. neurona'' do not exhibit neurological symptoms consistent with EPM. Causes EPM is caused primarily by the parasite ''Sarcocystis neurona.'' To complete its lifecycle, ''S. neurona'' requires two hosts: a definitive host, and an intermediate host. The definitive host is the opossum. In North America, the definitive host is the Virginia opossum (''Didelphis virginiana''); South American opossums can also act as the definitive host. A number of mammals can serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles. Clinically, spasticity results from the loss of inhibition of motor neurons, causing excessive velocity-dependent muscle contraction. This ultimately leads to hyperreflexia, an exaggerated deep tendon reflex. Spasticity is often treated with the drug baclofen, which acts as an agonist at GABA receptors, which are inhibitory. Spastic cerebral palsy is the most common form of cerebral palsy, which is a group of permanent movement problems that do not get worse over time. GABA's inhibitory actions contribute to baclofen's efficacy as an anti-spasticity agent. Pathophysiology Spasticity is usually caused by damage to nerve pathways within the brain or spinal cord that control muscle movement. This can cause an imbalance in the inhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isolation (microbiology)
In microbiology, the term isolation refers to the separation of a strain from a natural, mixed population of living microbes, as present in the environment, for example in water or soil, or from living beings with skin flora, oral flora or gut flora, in order to identify the microbe(s) of interest. Historically, the laboratory techniques of isolation first developed in the field of bacteriology and parasitology (during the 19th century), before those in virology during the 20th century. History The laboratory techniques of isolating microbes first developed during the 19th century in the field of bacteriology and parasitology using light microscopy. 1860 marked the successful introduction of liquid medium by Louis Pasteur. The liquid culture pasteur developed allowed for the visulization of promoting or inhibiting growth of specific bacteria. This same technique is utilized today through various mediums like Mannitol salt agar, a solid medium. Solid cultures were developed in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinary Parasitology (journal)
''Veterinary Parasitology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication designed to further the progress of science by disseminating new research findings to the scientific community. These journals serve as a platform for researchers, schola ... in the discipline of veterinary parasitology. It is the official organ of the American Association of Veterinary Parasitologists, the European Veterinary Parasitology College, and the World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology. References External links * Veterinary medicine journals Parasitology journals Elsevier academic journals Academic journals established in 1975 {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diclazuril
Diclazuril (trade name Vecoxan) is a coccidiostat. See also * Clazuril * Ponazuril * Toltrazuril Toltrazuril is an antiparasitic medication used primarily to treat coccidiosis in animals. Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease caused by coccidia, which are microscopic, spore-forming, single-celled obligate intracellular parasites belonging to ... References Antiparasitic agents Nitriles Chlorobenzene derivatives Triazines Lactams Ureas 4-Chlorophenyl compounds {{antiinfective-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponazuril
Ponazuril (INN), sold by Merial, Inc., now part of Boehringer Ingelheim, under the trade name Marquis (15% w/w ponazuril), is a drug currently approved for the treatment of equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM) in horses, caused by coccidia ''Sarcocystis neurona''. Veterinarians have been preparing a formulary version of the medication for use in small animals such as cats, dogs, and rabbits against coccidia as an intestinal parasite. Treatment for intestinal coccidia in small animals is far shorter than treatment for EPM. NOTE: Dogs suffering from seizures due to Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, Neospora hughesi, Sarcocystis neurona, or other obligate intracellular coccidian protozoal parasites known to cause brain and spinal column disease, can be effectively treated using Ponazuril for a minimum of 90 days. Ponazuril is coccidiocidal, meaning that if treatment is continuous for 90 days or more, seizures may cease in dogs and other companion animals. Testi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
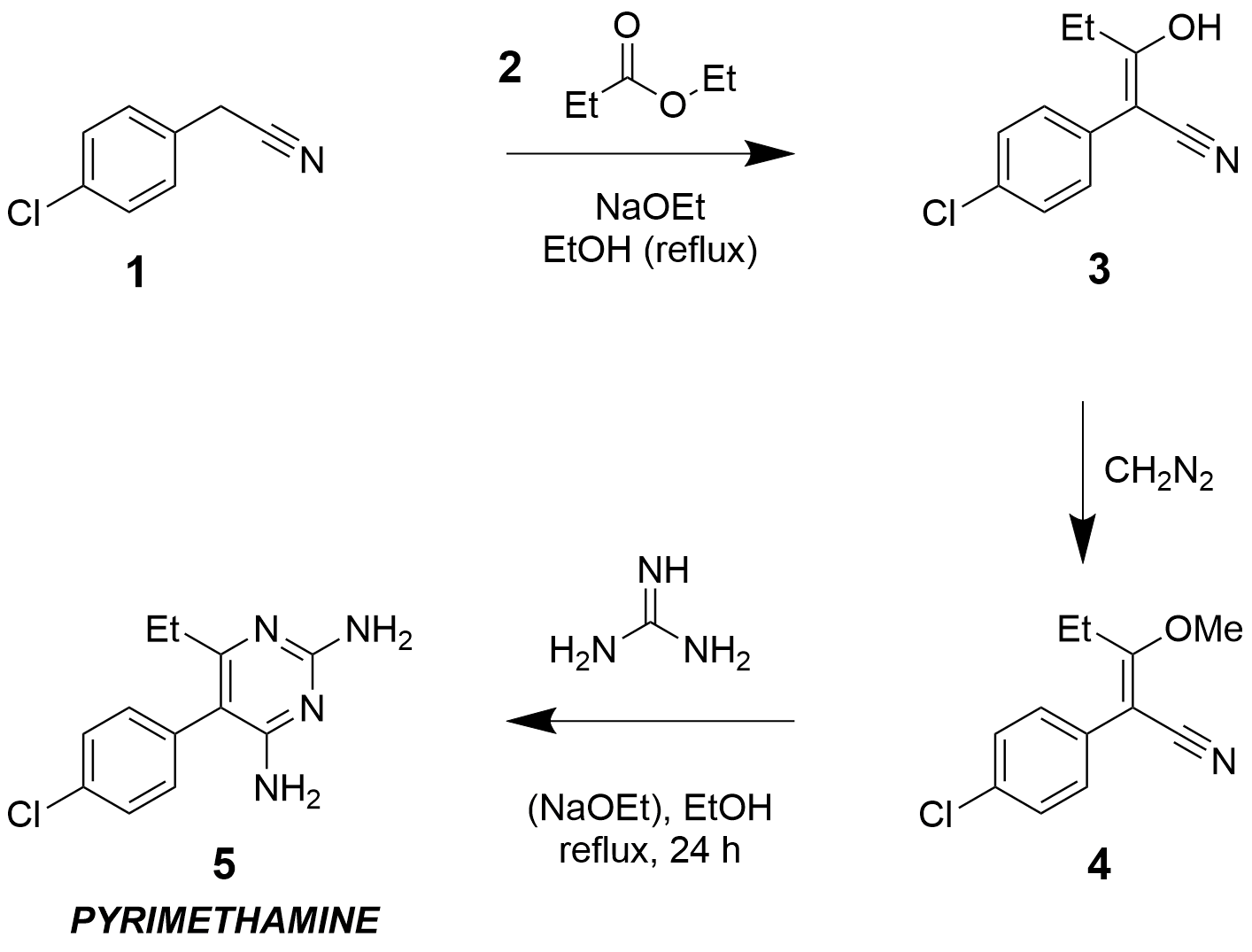
Pyrimethamine
Pyrimethamine, sold under the brand name Daraprim among others, is a medication used with leucovorin (leucovorin is used to decrease side effects of pyrimethamine; it does not have intrinsic anti-parasitic activity) to treat the parasitic diseases toxoplasmosis and cystoisosporiasis. It is also used with dapsone as a second-line option to prevent Pneumocystis pneumonia, ''Pneumocystis jiroveci'' pneumonia in people with HIV/AIDS. It was previously used for malaria but is no longer recommended due to resistance. Pyrimethamine is oral administration, taken by mouth. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, severe allergic reactions, and bone marrow suppression. It should not be used by people with folate deficiency that has resulted in anemia. There is concern that it may increase the risk of cancer. While occasionally used in pregnancy it is unclear if pyrimethamine is safe for the baby. Pyrimethamine is classified as a folic acid antagonist. It works by inhibiting f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfadiazine
Sulfadiazine is an antibiotic. Used together with pyrimethamine, a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, it is the treatment of choice for toxoplasmosis, which is caused by a protozoan parasite. It is a second-line treatment for otitis media, prophylaxis of rheumatic fever, chancroid, chlamydia, and infections by ''Haemophilus influenzae''. It is also used as adjunct therapy for chloroquine-resistant malaria and several forms of bacterial meningitis. It is taken by mouth. Sulfadiazine is available in multiple generic tablets of 500 mg. For urinary tract infections, the usual dose is 4 to 6 grams daily in 3 to 6 divided doses. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headache, fever, rash, depression, and pancreatitis. It should not be used in people who have severe liver problems, kidney problems, or porphyria. If used during pregnancy, it may increase the risk of kernicterus in the baby. While the company that makes it does not recommend use during breastfeeding, use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cells
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snoring
Snoring is an abnormal breath sound caused by partially obstructed, turbulent airflow and vibration of tissues in the upper respiratory tract (e.g., uvula, soft palate, base of tongue) which occurs during sleep. It usually happens during inhalations (breathing in). Primary snoring is snoring without any associated sleep disorders and usually without any serious health effects. It is usually defined as apnea–hypopnea index score or respiratory disturbance index score less than 5 events per hour (as diagnosed with polysomnography or home sleep apnea test) and lack of daytime sleepiness. Snoring may also be a symptom of upper airway resistance syndrome or obstructive sleep apnea (apneic snoring). In obstructive sleep apnea, snoring occurs in combination with breath holding, gasping, or choking. Classification In the International Classification of Sleep Disorders third edition (ICSD-3), snoring is listed under "Isolated symptoms and normal variants" in the section " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngeal Hemiplegia
Laryngeal paralysis in animals is a condition in which the nerves and muscles that control the movements of one or both arytenoid cartilages of the larynx cease to function, and instead of opening during aspiration and closing during swallowing, the arytenoids remain stationary in a somewhat neutral position. Specifically, the muscle that causes abduction of the arytenoid cartilage, the cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle, ceases to function. This leads to inadequate ventilation during exercise and during thermoregulatory panting as well as incomplete protection of the airway during swallowing. One of the most common forms of laryngeal paralysis develops in geriatric medium to large breed dogs, in particular the Labrador retriever, but also some other breeds. This had been traditionally known as idiopathic laryngeal paralysis ("ILP": idiopathic means "of unknown cause"), and was believed to be a result of a condition affecting the nerves of the larynx (bilateral mononeuropathy of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |