|
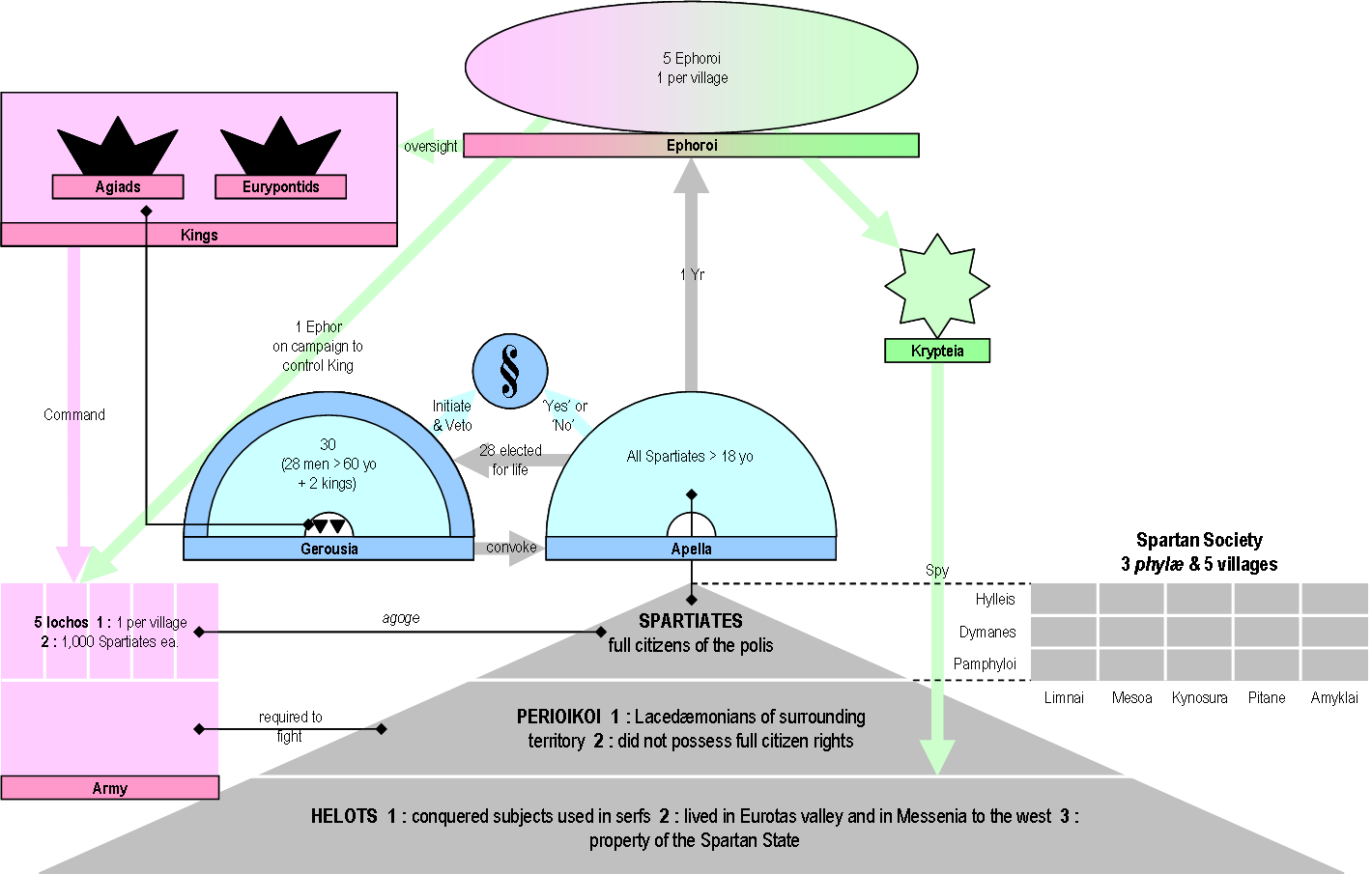
Ephor
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions. Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. p. 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cyre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan Constitution
The Spartan Constitution (or Spartan politeia) are the government and laws of the Classical Greece, classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its unique features, which supported a rigidly layered social system and a strong hoplite army. The Spartans had no historical records, literature, or written laws, which were, according to tradition, prohibited. Attributed to the mythical figure of Lycurgus of Sparta, Lycurgus, the legendary law-giver, the Spartan system of government is known mostly from the ''Constitution of the Lacedaemonians'', a treatise attributed to the ancient Greek historian Xenophon, describing the institutions, customs, and practices of the ancient Spartans. The act of the foundation Great Rhetra According to Plutarch, Lycurgus of Sparta, Lycurgus (to whom is attributed the establishment of the severe reforms for which Sparta has become renown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias Of Sparta
Pausanias () was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander. Pausanias became king in 445 BC, when his father Pleistoanax was forced into exile because he made a peace settlement with Athens, which was deemed dishonourable in Sparta. Too young to reign, his uncle Cleomenes acted as regent. Pleistoanax then returned in 427 BC and resumed his reign. Pausanias effectively became king in 409, at the death of his father. As he continued the conciliatory policy with Athens favoured by Pleistoanax, Pausanias clashed with Lysander, the Spartan general who had won the Peloponnesian War against Athens in 404 BC and supported an imperialist policy in the Aegean Sea. In 403 BC, Pausanias engineered the restoration of the Athenian democracy, which had been replaced by the regime of the Thirty Tyrants installed by L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycurgus (lawgiver)
Lycurgus (; ) was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta, credited with the formation of its (), involving political, economic, and social reforms to produce a military-oriented Spartan society in accordance with the Delphic oracle. The Spartans in the historical period honoured him as a god. As a historical figure, almost nothing is known for certain about him, including when he lived and what he did in life. The stories of him place him at multiple times. Nor is it clear when the political reforms attributed to him, called the Great Rhetra, occurred. Ancient dates range from – putting aside the implausibly early Xenophonic 11th century BC – the early ninth century () to as late as early eighth century (). There remains no consensus as to when he lived; some modern scholars deny that he existed at all. The reforms at various times attributed to him touch all aspects of Spartan society. They included the creation of the Spartan constitution (in most traditions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (king Of Sparta)
Pausanias () was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander. Pausanias became king in 445 BC, when his father Pleistoanax was forced into exile because he made a peace settlement with Athens, which was deemed dishonourable in Sparta. Too young to reign, his uncle Cleomenes acted as regent. Pleistoanax then returned in 427 BC and resumed his reign. Pausanias effectively became king in 409, at the death of his father. As he continued the conciliatory policy with Athens favoured by Pleistoanax, Pausanias clashed with Lysander, the Spartan general who had won the Peloponnesian War against Athens in 404 BC and supported an imperialist policy in the Aegean Sea. In 403 BC, Pausanias engineered the restoration of the Athenian democracy, which had been replaced by the regime of the Thirty Tyrants installed by L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apella
The ecclesia or ekklesia ( Greek: ἐκκλησία) was the citizens' assembly in the Ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. Unlike its more famous counterpart in Athens, the Spartan assembly had limited powers, as it did not debate; citizens could only vote for or against proposals. In the pre-War literature, the assembly was often called the apella (), but this word refers to a festival of Apollo, the Apellai, during which the ekklesia originally met. Name The pre-War academic literature often refers to the Spartan ekklesia as the apella. However, this word is never found in ancient sources in the singular, and never in a political context.Ste. Croix, ''Origins of the Peloponnesian War'', p. 347. The Apellai were a festival of Apollo during which the ekklesia originally met. They were organised once a month, with perhaps one more important feast once a year (called Apellaios), during which elections were presumably organised. In later times, the two events (religious and po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecclesia (Sparta)
The ecclesia or ekklesia (Greek language, Greek: ἐκκλησία) was the citizens' assembly in the Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Polis, city-state of Sparta. Unlike its more Ecclesia (ancient Greece), famous counterpart in Classical Athens, Athens, the Spartan assembly had limited powers, as it did not debate; citizens could only vote for or against proposals. In the pre-War literature, the assembly was often called the apella (), but this word refers to a festival of Apollo, the Apellai, during which the ekklesia originally met. Name The pre-War academic literature often refers to the Spartan ekklesia as the apella. However, this word is never found in ancient sources in the singular, and never in a political context.Ste. Croix, ''Origins of the Peloponnesian War'', p. 347. The Apellai were a festival of Apollo during which the ekklesia originally met. They were organised once a month, with perhaps one more important feast once a year (called Apellaios), during which elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the Evrotas Valley, valley of Evrotas (river), Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless recovered m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to repressive means. The original Greek term meant an absolute sovereign who came to power without constitutional right, yet the word had a neutral connotation during the Archaic and early Classical periods. However, Greek philosopher Plato saw ''tyrannos'' as a negative form of government, and on account of the decisive influence of philosophy on politics, deemed tyranny the "fourth and worst disorder of a state."Plato, ''The Republic'' Book VIII The philosophers Plato and Aristotle defined a tyrant as a person who rules without law, using extreme and cruel methods against both his own people and others. The ''Encyclopédie'' defined the term as a usurper of sovereign power who makes "his subjects the victims of his passions and unjust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been part of Cyrus the Younger's attempt to seize control of the Achaemenid Empire. As the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge wrote, "the centuries since have devised nothing to surpass the genius of this warrior". For at least two millennia, it has been debated whether or not Xenophon was first and foremost a general, historian, or philosopher. For the majority of time in the past two millennia, Xenophon was recognized as a philosopher. Quintilian in Institutio Oratoria, ''The Orator's Education'' discusses the most prominent historians, orators and philosophers as examples of eloquence and recognizes Xenophon's historical work, but ultimately places Xenophon next to Plato as a philosopher. Today, Xenophon is recognized as one of the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agiad Dynasty
The Agiad dynasty (, ''Agiádai'') was one of the two royal families of the ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. They ruled jointly along with the Eurypontid dynasty, possibly from the 8th century BC onwards, being the senior of the two houses. The hypothetical founder of the dynasty was Agis I, possibly the first king of Sparta at the end of the 10th century BC, who subsequently gave his name to the dynasty. The two lines, who maintained an enduring rivalry, were, according to tradition, respectively descended from the twins Eurysthenes and Procles, both descendants of Heracles. The most famous member of the Agiad dynasty was Leonidas I, known for his heroic death at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. The last Agiad king was Agesipolis III, deposed by the Eurypontid Lycurgus in 215 BC. History In order to explain the peculiarity of the Spartan two kings, the Spartans elaborated a legend saying that Aristodemos—the first king of Sparta—had twins, Eurysthenes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerousia
The Gerousia (γερουσία) was the council of elders in ancient Sparta. Sometimes called Spartan senate in the literature, it was made up of the two Spartan kings, plus 28 Spartiates over the age of sixty, known as gerontes. The Gerousia was a prestigious body, holding extensive judicial and legislative powers, which shaped Sparta's policies. Ancient Greeks considered that the Gerousia was created by the mythical Spartan lawgiver Lycurgus in his Great Rhetra, the constitution of Sparta. The gerontes were elected through peculiar shouting elections, which were open to manipulation, especially from the kings. Membership The ''Gerousia'' consisted of thirty members in total. Twenty-eight elected members (called gerontes) and the two kings, who were members by right, entering the chamber upon their accession. Unlike the kings, the 28 gerontes had to be at least 60 years old—the age when Spartan citizens were no longer required to serve in the army. Membership ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base. Founded by Spartans in the 8th century BC during the period of Greek colonisation, Taranto was among the most important '' poleis'' in Magna Graecia, becoming a cultural, economic and military power that gave birth to philosophers, strategists, writers and athletes such as Archytas, Aristoxenus, Livius Andronicus, Heracleides, Iccus, Cleinias, Leonidas, Lysis and Sosibius. By 500 BC, the city was among the largest in the world, with a population estimated up to 300,000 people. The seven-year rule of Archytas marked the apex of its development and recognition of its hegemony over other Greek colonies of southern Italy. During the Norman period, it became the capital of the Principality of Taranto, which covered almost all of the heel of Apulia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |