|
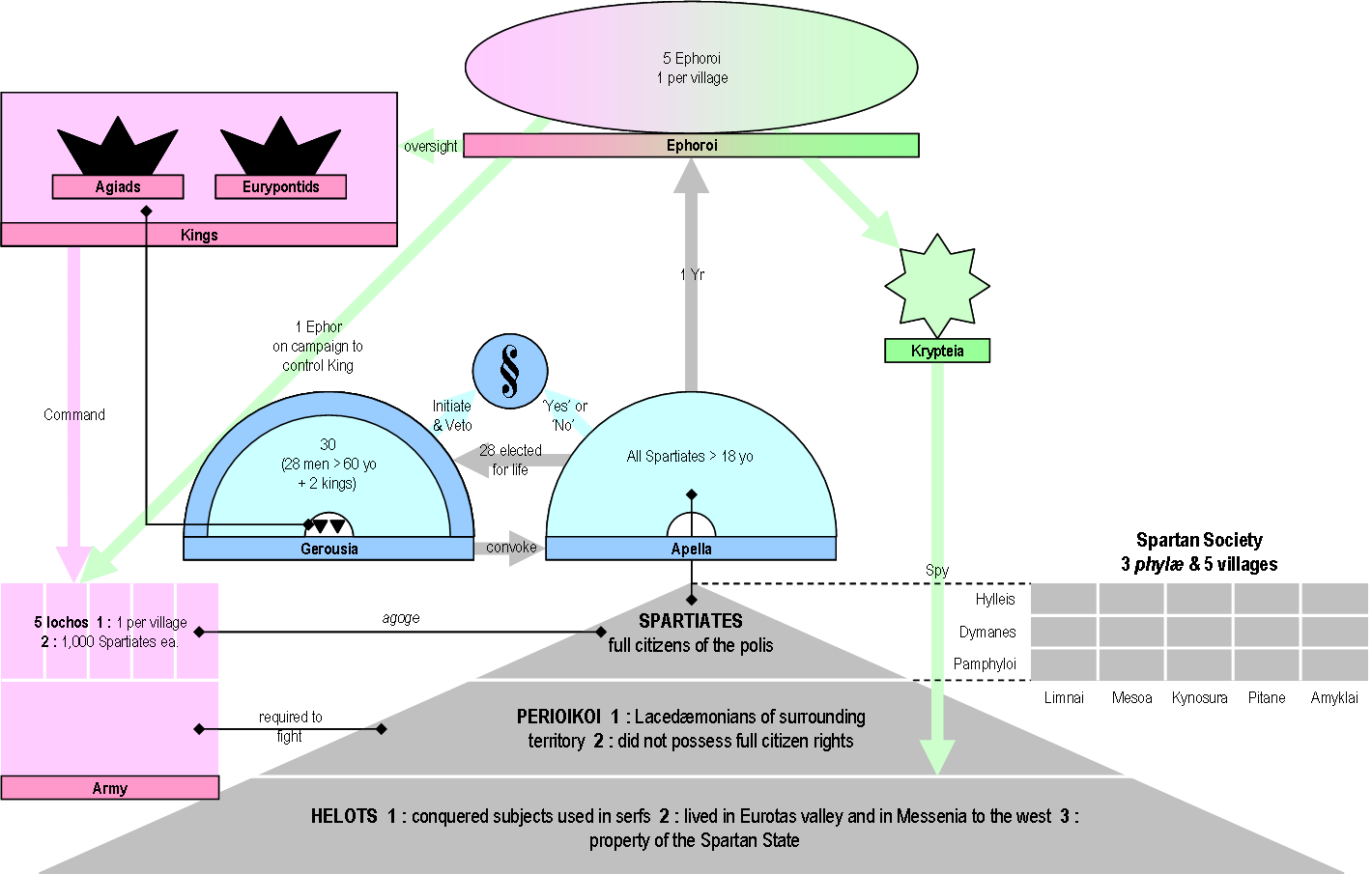
Gerousia
The Gerousia (γερουσία) was the council of elders in ancient Sparta. Sometimes called Spartan senate in the literature, it was made up of the two Spartan kings, plus 28 Spartiates over the age of sixty, known as gerontes. The Gerousia was a prestigious body, holding extensive judicial and legislative powers, which shaped Sparta's policies. Ancient Greeks considered that the Gerousia was created by the mythical Spartan lawgiver Lycurgus in his Great Rhetra, the constitution of Sparta. The gerontes were elected through peculiar shouting elections, which were open to manipulation, especially from the kings. Membership The ''Gerousia'' consisted of thirty members in total. Twenty-eight elected members (called gerontes) and the two kings, who were members by right, entering the chamber upon their accession. Unlike the kings, the 28 gerontes had to be at least 60 years old—the age when Spartan citizens were no longer required to serve in the army. Membership ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphodrias
Sphodrias () (d. 371 BC) was a Spartan general during the Spartan Hegemony over Greece. As governor of Thespiai in 378 BC, he made an unsuccessful attack against Athens without any order from Sparta. He was put on trial for this act, but unexpectedly acquitted, thanks to the support of the two Spartan kings, Cleombrotus I and Agesilaus II. This acquittal greatly upset Athens which rapidly concluded an alliance with Thebes against Sparta as a result. Sphodrias later died at the battle of Leuctra against Thebes in 371 BC. Life Sphodrias was a Spartan officer from the circle of the Agiad king Cleombrotus I (r. 380–371), who likely used his influence to appoint him harmost (military governor) of Thespiai in Boeotia, in central Greece.Cartledge, ''Agesilaos'', p. 136. In a night of March 378, Sphodrias attempted to take control of Piraeus—the harbour of Athens—during a surprise night attack, while a Spartan delegation was precisely in Athens to conduct negotiations.Ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephor
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions. Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. p. 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cyre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan Constitution
The Spartan Constitution (or Spartan politeia) are the government and laws of the Classical Greece, classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its unique features, which supported a rigidly layered social system and a strong hoplite army. The Spartans had no historical records, literature, or written laws, which were, according to tradition, prohibited. Attributed to the mythical figure of Lycurgus of Sparta, Lycurgus, the legendary law-giver, the Spartan system of government is known mostly from the ''Constitution of the Lacedaemonians'', a treatise attributed to the ancient Greek historian Xenophon, describing the institutions, customs, and practices of the ancient Spartans. The act of the foundation Great Rhetra According to Plutarch, Lycurgus of Sparta, Lycurgus (to whom is attributed the establishment of the severe reforms for which Sparta has become renown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (king Of Sparta)
Pausanias () was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander. Pausanias became king in 445 BC, when his father Pleistoanax was forced into exile because he made a peace settlement with Athens, which was deemed dishonourable in Sparta. Too young to reign, his uncle Cleomenes acted as regent. Pleistoanax then returned in 427 BC and resumed his reign. Pausanias effectively became king in 409, at the death of his father. As he continued the conciliatory policy with Athens favoured by Pleistoanax, Pausanias clashed with Lysander, the Spartan general who had won the Peloponnesian War against Athens in 404 BC and supported an imperialist policy in the Aegean Sea. In 403 BC, Pausanias engineered the restoration of the Athenian democracy, which had been replaced by the regime of the Thirty Tyrants installed by L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleomenes I
Cleomenes I (; Greek Κλεομένης; died c. 490 BC) was Agiad King of Sparta from c. 524 to c. 490 BC. One of the most important Spartan kings, Cleomenes was instrumental in organising the Greek resistance against the Persian Empire of Darius, as well as shaping the geopolitical balance of Classical Greece. Herodotus' account Most of the life of Cleomenes is known through the '' Histories'' of Herodotus, an Athenian historian of the second half of the 5th century. He is one the most important characters of books 5 and 6, covering the decades before the Persian Wars. Herodotus' account however contains many mistakes, especially on the chronology of several major events, and is also very biased against Cleomenes. It seems that Herodotus got his information on Cleomenes from his opponents: the descendants of his half-brothers Leonidas and Cleombrotus, as well as those of Demaratus, the other Spartan king who was deposed by Cleomenes in 491.Cartledge, ''Sparta and Lakonia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Senate
The Greek Senate () was the upper chamber of the parliament in Greece, extant several times in the country's history. Local senates during the War of Independence During the early stages of the Greek War of Independence, prior to the establishment of a centralized administration, a number of regional councils were established, most of which were termed "senate", but which were unicameral bodies: the Senate of Western Continental Greece, the Areopagus of Eastern Continental Greece (sometimes referred to as "senate"), and the Peloponnesian Senate. 1829–1833 A unicameral body with purely advisory functions, the Senate was established in 1829 by the Fourth National Assembly at Argos in replacement of the '' Panellinion'', established the previous year. It had 27 members, 21 of whom were chosen by the Governor (Ioannis Kapodistrias) from 63 candidates nominated by the Assembly, and further six who were appointed directly by the Governor.Kitromilides, Paschalis M. ''The Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voice Vote
In parliamentary procedure, a voice vote (from the Latin ''viva voce'', meaning "by live voice") or acclamation is a voting method in deliberative assemblies (such as legislatures) in which a group vote is taken on a topic or motion by responding vocally. Despite not being the same thing, voice votes and votes by viva voce are often confused because they have the same Latin roots. Voice votes gather the vocal response of the full assembly at once whereas viva voce are often done by roll call and record the response and name of the individual voters. The voice vote is considered the simplest and quickest of voting methods used by deliberative assemblies. The presiding officer or chair of the assembly will put the question to the assembly, asking first for all those in favor of the motion to indicate so orally ("aye" or "yea"), and then ask second all those opposed to the motion to indicate so verbally ("no" or "nay"). The chair will then make an estimate of the count on each s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan Army
The Spartan army was the principal ground force of Sparta. It stood at the center of the ancient Greek city-state, consisting of citizens trained in the disciplines and honor of a warrior society.Connolly (2006), p. 38 Subjected to military drills since early manhood, the Spartans became one of the most feared and formidable military forces in the Greek world, attaining legendary status in their wars against Persia. At the height of Sparta's power—between the 6th and 4th centuries BC—other Greeks commonly accepted that "one Spartan was worth several men of any other state." 200px, Spartan helmet on display at the British Museum. The helmet has been damaged and the top has sustained a blow. Tradition states that the semi-mythical Spartan legislator Lycurgus first founded the iconic army. Referring to Sparta as having a "wall of men, instead of bricks," he proposed reforming the Spartan society to develop a military-focused lifestyle following "proper virtues" such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Rhetra
The Great Rhetra (, literally: Great "Saying" or "Proclamation", charter) was used in two senses by the classical authors. In one sense, it was the Spartan Constitution, believed to have been formulated and established by the quasi-legendary lawgiver, Lycurgus. In the legend, Lycurgus forbade any written constitution. It was therefore presumed to have been oral. In a second sense, the rhetra refers to an oracle of Delphi, which was believed to have contained the entire constitution in verse. The credo of being unwritten fails in this case, as a written record of all oracles was maintained by the priests at Delphi. They and others consulted it frequently. It survived long after the demise of the oracle but is missing now, except for fragments handed down by classical authors. The classical authors and the literate population of Sparta knew better than to suppose that the rhetra went into effect as written by an oracle and remained unchanged. A double tradition developed: tales o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichas
In Greek mythology, Lichas ( ; ) was Heracles' servant, who brought the The Shirt of Nessus, poisoned shirt from Deianira to Hercules because of Deianira's jealousy of Iole, which killed him. Mythology Lichas brought to his master the deadly garment, and as a punishment, was thrown by him into the sea, where the Lichades, Lichadian islands, between Euboea and the coast of Locris, were believed to have derived their name from him. The story is recounted in Sophocles' ''Women of Trachis'' and Ovid's ''Metamorphoses''.Ovid. ''Metamorphoses, Book 9.155 & 211'' compare with Gaius Julius Hyginus, Hyginus. ''Fabulae'', 36 Ovid's account Cape Lichada is said to be where Hercules flung Lichas into the sea: So, in his frenzy, as he wandered there,he chanced upon the trembling Lichas, crouchedin the close covert of a hollow rock.Then in a savage fury he cried out,"Was it you, Lichas, brought this fatal gift?Shall you be called the author of my death?"Lichas, in terror, groveled at h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agis II
Agis II (; died 399 BC) was the 18th Eurypontid king of Sparta, the eldest son of Archidamus II by his first wife, and half-brother of Agesilaus II. He ruled with his Agiad co-monarch Pausanias.Agis II fro Livius.Org Life Agis succeeded his father Archidamus II in 427 BC, and reigned a little more than 26 years. In the summer of 426 BC, he led an army of Peloponnesians and their allies as far as the , with the intention of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracleidae
The Heracleidae (; ) or Heraclids were the numerous descendants of Heracles, especially applied in a narrower sense to the descendants of Hyllus, the eldest of his four sons by Deianira (Hyllus was also sometimes thought of as Heracles' son by Melite). Other Heracleidae included Macaria, Lamos, Manto, Bianor, Tlepolemus, and Telephus. These Heraclids were a group of Dorian kings who conquered the Peloponnesian kingdoms of Mycenae, Sparta and Argos; according to the literary tradition in Greek mythology, they claimed a right to rule through their ancestor. Since Karl Otfried Müller's ''Die Dorier'' (1830, English translation 1839), I. ch. 3, their rise to dominance has been associated with a " Dorian invasion". Though details of genealogy differ from one ancient author to another, the cultural significance of the mythic theme, that the descendants of Heracles, exiled after his death, returned some generations later to reclaim land that their ancestors had held in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |