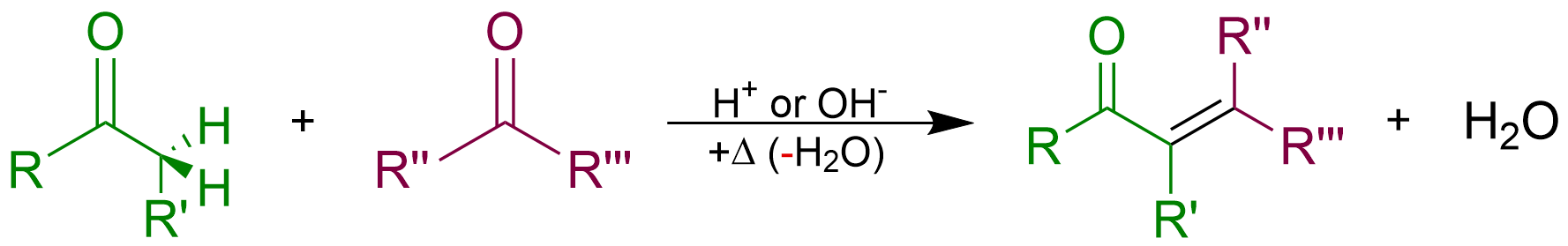|
Dimethyl Oxalate
Dimethyl oxalate is an organic compound with the formula or . It is the dimethyl ester of oxalic acid. Dimethyl oxalate is a colorless or white solid that is soluble in water. Production Dimethyl oxalate can be obtained by esterification of oxalic acid with methanol using sulfuric acid as a catalyst: :\rm 2\ CH_3OH + (CO_2H)_2\ \xrightarrow\ (CO_2CH_3)_2 + 2\ H_2O Oxidative carbonylation route The preparation by oxidative carbonylation has attracted interest because it requires only C1 precursors: :\rm 4 \ CH_3OH + 4 \ CO + O_2 \xrightarrow\ 2 \ (CO_2CH_3)_2 + 2 \ H_2O The reaction is catalyzed by Pd2+.E. Amadio''Oxidative Carbonylation of Alkanols Catalyzed by Pd(II)-Phosphine Complexes'' PhD Thesis, Ca'Foscari University Venice, 2009 The synthesis gas is mostly obtained from coal or biomass. The oxidation proceeds via dinitrogen trioxide, which is formed according to (1) of nitrogen monoxide and oxygen and then reacts according to (2) with methanol forming methyl nitrite: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenyl Oxalate
Diphenyl oxalate (trademark name Cyalume) is a solid whose oxidation products are responsible for the chemiluminescence in a glowstick. This chemical is the double ester of phenol with oxalic acid. Upon reaction with hydrogen peroxide, 1,2-dioxetanedione is formed, along with release of the two phenols. The dioxetanedione then reacts with a dye molecule, decomposing to form carbon dioxide and leaving the dye in an excited state. As the dye relaxes back to its unexcited state, it releases a photon of visible light. : The reaction rate is pH dependent, and slightly alkaline conditions, achieved by adding a weak base, such as sodium salicylate, give a faster reaction and therefore produce brighter light. The TCPO, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol ester is a solid and thus easier to handle. Furthermore, since trichlorophenolate is the better leaving group, the reaction will proceed faster, again producing brighter light, as compared to the phenol ester. The following colors can be produced by us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Nitrite
Methyl nitrite is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a gas, and is the simplest alkyl nitrite. Structure At room temperature, methyl nitrite exists as a mixture of ''cis'' and ''trans'' conformers. The ''cis'' conformer is 3.13 kJ mol−1, more stable than the ''trans'' form, with an energy barrier to rotation of 45.3 kJ mol−1. The cis and trans structure have also been determined by microwave spectroscopy (see external links). Synthesis Methyl nitrite can be prepared by the reaction of silver nitrite with iodomethane: Silver nitrite (AgNO2) exists in solution as the silver ion, Ag+ and the nitrite ion, NO2−. One of the lone pairs on an oxygen from nitrite ion attacks the methyl group (−CH3), releasing the iodide ion into solution. Unlike silver nitrite, silver iodide is highly insoluble in water and thus forms a solid. Note that nitrogen is a better nucleophile than oxygen and most nitrites would react via an SN2-like mechanism and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. History and synthesis The compound was discovered by in 1888 among the products of AC electrolysis of slightly acidified water solutions of phenol. He named it hydrophenoketone and correctly suggested that phenol was first hydrogenated by electrolytic hydrogen to cyclohexanol, which he wasn't able to isolate, and then oxidized by electrolytic oxygen. Laboratory synthesis Cyclohexanone can be prepared from cyclohexanol by oxidation with chromium trioxide ( Jones oxidation). An alternative method utilizes the safer and more readily avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Carbonylation With BQ Corr
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether. Preparation and structure Triphenylphosphine can be prepared in the laboratory by treatment of phosphorus trichloride with phenylmagnesium bromide or phenyllithium. The industrial synthesis involves the reaction between phosphorus trichloride, chlorobenzene, and sodium: :PCl3 + 3 PhCl + 6 Na → PPh3 + 6 NaCl Triphenylphosphine crystallizes in triclinic and monoclinic modification. In both cases, the molecule adopts a pyramidal structure with propeller-like arrangement of the thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium(II) Acetate
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form together a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification, chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,4-Benzoquinone
1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as ''para''-quinone, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound. Preparation 1,4-Benzoquinone is prepared industrially by oxidation of hydroquinone, which can be obtained by several routes. One route involves oxidation of Diisopropylbenzenes, diisopropylbenzene and the Hock rearrangem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |