|
Diimide
Diimide, also called diazene or diimine, is a compound having the formula HN=NH. It exists as two geometric isomers, ''E'' (''trans'') and ''Z'' (''cis''). The term diazene is more common for organic derivatives of diimide. Thus, azobenzene is an example of an organic diazene. Synthesis A traditional route to diimide involves oxidation of hydrazine with hydrogen peroxide or air. : Alternatively the hydrolysis of diethyl azodicarboxylate or azodicarbonamide affords diimide: : Nowadays, diimide is generated by thermal decomposition of 2,4,6‐triisopropylbenzenesulfonylhydrazide. Because of its instability, diimide is generated and used ''in-situ''. A mixture of both the ''cis'' (''Z-'') and ''trans'' (''E-'') isomers is produced. Both isomers are unstable, and they undergo a slow interconversion. The ''trans'' isomer is more stable, but the ''cis'' isomer is the one that reacts with unsaturated substrates, therefore the equilibrium between them shifts towards the ''cis'' isomer d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly hazardous unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing Polymeric foam, polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor (chemistry), precursor to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-outer space, space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket propellant, rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in airbags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. , approximately 120,000 tons of hydrazine hydrate (corresponding to a 64% solution of hydrazine in water by weight) we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Difluoride
Dinitrogen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a gas at room temperature, and was first identified in 1952 as the thermal decomposition product of the fluorine azide (). It has the structure and exists in both ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers, as typical for diimides. Isomers The ''cis'' isomer has C2v symmetry and the ''trans'' isomer has C2h symmetry. These isomers can interconvert, but the process is slow enough at low temperature that the two can separated by low-temperature fractionation. The ''trans'' isomer is less thermodynamically stable but can be stored in glass vessels. The ''cis'' isomer attacks glass over a time scale of about 2 weeks to form silicon tetrafluoride and nitrous oxide: : Preparation Most preparations of dinitrogen difluoride give mixtures of the two isomers, but they can be prepared independently. An aqueous method involves ''N'',''N''-difluorourea with concentrated potassium hydroxide. This gives a 40% yield with three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
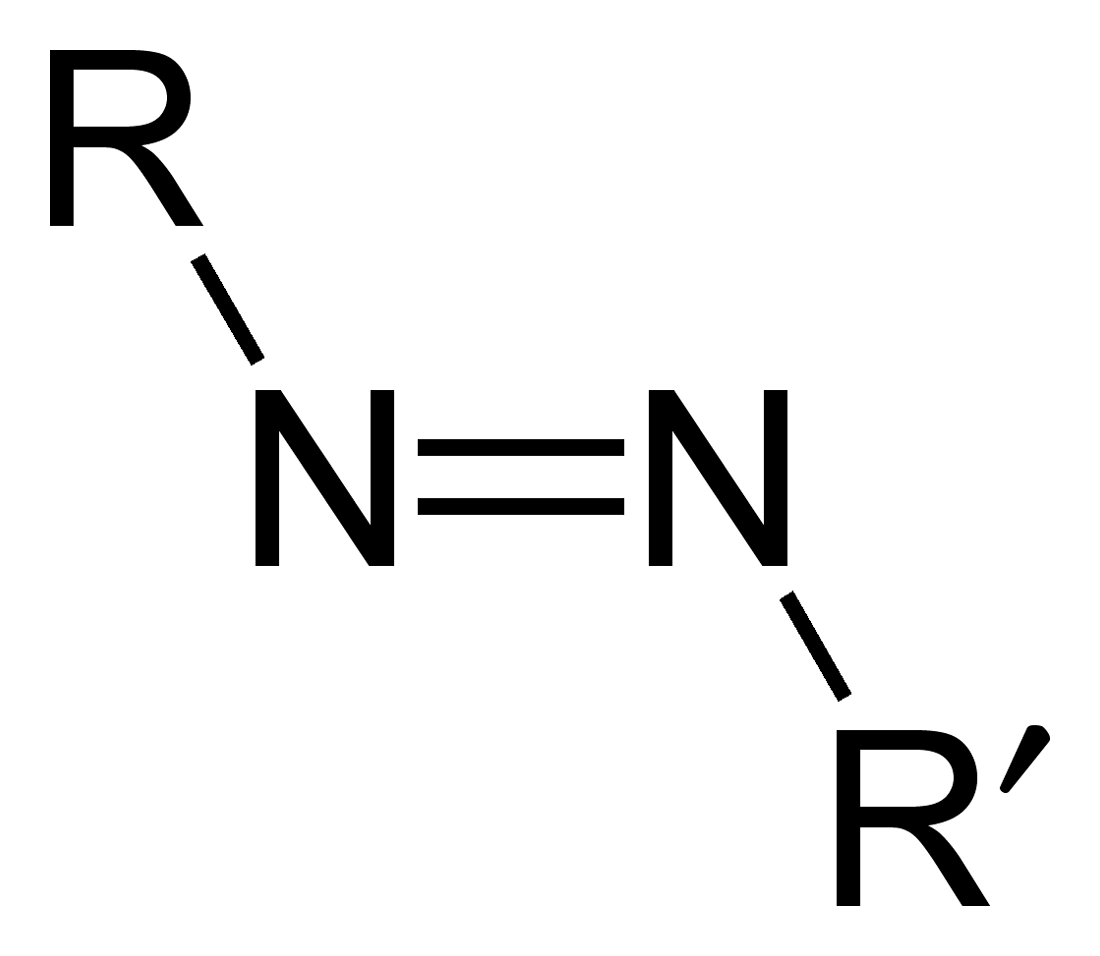
Azo Compound
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene.", where Ph stands for phenyl group. The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds urinary tract infections">Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the Cis-trans isomerism, ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the Cis-trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Difluoride
Dinitrogen difluoride is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a gas at room temperature, and was first identified in 1952 as the thermal decomposition product of the fluorine azide (). It has the structure and exists in both ''cis'' and ''trans'' isomers, as typical for diimides. Isomers The ''cis'' isomer has C2v symmetry and the ''trans'' isomer has C2h symmetry. These isomers can interconvert, but the process is slow enough at low temperature that the two can separated by low-temperature fractionation. The ''trans'' isomer is less thermodynamically stable but can be stored in glass vessels. The ''cis'' isomer attacks glass over a time scale of about 2 weeks to form silicon tetrafluoride and nitrous oxide: : Preparation Most preparations of dinitrogen difluoride give mixtures of the two isomers, but they can be prepared independently. An aqueous method involves ''N'',''N''-difluorourea with concentrated potassium hydroxide. This gives a 40% yield with three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azo Compounds
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene.", where Ph stands for phenyl group. The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds urinary tract infections">Phenazopyridine, an aryl azo compound, is used to treat urinary tract infections">150px Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the Cis-trans isomerism, ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the Cis-trans isomerism, ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isodiazene
In organic chemistry, an isodiazene, also known by the incorrectly constructed (but commonly used) name 1,1-diazene or systematic name diazanylidene, is an organic derivative of the parent isodiazene (H2N+=N–, also called 1,1-diimide) with general formula R1R2N+=N–. The functional group has two major resonance forms, a diazen-2-ium-1-ide form, and an aminonitrene form: Although isodiazenes are formally Isoelectronicity, isoelectronic with Carbonyl compounds, ketones and aldehydes, the reactivity of this exotic functional group is very different. They are generally prepared by oxidation of the hydrazine (R2N–NH2), reduction of the 1,1-diazene oxide (R2N–N=O), 1,1-elimination of MX from R2N–NMX (M = Na, K; X = SO2Ar), or treatment of secondary amines with Angeli's salt, Na2N2O3, in the presence of acid. Isodiazenes participate in cycloaddition reactions with alkenes to generate ''N''-aminoaziridines. In the absence of other reactants, they undergo reactions in which N2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazene
Triazene is an unsaturated inorganic compound having the chemical formula N3 H3. It has one double bond and is the second-simplest member of the azene class of hydronitrogen compounds, after diimide. Triazenes are a class of organic compounds containing the functional group −N(H)−N=N−. Triazene, possibly along with its isomer triimide (HNNHNH), has been synthesized in electron-irradiated ices of ammonia and ammonia/dinitrogen and detected in the gas phase after sublimation. References External links *IUPAC Gold Book The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided initially into seven IUPAC Colour Books: Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and R ...br>definition {{Hydrides by group Nitrogen hydrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same catalysts and conditions that are used for hydrogenation reactions can also lead to isomerization of the alkenes fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
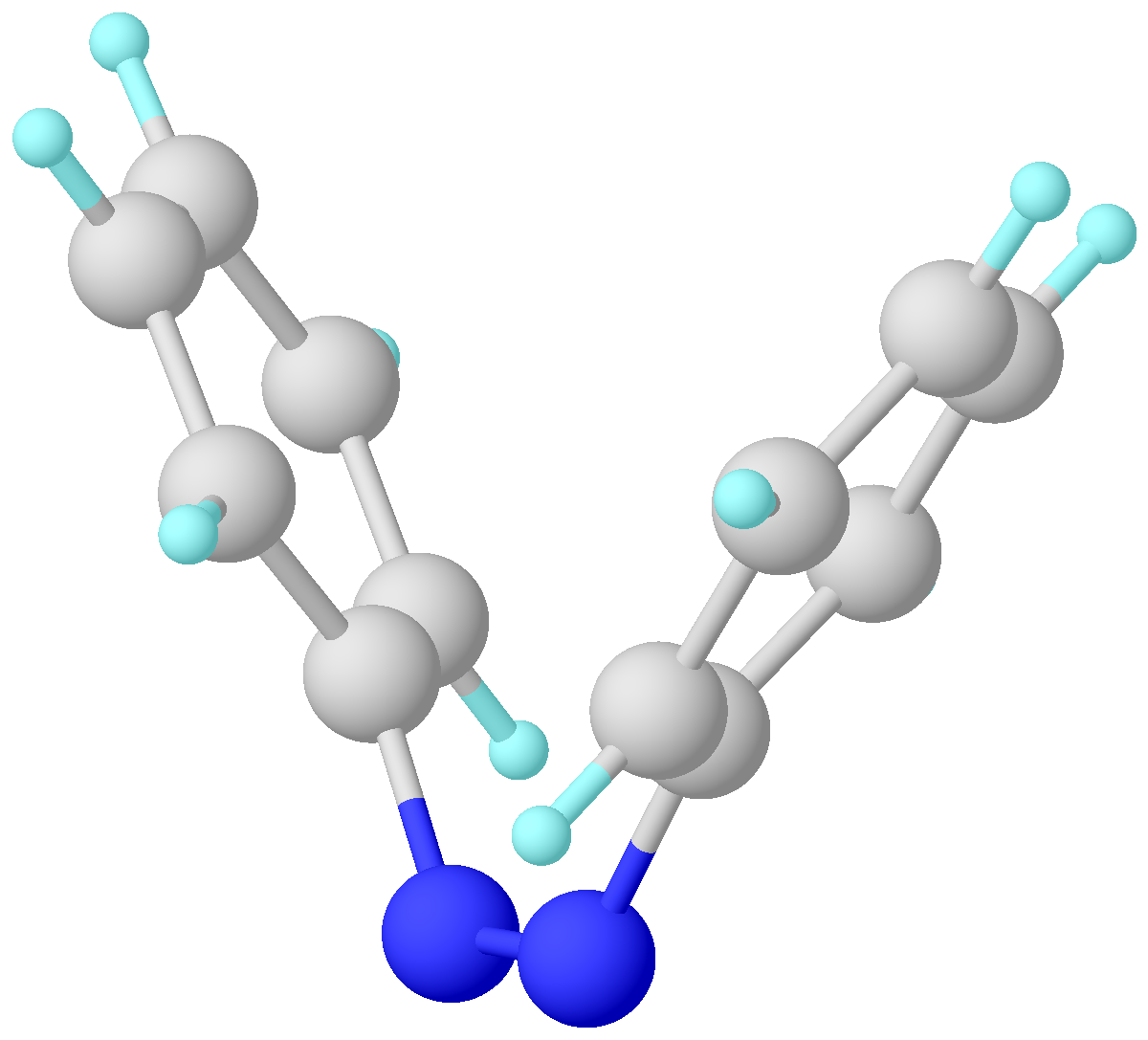
Azobenzene
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a azo compound, N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar Chemical compound, compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Different classes of azo dyes exist, most notably the ones substituted with heteroaryl rings. Structure and synthesis Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. Industrial electrosynthesis using nitrobenzene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dication
A dication is any cation, of general formula X2+, formed by the removal of two electrons from a neutral species. Diatomic dications corresponding to stable neutral species (e.g. formed by removal of two electrons from H2) often decay quickly into two singly charged particles (H+), due to the loss of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals. Energy levels of diatomic dications can be studied with good resolution by measuring the yield of pairs of zero-kinetic-energy electrons from double photoionization of a molecule as a function of the photoionizing wavelength (threshold photoelectrons coincidence spectroscopy – TPEsCO). The dication is kinetically stable. An example of a stable diatomic dication which is not formed by oxidation of a neutral diatomic molecule is the dimercury dication . An example of a polyatomic dication is , formed by oxidation of S8 and unstable with respect to further oxidation over time to form SO2. Many organic dications can be detected in mass spectro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl Halide
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents of hydrogen atom. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic, cabbage or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the smell of natural gas is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Nomenclature Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' (Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |