|
Cyclamin
Cyclamin is an organic compound that has been used by the pharmaceutical industry as an ingredient for nasal sprays. History Research on the cytotoxic and anticlastogenic activities of the cyclamen genus has been limited. In the 1950s and 1960s little research was done on the toxic saponin cyclamin, but no further investigation has recently been performed. Cyclamin, a triterpenoid pentasaccharidic saponin, has previously been extracted from different cyclamen species, including C''yclamen mirabile'', C''yclamen trocopteranthum'', C''yclamen libanoticum'' and C''ylamen persicum''. Available forms Cyclamin can be extracted from cyclamen plants such as the species ''mirabile'' and ''trocopteranthum''. Cyclamen are known houseplants; this raises concerns about the awareness of the toxicity of this flower. The compound cyclamin belongs to the family of triterpene saponins, which are derived from the saponin structure. Triterpenoid compounds contain one or more sugar moieties attach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclamen
''Cyclamen'' ( or ) is a genus of 23 species of perennial flowering plants in the family Primulaceae. In English, it is known by the common names sowbread or swinebread. ''Cyclamen'' species are native to Europe and the Mediterranean Basin east to the Caucasus and Iran, with one species in Somalia. They grow from tubers and are valued for their flowers with upswept petals and variably patterned leaves. It was traditionally classified in the family Primulaceae, was reclassified in the family Myrsinaceae in 2000 and finally, in 2009 with the introduction of the APG III system, was returned to the subfamily Myrsinoideae within the family Primulaceae. Names ''Cyclamen'' is Medieval Latin, from earlier Latin ''cyclamīnos'', from Ancient Greek κυκλάμινος, ''kyklā́mīnos'' (also ''kyklāmī́s''), from κύκλος, ''kýklos'' "circle", because of the round tuber. In English the species of the genus are commonly called by the genus name. Pliny the Elder des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion. A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and Epidermis (skin), epidermis, collectively referred to as the Cutis (anatomy), cutis. The instruments are usually a hypodermic needle and a syringe. Subcutaneous injections are highly effective in administering medications such as insulin, morphine, heroin, diacetylmorphine and goserelin. Subcutaneous administration may be List of medical abbreviations, abbreviated as SC, SQ, subcu, sub-Q, SubQ, or subcut. Subcut is the preferred abbreviation to reduce the risk of misunderstanding and potential errors. Subcutaneous tissue has few blood vessels and so drugs injected into it are intended for slow, sustained rates of absorption, often with some amount of depot injection, depot effect. Compared with other route of administration, routes of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the Colon (anatomy), colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include Lower gastrointestinal bleeding, blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, abdominal pain and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to lifestyle factors and genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol (drug), alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a adenoma, benign tumor, often in the form of a colorectal poly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascorbic Acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent. Ascorbic acid exists as two enantiomers (mirror-image isomers), commonly denoted "" (for "levo") and "" (for "dextro"). The isomer is the one most often encountered: it occurs naturally in many foods, and is one form (" vitamer") of vitamin C, an essential nutrient for humans and many animals. Deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy, formerly a major disease of sailors in long sea voyages. It is used as a food additive and a dietary supplement for its antioxidant properties. The "" form ( erythorbic acid) can be made by chemical synthesis, but has no significant biological role. Etymology The term ''ascorbic'' means antiscruvy and denotes the ability to fight off scurvy. It is related to combating Vitamin C deficiency. History The antiscor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechin
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids. The name of the catechin chemical family derives from ''catechu'', which is the tannic juice or boiled extract of ''Mimosa catechu'' (''Acacia catechu'' L.f.). Chemistry Catechin possesses two benzene rings (called the A and B rings) and a dihydropyran heterocycle (the C ring) with a hydroxyl group on carbon 3. The A ring is similar to a resorcinol moiety while the B ring is similar to a catechol moiety. There are two chirality (chemistry), chiral centers on the molecule on carbons 2 and 3. Therefore, it has four diastereoisomers. Two of the isomers are in trans configuration, ''trans'' configuration and are called ''catechin'' and the other two are in cis configuration, ''cis'' configuration and are called ''epicatechin''. The most common catechin isomer is (+)-catechin. The other stereoisomer is (−)-catechin or ''en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
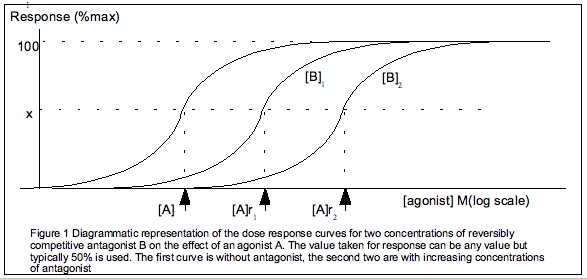
EC50
] Half maximal effective concentration (EC50) is a measure of the concentration of a drug, antibody or toxicant which induces a stimulus–response model, biological response halfway between the baseline and maximum after a specified exposure time. More simply, EC50 can be defined as the ''concentration required to obtain a 50% ..effect'' and may be also written as sub>50. It is commonly used as a measure of a drug's potency, although the use of EC50 is preferred over that of 'potency', which has been criticised for its vagueness. EC50 is a measure of concentration, expressed in molar units (M), where 1 M is equivalent to 1 mol/ L. The EC50 of a ''graded'' dose response curve therefore represents the concentration of a compound where 50% of its maximal effect is observed. The EC50 of a ''quantal'' dose response curve represents the concentration of a compound where 50% of the population exhibit a response, after a specified exposure duration. For clarification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC50
Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the potency of a substance in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. IC50 is a quantitative measure that indicates how much of a particular inhibitory substance (e.g. drug) is needed to inhibit, ''in vitro'', a given biological process or biological component by 50%. The biological component could be an enzyme, cell, cell receptor or microbe. IC50 values are typically expressed as molar concentration. IC50 is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency in pharmacological research. IC50 is comparable to other measures of potency, such as EC50 for excitatory drugs. EC50 represents the dose or plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect ''in vivo''. IC50 can be determined with functional assays or with competition binding assays. Sometimes, IC50 values are converted to the pIC50 scale. :\ce = -\log_ \ce Due to the minus sign, higher values of pIC50 indicate ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Inactive fibroblasts, called 'fibrocytes', are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have less RER. Although disjointed and scattered when covering large spaces, fibroblasts often locally align in parallel clusters when crowded together. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BxPC-3
BxPC-3 (BxPC3) is a human pancreatic cancer cell line used in the study of pancreatic adenocarcinomas and treatments thereof. BxPC-3 cells were derived from a 61-year-old female in 1986, and were confirmed to be tumorigenic in athymic nude mice, with moderate differentiation. The cells produce mucin, and exhibit an epithelial morphology. BxPC-3 cells lack a KRAS mutation, though it is commonly found in pancreatic cancers. BxPC-3 cells, along with JoPaca-1 cells, have high expression of cancer stem cell markers. BxPC-3 has been used in tumorigenicity studies, pancreatic cancer therapy research, and other biomedical applications. The cells have been additionally studied for their phenotypic and genotypic properties as they can be applied to pancreatic cancer drug development; in particular, BxPC-3 cells have high expression of the angiogenic factors IL-8, VEGF, and PGE2 Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), also known as dinoprostone, is a naturally occurring prostaglandin with oxytoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |