|
IC50
Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) is a measure of the potency of a substance in inhibiting a specific biological or biochemical function. IC50 is a quantitative measure that indicates how much of a particular inhibitory substance (e.g. drug) is needed to inhibit, ''in vitro'', a given biological process or biological component by 50%. The biological component could be an enzyme, cell, cell receptor or microbe. IC50 values are typically expressed as molar concentration. IC50 is commonly used as a measure of antagonist drug potency in pharmacological research. IC50 is comparable to other measures of potency, such as EC50 for excitatory drugs. EC50 represents the dose or plasma concentration required for obtaining 50% of a maximum effect ''in vivo''. IC50 can be determined with functional assays or with competition binding assays. Sometimes, IC50 values are converted to the pIC50 scale. :\ce = -\log_ \ce Due to the minus sign, higher values of pIC50 indicate ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EC50
] Half maximal effective concentration (EC50) is a measure of the concentration of a drug, antibody or toxicant which induces a stimulus–response model, biological response halfway between the baseline and maximum after a specified exposure time. More simply, EC50 can be defined as the ''concentration required to obtain a 50% ..effect'' and may be also written as sub>50. It is commonly used as a measure of a drug's potency, although the use of EC50 is preferred over that of 'potency', which has been criticised for its vagueness. EC50 is a measure of concentration, expressed in molar units (M), where 1 M is equivalent to 1 mol/ L. The EC50 of a ''graded'' dose response curve therefore represents the concentration of a compound where 50% of its maximal effect is observed. The EC50 of a ''quantal'' dose response curve represents the concentration of a compound where 50% of the population exhibit a response, after a specified exposure duration. For clarification, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibition Constant
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affinity (pharmacology)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potency (pharmacology)
In pharmacology, potency or biological potency is a measure of a drug's biological activity expressed in terms of the dose required to produce a pharmacological effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, clonazepam, risperidone, benperidol, bumetanide) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency (e.g. morphine, alprazolam, ziprasidone, haloperidol, furosemide) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness nor more side effects nor less side effects. Types of potency The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) has stated that "potency is an imprecise term that should always be further defined", and lists of types of potency as follows: Miscellaneous Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is one of the most potent psychoactive drug A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, mind-altering drug, consciousness-altering drug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheng Yung-chi
Yung-chi Cheng (traditional Chinese: 鄭永齊; pinyin: ''Zhèng Yǒngqí''; born December 29, 1944), also known as Tommy Cheng, is a Taiwanese-American pharmacologist. He is the Henry Bronson Professor of Pharmacology at Yale University, where he is the director of the Cheng laboratory at the Yale School of Medicine devoted to the study of antiviral drugs, and chairman of the Consortium for the Globalization of Chinese Medicine (CGCM). Early life and education Cheng was born in England on December 29, 1944, and later moved to Taiwan. After graduating from Tunghai University in 1966 with a Bachelor of Science (B.S.) in chemistry and biology, Cheng went to Canada and studied for a year at the University of Guelph. Because his wife was a graduate student at Brown University, Cheng decided to transfer to Brown and pursue graduate studies in the United States. He spent his first two years at Brown University studying medicine before earning a Ph.D. in biochemical pharmacology in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Prusoff
William Herman Prusoff (June 25, 1920 – April 3, 2011) was an American pharmacologist who was an early innovator in antiviral drugs, developing idoxuridine, the first antiviral agent approved by the FDA, in the 1950s, and co-developing (with Tai-shun Lin) stavudine, one of the earliest AIDS drugs, in the mid-1980s. Scientific career William Prusoff attended the University of Miami. After receiving his undergraduate degree in chemistry, he obtained his PhD from Columbia University and later completed his postdoctoral training in the laboratory of professor Arnold Welch at Case Western Reserve University. After Welch was recruited by Yale to head the Medical School's pharmacology department, Prusoff was invited to join the same department as an assistant professor and was subsequently promoted to the rank of professor. This relationship at Yale would span over the next 58 years, with William Prusoff becoming one of Yale's most well respected scientists and teachers. Pruso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LD50
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for "lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a given substance. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of higher toxicity. The term LD50 is generally attributed to John William Trevan. The test was created by J. W. Trevan in 1927. The term semilethal dose is occasionally used in the same sense, in particular with translations of foreign language text, but can also refer to a sublethal dose. LD50 is usually determined by tests on animals such as laboratory mice. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved alternative methods to LD50 for testing the cosmetic drug botox without animal tests. Conventions The LD50 is usually expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Certain Safety Factor
The therapeutic index (TI; also referred to as therapeutic ratio) is a quantitative measurement of the relative safety of a drug with regard to risk of overdose. It is a comparison of the amount of a therapeutic agent that causes toxicity to the amount that causes the therapeutic effect. The related terms therapeutic window or safety window refer to a range of doses optimized between efficacy and toxicity, achieving the greatest therapeutic benefit without resulting in unacceptable side-effects or toxicity. Classically, for clinical indications of an approved drug, TI refers to the ratio of the dose of the drug that causes adverse effects at an incidence/severity not compatible with the targeted indication (e.g. toxic dose in 50% of subjects, TD) to the dose that leads to the desired pharmacological effect (e.g. efficacious dose in 50% of subjects, ED). In contrast, in a drug development setting TI is calculated based on plasma exposure levels. In the early days of pharmaceu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (''K''D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into its component ions. The dissociation constant is the inverse of the association constant. In the special case of salts, the dissociation constant can also be called an ionization constant. For a general reaction: : A_\mathit B_\mathit \mathit A + \mathit B in which a complex \ce_x \ce_y breaks down into ''x'' A subunits and ''y'' B subunits, the dissociation constant is defined as : K_\mathrm = \frac where and ''x'' B''y''are the equilibrium concentrations of A, B, and the complex A''x'' B''y'', respectively. One reason for the popularity of the dissociation constant in biochemistry and pharmacology is that in the frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
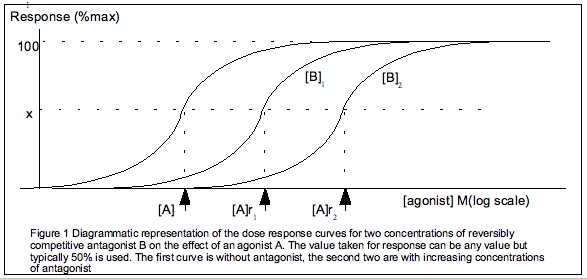
Receptor Antagonists
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves ." '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include s, |
Potency (pharmacology)
In pharmacology, potency or biological potency is a measure of a drug's biological activity expressed in terms of the dose required to produce a pharmacological effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, clonazepam, risperidone, benperidol, bumetanide) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency (e.g. morphine, alprazolam, ziprasidone, haloperidol, furosemide) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness nor more side effects nor less side effects. Types of potency The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) has stated that "potency is an imprecise term that should always be further defined", and lists of types of potency as follows: Miscellaneous Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is one of the most potent psychoactive drug A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, mind-altering drug, consciousness-altering drug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |