|
Chlorophyllide Oxidoreductase
Chlorophyllide ''a'' and chlorophyllide ''b'' are the biosynthetic precursors of chlorophyll ''a'' and chlorophyll ''b'' respectively. Their propionic acid groups are converted to phytyl esters by the enzyme chlorophyll synthase in the final step of the pathway. Thus the main interest in these chemical compounds has been in the study of chlorophyll biosynthesis in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyllide ''a'' is also an intermediate in the biosynthesis of bacteriochlorophylls. Structures Chlorophyllide ''a'', is a carboxylic acid (R=H). In chlorophyllide ''b'', the methyl group at position 13 ( IUPAC numbering for chlorophyllide ''a'') and highlighted in the green box, is replaced with a formyl group. Biosynthesis steps up to formation of protoporphyrin IX In the early steps of the biosynthesis, which starts from glutamic acid, a tetrapyrrole is created by the enzymes deaminase and cosynthetase which transform aminolevulinic acid via porphobilinogen and hydroxymethylbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve as enzyme substrate (chemistry), substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex Product (chemistry), products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of Chemical compound, compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism (building up and breaking down) of comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology. Structure and bonding Aldehyde molecules have a central carbon atom that is connected by a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to hydrogen and another single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The bond length is about 120–122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor F430
F430 is the cofactor (sometimes called the coenzyme) of the enzyme methyl coenzyme M reductase (MCR). MCR catalyzes the reaction that releases methane in the final step of methanogenesis: : + HS–CoB → + CoB–S–S–CoM It is found only in methanogenic Archaea and anaerobic methanotrophic Archaea. It occurs in relatively high concentrations in archaea that are involved in reverse methanogenesis: these can contain up to 7% by weight of the nickel protein. Structure The trivial name cofactor F430 was assigned in 1978 based on the properties of a yellow sample extracted from '' Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum'', which had a spectroscopic maximum at 430 nm. It was identified as the MCR cofactor in 1982 and the complete structure was deduced by X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. Coenzyme F430 features a reduced porphyrin in a macrocyclic ring system called a corphin. In addition, it possesses two additional rings in comparison to the standard tetrapyrrole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siroheme
Siroheme (or sirohaem) is a heme-like prosthetic group at the active sites of some enzymes to accomplish the six-electron reduction of sulfur and nitrogen. It is a cofactor at the active site of sulfite reductase, which plays a major role in sulfur assimilation pathway, converting sulfite into sulfide, which can be incorporated into the organic compound homocysteine. Biosynthesis Like all tetrapyrrole Tetrapyrroles are a class of chemical compounds that contain four pyrrole or pyrrole-like rings. The pyrrole/pyrrole derivatives are linked by ( or units), in either a linear or a cyclic fashion. Pyrroles are a five-atom ring with four carbon ...s, the macrocyclic ligand in siroheme is derived from uroporphyrinogen III. This porphyrinogen is methylated at two adjacent pyrrole rings to give dihydrosirohydrochlorin, which is subsequently oxidized to give sirohydrochlorin. A ferrochelatase then inserts iron into the macrocycle to give siroheme. See also * Ferredoxin-ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prosthetic group, component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 Vinyl group, vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. Heme plays a critical role in multiple different redox reactions in mammals, due to its ability to carry the oxygen molecule. Reactions include oxidative metabolism (cytochrome c oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase), xenobiotic detoxification via cytochrome P450 pathways (including Drug metabolism, metabolism of some drugs), gas sensing (Guanylate cyclase, guanyl cyclases, nitric oxide synthase), and microRNA processing (DGCR8). Heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocycle
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry. Synthesis The formation of macrocycles by ring-closure is called macrocyclization. The central challenge to macrocyclization is that ring-closing reactions do not favor the formation of large rings. Instead, medium sized rings or polymers tend to form. Early macrocyclizations were achieved ketonic decarboxylations for the preparation of terpenoid macrocycles. So, while Ružička was able to produce various macrocycles, the yields were low. This kinetic problem can be addressed by using high-dilution reactions, whereby intramolecular processes are favored relative to polymerizations. Reactions amenable to high dilution include Dieckmann condensation and related based-induced reactions of esters with remote halides. Some macrocyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen III
Uroporphyrinogen III is a tetrapyrrole, the first macrocycle, macrocyclic intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and siroheme. It is a colorless compound, like other porphyrinogens. Structure The molecular structure of uroporphyrinogen III can be described as a hexahydroporphine core, where each pyrrole ring has the hydrogen atoms on its two outermost carbons replaced by an acetic acid group (, "A") and a propionic acid group (, "P"). The groups are attached in an asymmetric way: going around the macrocycle, the order is AP-AP-AP-PA. Biosynthesis and metabolism In the general porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, uroporphyrinogen III is derived from the linear tetrapyrrole preuroporphyrinogen (a substituted hydroxymethylbilane) by the action of the enzyme uroporphyrinogen-III synthase, uroporphyrinogen-III cosynthase. The conversion entails a reversal of the last pyrrole unit (thus swapping the acetic and propionic acid groups) and a condensation reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxymethylbilane
Hydroxymethylbilane, also known as preuroporphyrinogen, is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms during the synthesis of porphyrins, a group of critical substances that include haemoglobin, myoglobin, and chlorophyll. The name is often abbreviated as HMB. Structure The compound is a substituted bilane, a chain of four pyrrole rings interconnected by methylene bridges . The chain starts with a hydroxymethyl group and ends with a hydrogen, in place of the respective methylene bridges. The other two carbon atoms of each pyrrole cycle are connected to an acetic acid group and a propionic acid group , in that order. Metabolism HMB is generated from four molecules of porphobilinogen by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase: The enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase closes the chain to form uroporphyrinogen III: Uroporphyrinogen III is a porphyrinogen, which is a class of compounds with the hexahydroporphine macrocycle Macrocycles are often described as mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
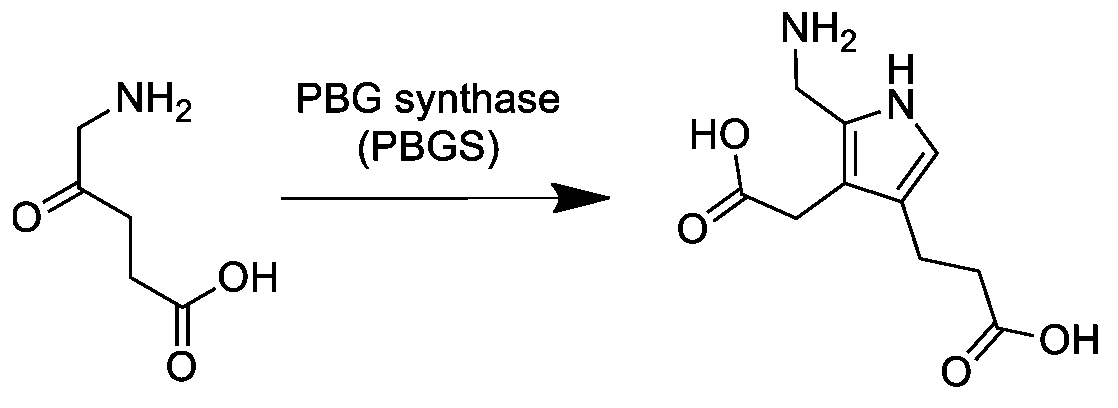
Porphobilinogen
Porphobilinogen (PBG) is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of porphyrins, which include critical substances like hemoglobin and chlorophyll. The structure of the molecule can be described as molecule of pyrrole with sidechains substituted for hydrogen atoms at positions 2, 3 and 4 in the ring (1 being the nitrogen atom); respectively, an aminomethyl group , an acetic acid (carboxymethyl) group , and a propionic acid (carboxyethyl) group . Biosynthesis In the first step of the porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, porphobilinogen is generated from aminolevulinate (ALA) by the enzyme ALA dehydratase. Metabolism In the typical porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, four molecules of porphobilinogen are concatenated by carbons 2 and 5 of the pyrrole ring (adjacent to the nitrogen atom) into hydroxymethyl bilane by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase, also known as hydroxymethylbilane synthase. Pathologies Acute intermittent porphyria c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminolevulinic Acid
δ-Aminolevulinic acid (also dALA, δ-ALA, 5ALA or 5-aminolevulinic acid), an endogenous non-proteinogenic amino acid, is the first compound in the porphyrin synthesis pathway, the pathway that leads to heme in mammals, as well as chlorophyll in plants. 5ALA is used in photodynamic detection and surgery of cancer.Wagnières, G.., Jichlinski, P., Lange, N., Kucera, P., Van den Bergh, H. (2014). Detection of Bladder Cancer by Fluorescence Cystoscopy: From Bench to Bedside - the Hexvix Story. Handbook of Photomedicine, 411-426. Medical uses As a precursor of a photosensitizer, 5ALA is also used as an add-on agent for photodynamic therapy. In contrast to larger photosensitizer molecules, it is predicted by computer simulations to be able to penetrate tumor cell membranes. Cancer diagnosis Photodynamic detection is the use of photosensitive drugs with a light source of the right wavelength for the detection of cancer, using fluorescence of the drug. 5ALA, or derivatives thereof, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uroporphyrinogen III Synthase
Uroporphyrinogen III synthase () is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the cyclic tetrapyrrole compound porphyrin. It is involved in the conversion of hydroxymethyl bilane into uroporphyrinogen III. This enzyme catalyses the inversion of the final pyrrole unit (ring D) of the linear tetrapyrrole molecule, linking it to the first pyrrole unit (ring A), thereby generating a large macrocyclic structure, uroporphyrinogen III. The enzyme folds into two alpha/beta domains connected by a beta-ladder, the active site being located between the two domains. Pathology A deficiency is associated with Gunther's disease, also known as congenital erythropoietic porphyria (CEP). This is an autosomal recessive In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The firs ... inborn error of metabolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphobilinogen Deaminase
Porphobilinogen deaminase (hydroxymethylbilane synthase, or uroporphyrinogen I synthase) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the HMBS gene. Porphobilinogen deaminase is involved in the third step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. It catalyzes the head to tail condensation of four porphobilinogen molecules into the linear hydroxymethylbilane while releasing four ammonia molecules: :4 porphobilinogen + H2O \rightleftharpoons hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH3 Structure and function Functionally, porphobilinogen deaminase catalyzes the loss of ammonia from the porphobilinogen monomer (deamination) and its subsequent polymerization to a linear tetrapyrrole, which is released as hydroxymethylbilane: The structure of 40-42 kDa porphobilinogen deaminase, which is highly conserved amongst organisms, consists of three domains. Domains 1 and 2 are structurally very similar: each consisting of five beta-sheets and three alpha helices in humans. Domain 3 is positioned between the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |