|
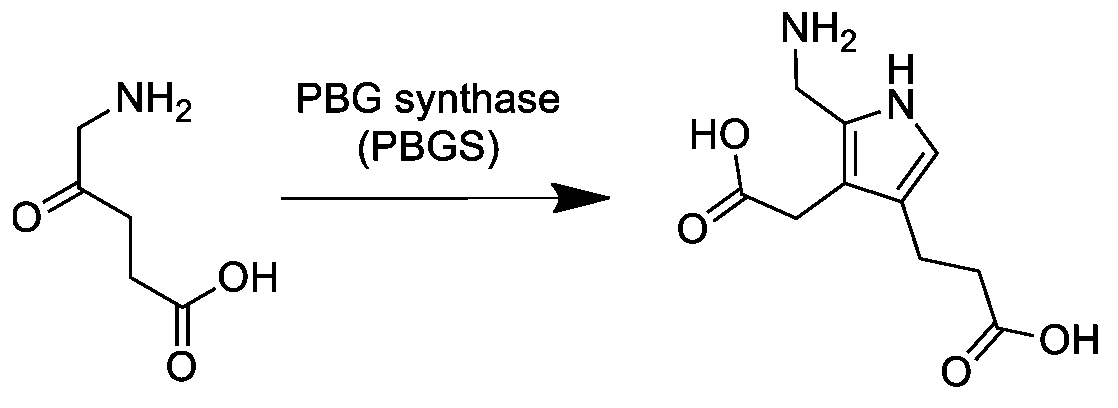
Porphobilinogen
Porphobilinogen (PBG) is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of porphyrins, which include critical substances like hemoglobin and chlorophyll. The structure of the molecule can be described as molecule of pyrrole with sidechains substituted for hydrogen atoms at positions 2, 3 and 4 in the ring (1 being the nitrogen atom); respectively, an aminomethyl group , an acetic acid (carboxymethyl) group , and a propionic acid (carboxyethyl) group . Biosynthesis In the first step of the porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, porphobilinogen is generated from aminolevulinate (ALA) by the enzyme ALA dehydratase. Metabolism In the typical porphyrin biosynthesis pathway, four molecules of porphobilinogen are concatenated by carbons 2 and 5 of the pyrrole ring (adjacent to the nitrogen atom) into hydroxymethyl bilane by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase, also known as hydroxymethylbilane synthase. Pathologies Acute intermittent porphyria c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxymethylbilane Synthase
Porphobilinogen deaminase (hydroxymethylbilane synthase, or uroporphyrinogen I synthase) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the HMBS gene. Porphobilinogen deaminase is involved in the third step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. It catalyzes the head to tail condensation of four porphobilinogen molecules into the linear hydroxymethylbilane while releasing four ammonia molecules: :4 porphobilinogen + H2O \rightleftharpoons hydroxymethylbilane + 4 NH3 Structure and function Functionally, porphobilinogen deaminase catalyzes the loss of ammonia from the porphobilinogen monomer (deamination) and its subsequent polymerization to a linear tetrapyrrole, which is released as hydroxymethylbilane: The structure of 40-42 kDa porphobilinogen deaminase, which is highly conserved amongst organisms, consists of three domains. Domains 1 and 2 are structurally very similar: each consisting of five beta-sheets and three alpha helices in humans. Domain 3 is positioned between the other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALA Dehydratase
Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (porphobilinogen synthase, or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) is an enzyme () that in humans is encoded by the ''ALAD'' gene. Porphobilinogen synthase (or ALA dehydratase, or aminolevulinate dehydratase) synthesizes porphobilinogen through the asymmetric condensation of two molecules of aminolevulinic acid. All natural tetrapyrroles, including hemes, chlorophylls and vitamin B12, share porphobilinogen as a common precursor. Porphobilinogen synthase is the prototype morpheein. Function It catalyzes the following reaction, the second step of the biosynthesis of porphyrin: :2 5-Aminolevulinic acid \rightleftharpoons porphobilinogen + 2 H2O It therefore catalyzes the condensation of 2 molecules of 5-aminolevulinate to form porphobilinogen (a precursor of heme, cytochromes and other hemoproteins). This reaction is the first common step in the biosynthesis of all biological tetrapyrroles. Zinc is essential for enzymatic activity. Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Intermittent Porphyria
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a rare Metabolism, metabolic disorder affecting the production of heme resulting from a deficiency of the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase. It is the most common of the acute porphyrias. Signs and symptoms The clinical presentation of AIP is highly variable and non-specific. The patients are typically asymptomatic, with most gene carriers having no family history because the condition had remained latent for several generations. The syndrome marked by acute attacks affects only 10% of gene carriers. The mean age at diagnosis is 33 years old. Like other porphyrias, AIP is more likely to present in women. A distinguishing feature of AIP that separates it from other porphyrias is the absence of Photosensitivity, photosensitive Skin, cutaneous symptoms that occur in addition to acute attacks. Acute attacks AIP is one of the four porphyrias that presents as an acute attack. 90% of affected individuals never experience an Acute (medicine), acute a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxymethyl Bilane
Hydroxymethylbilane, also known as preuroporphyrinogen, is an organic compound that occurs in living organisms during the synthesis of porphyrins, a group of critical substances that include haemoglobin, myoglobin, and chlorophyll. The name is often abbreviated as HMB. Structure The compound is a substituted bilane, a chain of four pyrrole rings interconnected by methylene bridges . The chain starts with a hydroxymethyl group and ends with a hydrogen, in place of the respective methylene bridges. The other two carbon atoms of each pyrrole cycle are connected to an acetic acid group and a propionic acid group , in that order. Metabolism HMB is generated from four molecules of porphobilinogen by the enzyme porphobilinogen deaminase: The enzyme uroporphyrinogen III synthase closes the chain to form uroporphyrinogen III: Uroporphyrinogen III is a porphyrinogen, which is a class of compounds with the hexahydroporphine macrocycle Macrocycles are often described as mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin Biosynthesis
Porphyrins ( ) are heterocyclic, macrocyclic, organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (). In vertebrates, an essential member of the porphyrin group is heme, which is a component of hemoproteins, whose functions include carrying oxygen in the bloodstream. In plants, an essential porphyrin derivative is chlorophyll, which is involved in light harvesting and electron transfer in photosynthesis. The parent of porphyrins is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons the porphyrin ring structure is a coordinated aromatic system. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives . Structure Porphyrin complexes consist of a square planar MN4 core. The periph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyrin
Porphyrins ( ) are heterocyclic, macrocyclic, organic compounds, composed of four modified pyrrole subunits interconnected at their α carbon atoms via methine bridges (). In vertebrates, an essential member of the porphyrin group is heme, which is a component of hemoproteins, whose functions include carrying oxygen in the bloodstream. In plants, an essential porphyrin derivative is chlorophyll, which is involved in light harvesting and electron transfer in photosynthesis. The parent of porphyrins is porphine, a rare chemical compound of exclusively theoretical interest. Substituted porphines are called porphyrins. With a total of 26 π-electrons the porphyrin ring structure is a coordinated aromatic system. One result of the large conjugated system is that porphyrins absorb strongly in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The name "porphyrin" derives . Structure Porphyrin complexes consist of a square planar MN4 core. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrroles
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, Aromaticity, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered Ring (chemistry), ring with the chemical formula, formula . It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrole, . Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme. Pyrroles are components of more complex macrocycles, including the porphyrinogens and products derived therefrom, including porphyrins of heme, the chlorins, bacteriochlorins, and chlorophylls. Properties, structure, bonding Pyrrole is a colorless volatility (chemistry), volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air, and is usually purified by distillation immediately before use. Pyrrole has a nutty odor. Pyrrole is a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle, like furan and thiophene. Unlike furan and thiophene, it has a dipole in which the positive end lies on the side of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula . It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrole, . Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme. Pyrroles are components of more complex macrocycles, including the porphyrinogens and products derived therefrom, including porphyrins of heme, the chlorins, bacteriochlorins, and chlorophylls. Properties, structure, bonding Pyrrole is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air, and is usually purified by distillation immediately before use. Pyrrole has a nutty odor. Pyrrole is a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle, like furan and thiophene. Unlike furan and thiophene, it has a dipole in which the positive end lies on the side of the heteroatom, with a dipole moment of 1.58 D. In CDCl3, it ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |