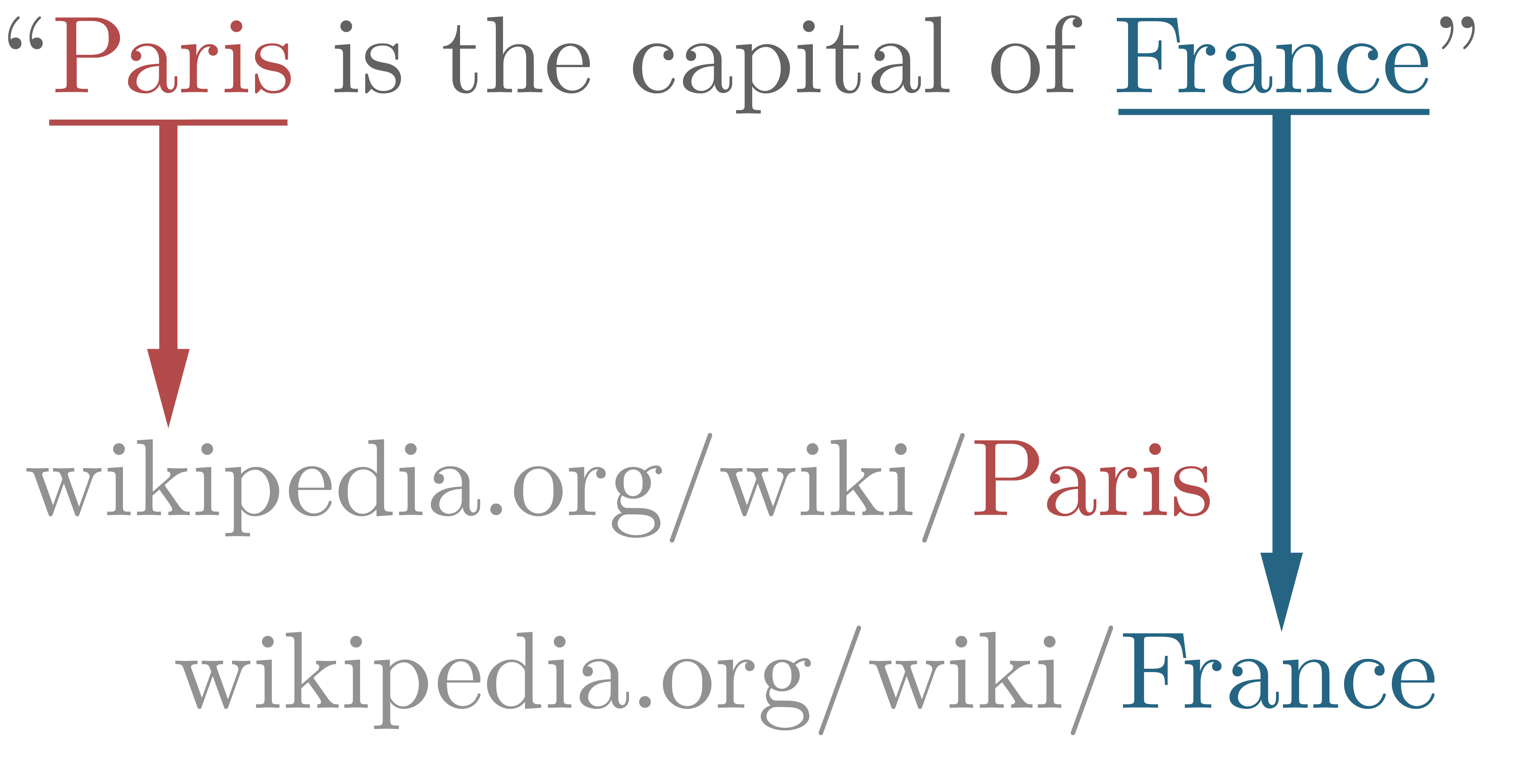|
Annotate
An annotation is extra information associated with a particular point in a document or other piece of information. It can be a note that includes a comment or explanation. Annotations are sometimes presented in the margin of book pages. For annotations of different digital media, see web annotation and text annotation. Literature, grammar and educational purposes Practising visually Annotation Practices are highlighting a phrase or sentence and including a comment, circling a word that needs defining, posing a question when something is not fully understood and writing a short summary of a key section. It also invites students to "(re)construct a history through material engagement and exciting DIY (Do-It-Yourself) annotation practices." Annotation practices that are available today offer a remarkable set of tools for students to begin to work, and in a more collaborative, connected way than has been previously possible. Text and film annotation Text and Film Annotation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Tree
A decision tree is a decision support system, decision support recursive partitioning structure that uses a Tree (graph theory), tree-like Causal model, model of decisions and their possible consequences, including probability, chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility. It is one way to display an algorithm that only contains conditional control statements. Decision trees are commonly used in operations research, specifically in decision analysis, to help identify a strategy most likely to reach a goal, but are also a popular tool in Decision tree learning, machine learning. Overview A decision tree is a flowchart-like structure in which each internal node represents a test on an attribute (e.g. whether a coin flip comes up heads or tails), each branch represents the outcome of the test, and each leaf node represents a class label (decision taken after computing all attributes). The paths from root to leaf represent classification rules. In decision analysis, a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is a bibliography Bibliography (from and ), as a discipline, is traditionally the academic study of books as physical, cultural objects; in this sense, it is also known as bibliology (from ). English author and bibliographer John Carter describes ''bibliograph ... that gives a summary of each of the entries. The purpose of annotations is to provide the reader with a summary and an evaluation of each source. Each summary should be a concise exposition of the source's central idea(s) and give the reader a general idea of the source's content. Main components of annotated bibliographies The following are the main components of an annotated bibliography. Not all these fields are used; fields may vary depending on the type of annotated bibliography and instructions from the instructor if it is part of a school assignment. * Full bibliographic citation: the necessary and complete bibliographical information i.e. (author, title, publisher and date, etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Document
A document is a writing, written, drawing, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of nonfiction, non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ', which denotes a "teaching" or "lesson": the verb ' denotes "to teach". In the past, the word was usually used to denote written proof useful as evidence of a truth or fact. In the computer age, Computer Age, "document" usually denotes a primarily textual computer file, including its structure and format, e.g. fonts, colors, and Computer-generated imagery, images. Contemporarily, "document" is not defined by its transmission medium, e.g., paper, given the existence of electronic documents. "Documentation" is distinct because it has more denotations than "document". Documents are also distinguished from "Realia (library science), realia", which are three-dimensional objects that would otherwise satisfy the definition of "document" because they memorialize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontologies
In information science, an ontology encompasses a representation, formal naming, and definitions of the categories, properties, and relations between the concepts, data, or entities that pertain to one, many, or all domains of discourse. More simply, an ontology is a way of showing the properties of a subject area and how they are related, by defining a set of terms and relational expressions that represent the entities in that subject area. The field which studies ontologies so conceived is sometimes referred to as ''applied ontology''. Every academic discipline or field, in creating its terminology, thereby lays the groundwork for an ontology. Each uses ontological assumptions to frame explicit theories, research and applications. Improved ontologies may improve problem solving within that domain, interoperability of data systems, and discoverability of data. Translating research papers within every field is a problem made easier when experts from different countries mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entity Linking
In natural language processing, Entity Linking, also referred to as named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD), named-entity normalization (NEN), or Concept Recognition, is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities (such as famous individuals, locations, or companies) mentioned in text. For example, given the sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the main idea is to first identify ''"Paris"'' and ''"France"'' as named entities, and then to determine that ''"Paris"'' refers to the city of Paris and not to Paris Hilton or any other entity that could be referred to as ''"Paris"'' and ''"France"'' to the french country. The Entity Linking task is composed of 3 subtasks. # Named Entity Recognition: Extraction of named entities from a text. # Candidate Generation: For each named entity, select possible candidates from a Knowledge Base (e.g. Wikipedia, Wikidata, DBPedia, ...). # Disambiguation: Choose the correct entit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PageRank
PageRank (PR) is an algorithm used by Google Search to rank web pages in their search engine results. It is named after both the term "web page" and co-founder Larry Page. PageRank is a way of measuring the importance of website pages. According to Google: Currently, PageRank is not the only algorithm used by Google to order search results, but it is the first algorithm that was used by the company, and it is the best known. As of September 24, 2019, all patents associated with PageRank have expired. Description PageRank is a link analysis algorithm and it assigns a numerical weighting to each element of a hyperlinked set of documents, such as the World Wide Web, with the purpose of "measuring" its relative importance within the set. The algorithm may be applied to any collection of entities with reciprocal quotations and references. The numerical weight that it assigns to any given element ''E'' is referred to as the ''PageRank of E'' and denoted by PR(E). A PageRank resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support-vector Machine
In machine learning, support vector machines (SVMs, also support vector networks) are supervised learning, supervised Maximum-margin hyperplane, max-margin models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data for Statistical classification, classification and regression analysis. Developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories, SVMs are one of the most studied models, being based on statistical learning frameworks of VC theory proposed by Vladimir Vapnik, Vapnik (1982, 1995) and Alexey Chervonenkis, Chervonenkis (1974). In addition to performing linear classifier, linear classification, SVMs can efficiently perform non-linear classification using the Kernel method#Mathematics: the kernel trick, ''kernel trick'', representing the data only through a set of pairwise similarity comparisons between the original data points using a kernel function, which transforms them into coordinates in a higher-dimensional feature space. Thus, SVMs use the kernel trick to implicitly map their inputs int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Model
A graphical model or probabilistic graphical model (PGM) or structured probabilistic model is a probabilistic model for which a graph expresses the conditional dependence structure between random variables. Graphical models are commonly used in probability theory, statistics—particularly Bayesian statistics—and machine learning. Types of graphical models Generally, probabilistic graphical models use a graph-based representation as the foundation for encoding a distribution over a multi-dimensional space and a graph that is a compact or factorized representation of a set of independences that hold in the specific distribution. Two branches of graphical representations of distributions are commonly used, namely, Bayesian networks and Markov random fields. Both families encompass the properties of factorization and independences, but they differ in the set of independences they can encode and the factorization of the distribution that they induce. Undirected Graphical Model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzzy Clustering
Fuzzy clustering (also referred to as soft clustering or soft ''k''-means) is a form of clustering in which each data point can belong to more than one cluster. Clustering or cluster analysis involves assigning data points to clusters such that items in the same cluster are as similar as possible, while items belonging to different clusters are as dissimilar as possible. Clusters are identified via similarity measures. These similarity measures include distance, connectivity, and intensity. Different similarity measures may be chosen based on the data or the application. Comparison to hard clustering In non-fuzzy clustering (also known as hard clustering), data are divided into distinct clusters, where each data point can only belong to exactly one cluster. In fuzzy clustering, data points can potentially belong to multiple clusters. For example, an apple can be red or green (hard clustering), but an apple can also be red AND green (fuzzy clustering). Here, the apple can be red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test
In statistics, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (also K–S test or KS test) is a nonparametric statistics, nonparametric test of the equality of continuous (or discontinuous, see #Discrete and mixed null distribution, Section 2.2), one-dimensional probability distributions. It can be used to test whether a random sample, sample came from a given reference probability distribution (one-sample K–S test), or to test whether two samples came from the same distribution (two-sample K–S test). Intuitively, it provides a method to qualitatively answer the question "How likely is it that we would see a collection of samples like this if they were drawn from that probability distribution?" or, in the second case, "How likely is it that we would see two sets of samples like this if they were drawn from the same (but unknown) probability distribution?". It is named after Andrey Kolmogorov and Nikolai Smirnov (mathematician), Nikolai Smirnov. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistic quantifies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
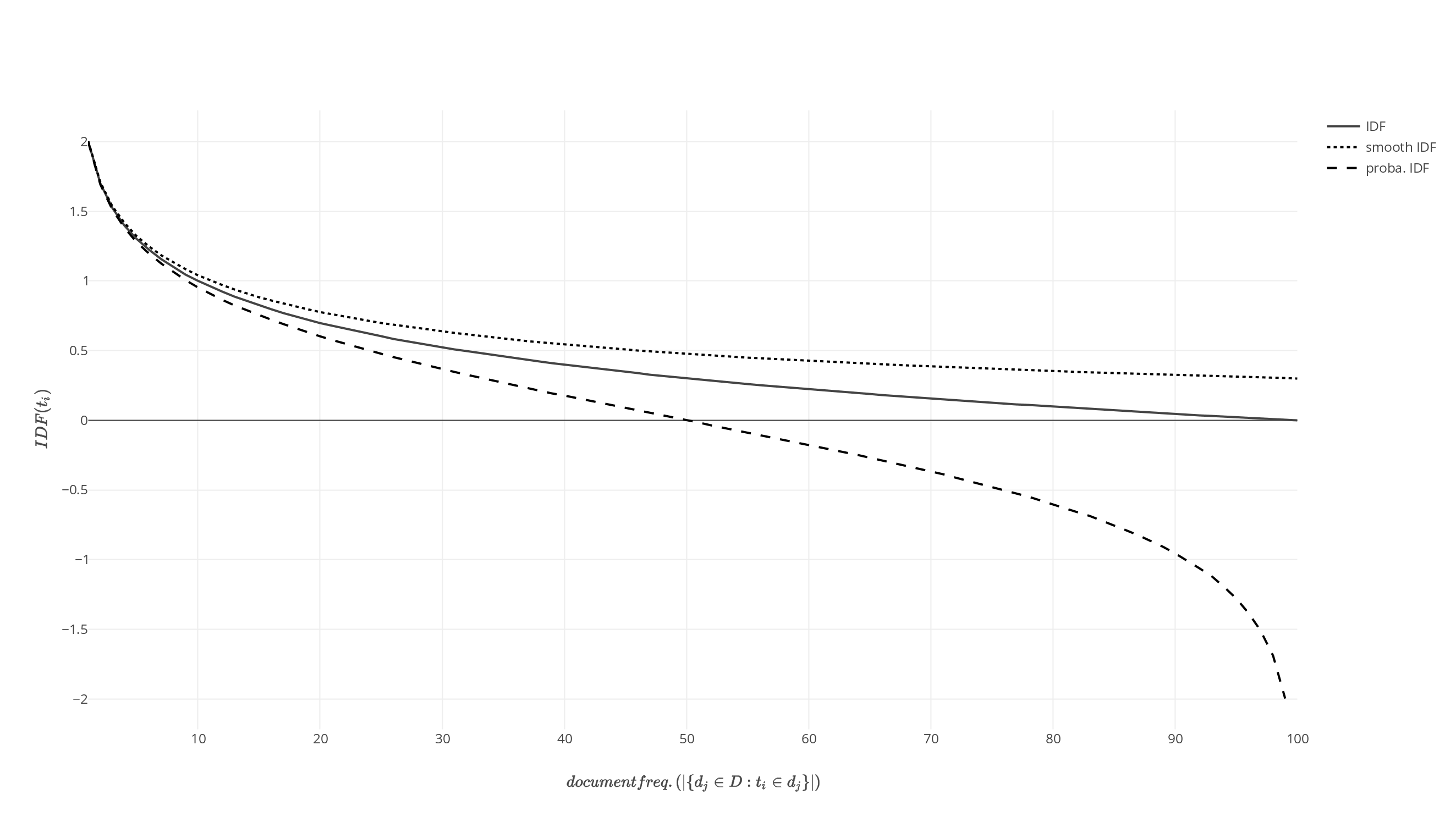
Tf–idf
In information retrieval, tf–idf (term frequency–inverse document frequency, TF*IDF, TFIDF, TF–IDF, or Tf–idf) is a measure of importance of a word to a document in a collection or Text corpus, corpus, adjusted for the fact that some words appear more frequently in general. Like the bag-of-words model, it models a document as a multiset of words, without word order. It is a refinement over the simple bag-of-words model, by allowing the weight of words to depend on the rest of the corpus. It was often used as a weighting factor in searches of information retrieval, text mining, and user modeling. A survey conducted in 2015 showed that 83% of text-based recommender systems in digital libraries used tf–idf. Variations of the tf–idf weighting scheme were often used by search engines as a central tool in scoring and ranking a document's Relevance (information retrieval), relevance given a user Information retrieval, query. One of the simplest ranking functions is computed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
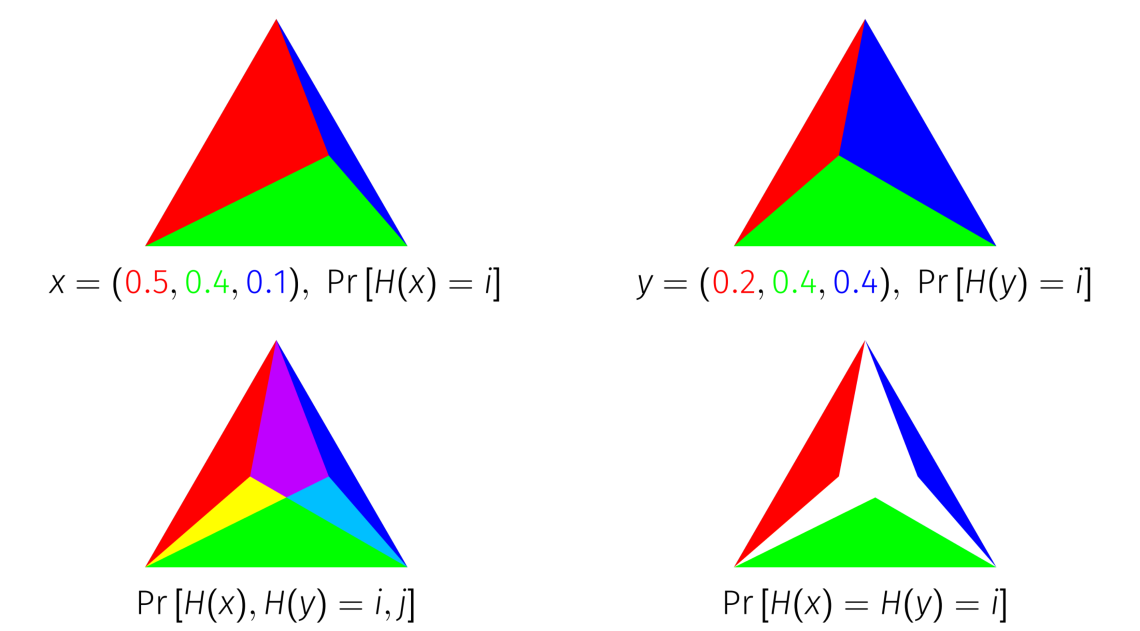
Jaccard Index
The Jaccard index is a statistic used for gauging the similarity and diversity of sample sets. It is defined in general taking the ratio of two sizes (areas or volumes), the intersection size divided by the union size, also called intersection over union (IoU). It was developed by Grove Karl Gilbert in 1884 as his ratio of verification (v) and now is often called the critical success index in meteorology. It was later developed independently by Paul Jaccard, originally giving the French name (coefficient of community), and independently formulated again by Taffee Tadashi Tanimoto. Thus, it is also called Tanimoto index or Tanimoto coefficient in some fields. Overview The Jaccard index measures similarity between finite non-empty sample sets and is defined as the size of the intersection divided by the size of the union of the sample sets: : J(A, B) = \frac = \frac. Note that by design, 0 \le J(A, B) \le 1. If the sets A and B have no elements in common, their intersectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |