entity linking on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 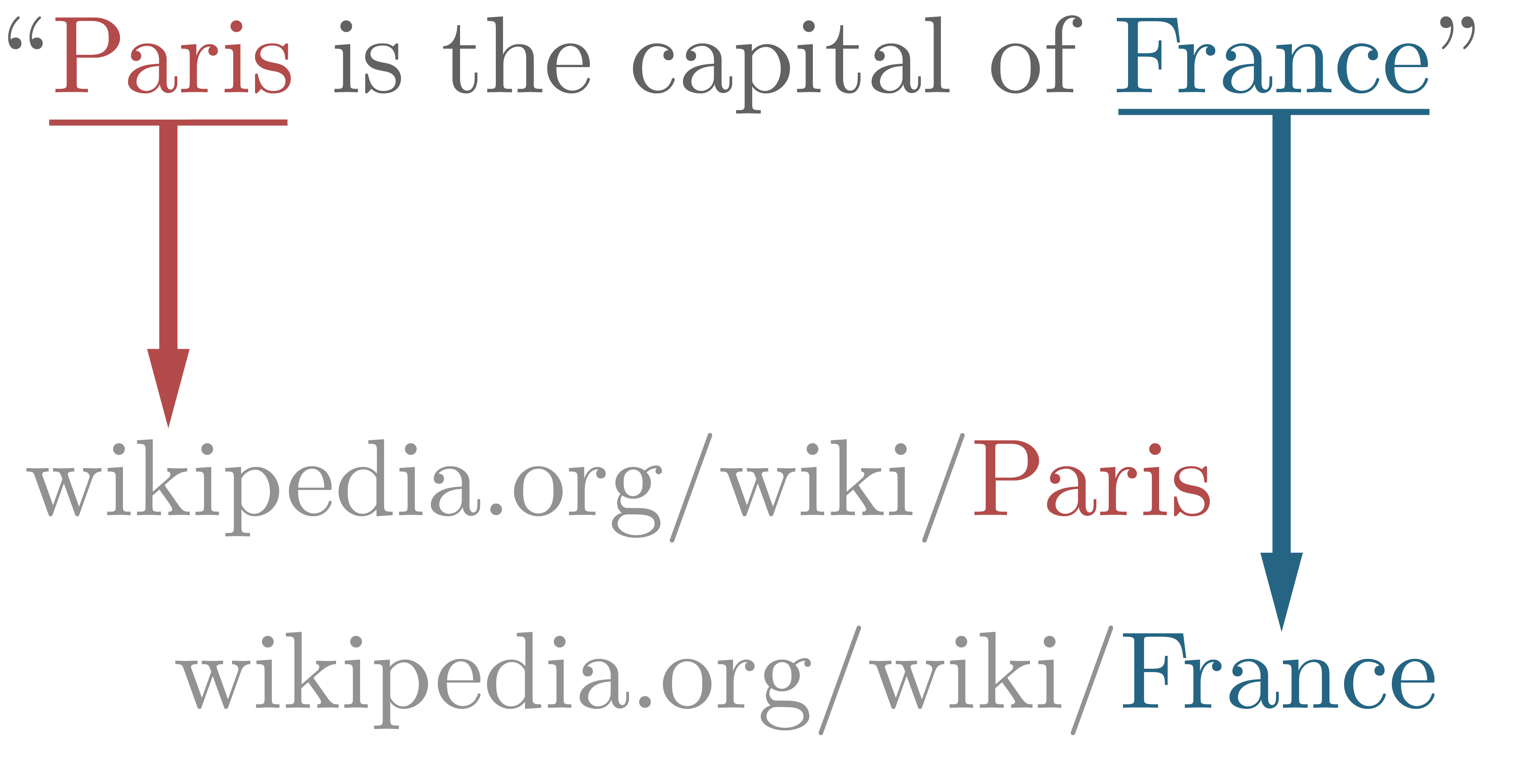
Wikify! Linking Documents to Encyclopedic Knowledge
Proc. CIKM. Considering again the example sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the expected output of an entity linking system will be
The impact of named entity normalization on information retrieval for question answering
Proc. ECIR. and to improve search performance on digital libraries.Hui Han, Hongyuan Zha, C. Lee Giles, "Name disambiguation in author citations using a K-way spectral clustering method," ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries 2005 (JCDL 2005): 334-343, 2005 Entity linking is also a key input for semantic search.

natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
, Entity Linking, also referred to as named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD), named-entity normalization (NEN), or Concept Recognition, is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities (such as famous individuals, locations, or companies) mentioned in text. For example, given the sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the main idea is to first identify ''"Paris"'' and ''"France"'' as named entities, and then to determine that ''"Paris"'' refers to the city of Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
and not to Paris Hilton or any other entity that could be referred to as ''"Paris"'' and ''"France"'' to the french country.
The Entity Linking task is composed of 3 subtasks.
# Named Entity Recognition: Extraction of named entities from a text.
# Candidate Generation: For each named entity, select possible candidates from a Knowledge Base
In computer science, a knowledge base (KB) is a set of sentences, each sentence given in a knowledge representation language, with interfaces to tell new sentences and to ask questions about what is known, where either of these interfaces migh ...
(e.g. Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a free content, free Online content, online encyclopedia that is written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and the wiki software MediaWiki. Founded by Jimmy Wales and La ...
, Wikidata, DBPedia
DBpedia (from "DB" for "database") is a project aiming to extract structured content from the information created in the Wikipedia project. This structured information is made available on the World Wide Web using OpenLink Virtuoso. DBpedia a ...
, ...).
# Disambiguation: Choose the correct entity from this set of candidates.
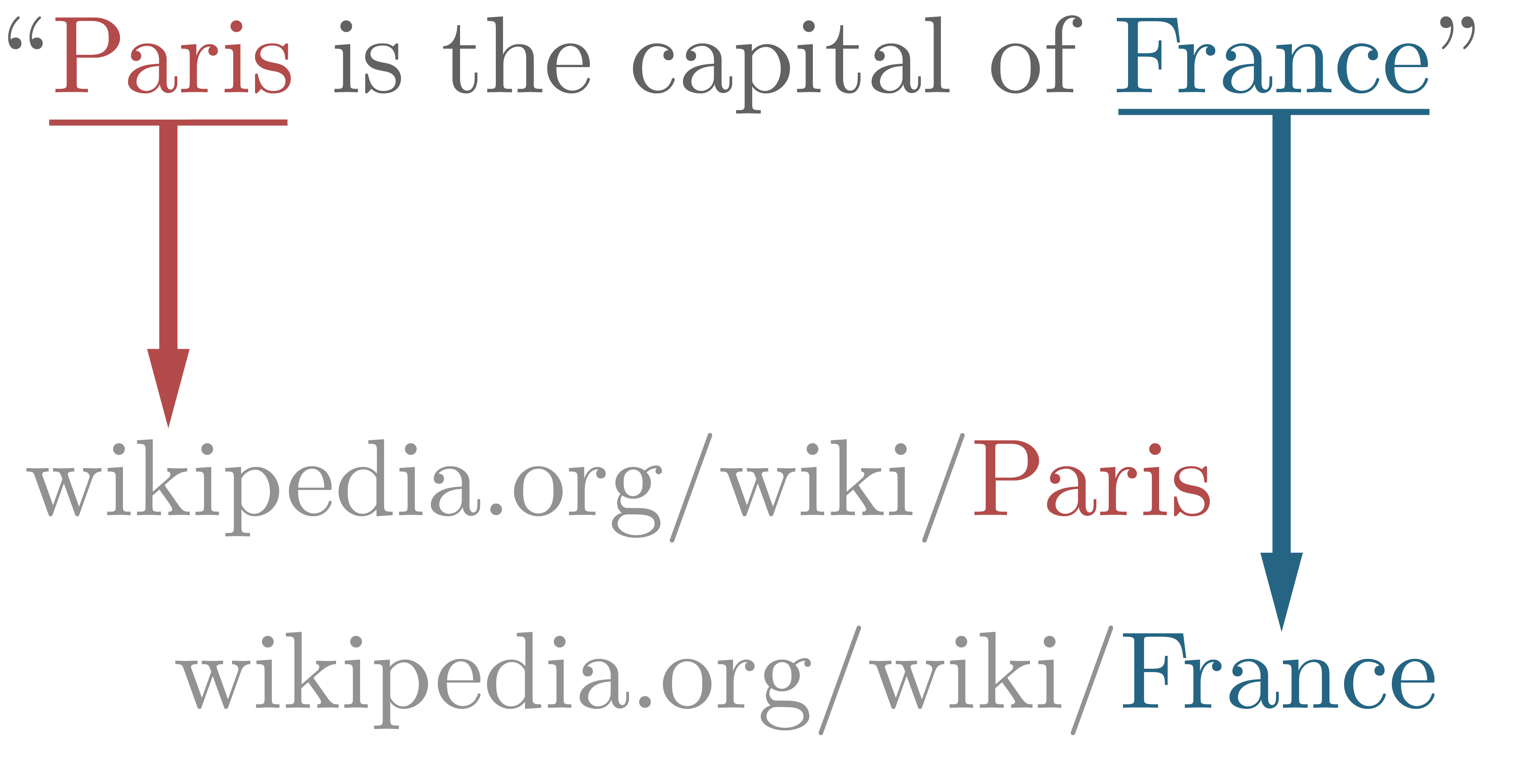
Introduction
In entity linking, words of interest (names of persons, locations and companies) are mapped from an input text to corresponding unique entities in a targetknowledge base
In computer science, a knowledge base (KB) is a set of sentences, each sentence given in a knowledge representation language, with interfaces to tell new sentences and to ask questions about what is known, where either of these interfaces migh ...
. Words of interest are called named entities (NEs), mentions, or surface forms. The target knowledge base depends on the intended application, but for entity linking systems intended to work on open-domain text it is common to use knowledge-bases derived from Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a free content, free Online content, online encyclopedia that is written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and the wiki software MediaWiki. Founded by Jimmy Wales and La ...
(such as Wikidata or DBpedia
DBpedia (from "DB" for "database") is a project aiming to extract structured content from the information created in the Wikipedia project. This structured information is made available on the World Wide Web using OpenLink Virtuoso. DBpedia a ...
). In this case, each individual Wikipedia page is regarded as a separate entity. Entity linking techniques that map named entities to Wikipedia entities are also called wikification.Rada Mihalcea and Andras Csomai (200Wikify! Linking Documents to Encyclopedic Knowledge
Proc. CIKM. Considering again the example sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the expected output of an entity linking system will be
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
. These uniform resource locators (URLs) can be used as unique uniform resource identifiers
(URIs) for the entities in the knowledge base. Using a different knowledge base will return different URIs, but for knowledge bases built starting from Wikipedia there exist one-to-one URI mappings.
In most cases, knowledge bases are manually built, Wikidata but in applications where large text corpora are available, the knowledge base can be inferred automatically from the available text.
Entity linking is a critical step to bridge web data with knowledge bases, which is beneficial for annotating the huge amount of raw and often noisy data on the Web and contributes to the vision of the Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
To enable the encoding o ...
. In addition to entity linking, there are other critical steps including but not limited to event extraction, and event linking etc.
Applications
Entity linking is beneficial in fields that need to extract abstract representations from text, as it happens in text analysis, recommender systems, semantic search and chatbots. In all these fields, concepts relevant to the application are separated from text and other non-meaningful data. For example, a common task performed by search engines is to find documents that are similar to one given as input, or to find additional information about the persons that are mentioned in it. Consider a sentence that contains the expression ''"the capital of France"'': without entity linking, the search engine that looks at the content of documents would not be able to directly retrieve documents containing the word ''"Paris"'', leading to so-called false negatives (FN). Even worse, the search engine might produce spurious matches (or false positives (FP)), such as retrieving documents referring to ''"France"'' as a country. Many approaches orthogonal to entity linking exist to retrieve documents similar to an input document. For example,latent semantic analysis
Latent semantic analysis (LSA) is a technique in natural language processing, in particular distributional semantics, of analyzing relationships between a set of documents and the terms they contain by producing a set of concepts related to the d ...
(LSA) or comparing document embeddings obtained with
doc2vec. However, these techniques do not allow the same fine-grained control that is offered by entity linking, as they will return other
documents instead of creating high-level representations of the original one. For example, obtaining schematic information about ''"Paris"'', as presented by Wikipedia infobox
An infobox is a digital or physical Table (information), table used to collect and present a subset of information about its subject, such as a document. It is a structured document containing a set of attribute–value pairs, and in Wikipedia r ...
es would be much less straightforward, or sometimes even unfeasible, depending on the query complexity.
Moreover, entity linking has been used to improve the performance of information retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an Information needs, information need. The information need can be specified in the form ...
systemsM. A. Khalid, V. Jijkoun and M. de Rijke (2008)The impact of named entity normalization on information retrieval for question answering
Proc. ECIR. and to improve search performance on digital libraries.Hui Han, Hongyuan Zha, C. Lee Giles, "Name disambiguation in author citations using a K-way spectral clustering method," ACM/IEEE Joint Conference on Digital Libraries 2005 (JCDL 2005): 334-343, 2005 Entity linking is also a key input for semantic search.
Challenges
There are various difficulties in performing entity linking. Some of these are intrinsic to the task, such as text ambiguity. Others are relevant in real-world use, such as scalability and execution time. * Name variations: the same entity might appear with textual representations. Sources of these variations include abbreviations (''New York'', ''NY''), aliases (''New York'', ''Big Apple''), or spelling variations and errors ('). * Ambiguity: the same mention can often refer to many different entities, depending on the context, as many entity names tend to be homonyms (the same sequence of letters applies to different concepts with distinct meanings, e.g., "bank" can mean a financial institution or the land immediately adjacent to a river) or polysemous. (Polysemy is a subtype of homonymy where the meanings are related by historical or linguistic origin.). The word ''Paris'', among other things, could be referring to the French capital or to Paris Hilton. In some cases, there may be no textual similarity between a mention in the text (e.g., "We visited ''France's capital'' last month") and the actual target entity (''Paris''). * Absence: named entities might not have a corresponding entity in the target knowledge base. This can happen if the entity is very specific or unusual, or is related to recent events and the knowledge base is stale, or if the knowledge base is domain-specific (for example, a biology knowledge base). In these cases, the system probably is expected to return aNIL entity link. Knowing when to return a NIL prediction is not straightforward, and many approaches have been proposed. Examples are thresholding a confidence score in the entity linking system, and including a NIL entity in the knowledge base, which is treated as any entity. However, in some cases, linking to an incorrect but related entity may be more useful to the user than having no result at all.
* Scale and speed: it is desirable for an industrial entity linking system to provide results in a reasonable time, and often in real-time. This requirement is critical for search engines, chat-bots and for entity linking systems offered by data-analytics platforms. Ensuring low execution time can be challenging when using large knowledge bases or when processing large documents. For example, Wikipedia contains nearly 9 million entities and more than 170 million relationships among them.
* Evolving information: an entity linking system should also deal with evolving information, and easily integrate updates in the knowledge base. The problem of evolving information is sometimes connected to the problem of missing entities, for example when processing recent news articles in which there are mentions of events that do not have a corresponding entry in the knowledge base due to their novelty.
* Multiple languages: an entity linking system might support queries performed in multiple languages. Ideally, the accuracy of the entity linking system should not be influenced by the input language, and entities in the knowledge base should be the same across different languages.
Related concepts
Entity linking related to other concepts. Definitions are often blurry and vary slightly between authors. * Named-entity disambiguation (NED) is usually considered the same as entity linking, but some authors (Alhelbawy ''et al.'') consider it a special case of entity linking that assumes that the entity is in the knowledge base. * Wikification is the task of linking textual mentions to entities in Wikipedia (generally, limiting the scope to the English Wikipedia in case of cross-lingual wikification). * Record linkage (RL) finds the same entity in multiple and often heterogeneous data-sets. It considered a broader concept than entity linking, and is a key process in digitalizing archives and joining of knowledge bases. * Named-entity recognition (NER) locates and classifies named entities in unstructured text into pre-defined categories such as names, organizations, locations, and more. For example, the following sentence: :would be processed by an NER system to obtain the following output: :NER is usually a preprocessing step of an entity linking system, as it can be useful to know in advance which words should be linked to entities of the knowledge base. * Coreference resolution understands whether multiple words in a text refer to the same entity. It can be useful, for example, to understand the word a pronoun refers to. Consider the following example: :In this example, a coreference resolution algorithm would identify that the pronoun ''It'' refers to ''Paris'', and not to ''France'' or to another entity. A notable distinction compared to entity linking is that Coreference Resolution does not assign any unique identity to the words it matches, but it simply says whether they refer to the same entity or not. In that sense, predictions from a coreference resolution system could be useful to a subsequent entity linking component.Approaches
Entity linking has been a hot topic in industry and academia for the last decade. Many challenges are unsolved, but many entity linking systems have been proposed, with widely different strengths and weaknesses. Broadly speaking, modern entity linking systems can be divided into two categories: * Text-based approaches, which make use of textual features extracted from large text corpora (e.g. Term frequency–Inverse document frequency (Tf–Idf), word co-occurrence probabilities, etc...). * Graph-based approaches, which use the structure of knowledge graphs to represent the context and the relation of entities. Often entity linking systems use both knowledge graphs and textual features extracted from, for example, the text corpora used to build the knowledge graphs themselves.
Text-based
The seminal work by Cucerzan in 2007 published one of the first entity linking systems. Specifically, it tackled the task of wikification, that is, linking textual mentions to Wikipedia pages. This system categorizes pages into entity, disambiguation, or list pages. The set of entities present in each entity page is used to build the entity's context. The final step is a collective disambiguation by comparing binary vectors of hand-crafted features each entity's context. Cucerzan's system is still used as baseline for recent work. Rao et al. proposed a two-step algorithm to link named entities to entities in a target knowledge base. First, candidate entities are chosen using string matching, acronyms, and known aliases. Then, the best link among the candidates is chosen with a ranking support vector machine (SVM) that uses linguistic features. Recent systems, such as by Tsai et al., useword embedding
In natural language processing, a word embedding is a representation of a word. The embedding is used in text analysis. Typically, the representation is a real-valued vector that encodes the meaning of the word in such a way that the words that ...
s obtained with a skip-gram model as language features, and can be applied to any language for which a large corpus to build word embeddings is available. Like most entity linking systems, it has two steps: an initial candidate selection, and ranking using linear SVM.
Various approaches have been tried to tackle the problem of entity ambiguity. The seminal approach of Milne and Witten uses supervised learning
In machine learning, supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm where a Statistical model, model is trained using input objects (e.g. a vector of predictor variables) and desired output values (also known as a ''supervisory signal''), which are often ...
using the anchor texts of Wikipedia entities as training data. Other approaches also collected training data based on unambiguous synonyms.
Graph-based
Modern entity linking systems also use large knowledge graphs created from knowledge bases such as Wikipedia, besides textual features generated from input documents or text corpora. Moreover, multilingual entity linking based onnatural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related ...
(NLP) is difficult, because it requires either large text corpora, which are absent for many languages, or hand-crafted grammar rules, which are widely different between languages. Graph-based entity linking uses features of the graph topology or multi-hop connections between entities, which are hidden to simple text analysis.
Han ''et al.'' propose the creation of a disambiguation graph (a subgraph of the knowledge base which contains candidate entities). This graph is used for collective ranking to select the best candidate entity for each textual mention.
Another famous approach is AIDA, which uses a series of complex graph algorithms and a greedy algorithm that identifies coherent mentions on a dense subgraph by also considering context similarities and vertex importance features to perform collective disambiguation.
Alhelbawy et al. presented an entity linking system that uses PageRank
PageRank (PR) is an algorithm used by Google Search to rank web pages in their search engine results. It is named after both the term "web page" and co-founder Larry Page. PageRank is a way of measuring the importance of website pages. Accordin ...
to perform collective entity linking on a disambiguation graph, and to understand which entities are more strongly related to each other and so would represent a better linking. Graph ranking (or vertex ranking) algorithms such as PageRank (PR) and Hyperlink-Induced Topic Search (HITS) aim to score node according their relative importance in the graph.
Mathematical
Mathematical expressions (symbols and formulae) can be linked to semantic entities (e.g.,Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a free content, free Online content, online encyclopedia that is written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and the wiki software MediaWiki. Founded by Jimmy Wales and La ...
articles or Wikidata items) labeled with their natural language meaning. This is essential for disambiguation, since symbols may have different meanings (e.g., "E" can be "energy" or "expectation value", etc.). The math entity linking process can be facilitated and accelerated through annotation recommendation, e.g., using the "AnnoMathTeX" system that is hosted by Wikimedia.
To facilitate the reproducibility of Mathematical Entity Linking (MathEL) experiments, the benchmark MathMLben was created. It contains formulae from Wikipedia, the arXiV and the
NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions (DLMF). Formulae entries in the benchmark are labeled and augmented by Wikidata markup. Furthermore, for two large corporae from the arXiv and zbMATH repository distributions of mathematical notation were examined. Mathematical Objects of Interest (MOI) are identified as potential candidates for MathEL.
Besides linking to Wikipedia, Schubotz and Scharpf et al. describe linking mathematical formula content to Wikidata, both in MathML and LaTeX
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
markup. To extend classical citations by mathematical, they call for a Formula Concept Discovery (FCD) and Formula Concept Recognition (FCR) challenge to elaborate automated MathEL. Their FCD approach yields a recall of 68% for retrieving equivalent representations of frequent formulae, and 72% for extracting the formula name from the surrounding text on the NTCIR arXiv dataset.
See also
*Controlled vocabulary
A controlled vocabulary provides a way to organize knowledge for subsequent retrieval. Controlled vocabularies are used in subject indexing schemes, subject headings, thesauri, taxonomies and other knowledge organization systems. Controlled v ...
* Explicit semantic analysis In natural language processing and information retrieval, explicit semantic analysis (ESA) is a Vector space model, vectoral representation of text (individual words or entire documents) that uses a document corpus as a knowledge base. Specifically, ...
* Geoparsing
* Information extraction
* Linked data
* Named entity
* Named-entity recognition
* Record linkage
* Word sense disambiguation
* Author Name Disambiguation
* Coreference
* Annotation
An annotation is extra information associated with a particular point in a document or other piece of information. It can be a note that includes a comment or explanation. Annotations are sometimes presented Marginalia, in the margin of book page ...
References
{{reflist, 30em Natural language processing Tasks of natural language processing