|
Optofluidics
Optofluidics is a research and technology area that combines the advantages of fluidics (in particular microfluidics) and optics. Applications of the technology include displays, biosensors, lab-on-chip devices, lenses, and molecular imaging tools and energy. History The idea of fluid-optical devices can be traced back at least as far as the 18th century, when spinning pools of mercury were proposed (and eventually developed) as liquid-mirror telescopes. In the 20th century new technologies such as dye lasers and liquid-core waveguides were developed that took advantage of the tunability and physical adaptability that liquids provided to these newly emerging photonic systems. The field of optofluidics formally began to emerge in the mid-2000s as the fields of microfluidics and nanophotonics were maturing and researchers began to look for synergies between these two areas. One of the primary applications of the field is for lab-on-a-chip and biophotonic products. Companies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluidics
Fluidics, or fluidic logic, is the use of a fluid to perform analog signal, analog or Digital data, digital operations similar to those performed with electronics. The physical basis of fluidics is pneumatics and hydraulics, based on the theoretical foundation of fluid dynamics. The term ''fluidics'' is normally used when devices have no moving parts, so ordinary hydraulic components such as hydraulic cylinders and spool valves are not considered or referred to as fluidic devices. A jet of fluid can be deflected by a weaker jet striking it at the side. This provides nonlinearity, nonlinear amplifier, amplification, similar to the transistor used in electronic digital logic. It is used mostly in environments where electronic digital logic would be unreliable, as in systems exposed to high levels of electromagnetic interference or ionizing radiation. Nanotechnology considers fluidics as one of its instruments. In this domain, effects such as fluid–solid and fluid–fluid interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
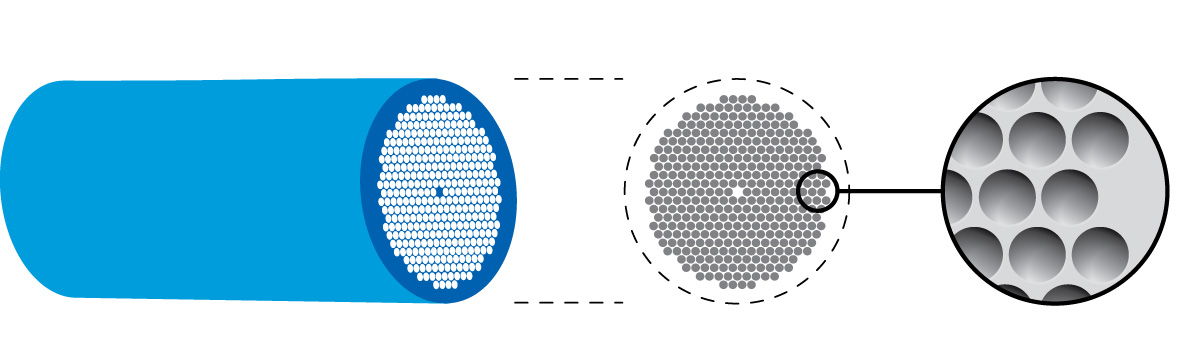
Photonic-crystal Fiber
Photonic-crystal fiber (PCF) is a class of optical fiber based on the properties of Photonic crystal, photonic crystals. It was first explored in 1996 at University of Bath, UK. Because of its ability to confine light in hollow cores or with confinement characteristics not possible in conventional optical fiber, PCF is now finding applications in Fiber-optic communication, fiber-optic communications, Fiber laser, fiber lasers, nonlinear devices, high-power transmission, highly sensitive gas sensors, and other areas. More specific categories of PCF include photonic-bandgap fiber (PCFs that confine light by band gap effects), holey fiber (PCFs using air holes in their cross-sections), ''hole-assisted'' fiber (PCFs guiding light by a conventional higher-index core modified by the presence of air holes), and Bragg fiber (photonic-bandgap fiber formed by concentric rings of multilayer film). Photonic crystal fibers may be considered a subgroup of a more general class of Microstructur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times, producing Mode (electromagnetism), modes with certain resonance, resonance frequencies. Modes can be decomposed into longitudinal modes that differ only in frequency and transverse modes that have different intensity patterns across the cross section of the beam. Many types of optical cavities produce standing wave modes. Different resonator types are distinguished by the focal lengths of the two mirrors and the distance between them. Flat mirrors are not often used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Dye
file:Coherent 899 dye laser.jpg, Close-up of a table-top dye laser using Rhodamine 6G as active medium. file:rhodamine 6G.svg, Molecular structure of Rhodamine 6G, perhaps the best known laser dye. A Laser dye is a dye used as laser medium in a dye laser. Laser dyes include the coumarins and the rhodamines. Coumarin dyes emit in the green region of the spectrum, whereas rhodamine dyes are used for emission in the yellow-red. The color emitted by the laser dyes depend upon the surrounding medium i.e.the medium in which they are dissolved. However, there are dozens of laser dyes that can be used to span continuously the emission spectrum from the near ultraviolet to the near infrared.F. J. Duarte, ''Tunable Laser Optics'' (Elsevier-Academic, New York, 2003) Appendix of Laser Dyes (includes more than 50 laser dyes) Laser dyes are also used to dope solid-state matrices, such as poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA), and Ormosil, ORMOSILs, to provide gain media for solid state dye las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubble Laser
An ordinary Bubble_(physics), bubble can serve as an optofluidics, optofluidic laser. These bubble lasers have been made of dye-doped soap solutions and Liquid crystal#Smectic_phases, smectic liquid crystal. In a bubble laser, the bubble itself serves as the optical cavity, optical resonator. Uniquely, bubble lasers exhibit hundreds of regularly spaced resonant frequencies called ''whispering gallery modes'', named for the Whispering Gallery in St. Paul's Cathedral in London. Researchers have found that the emission spectrum of a bubble laser is highly dependent on the bubble's environment; changing ambient air pressure or electric fields changes the size of the bubble (the optical resonator), and therefore the wavelengths of laser emission. Description Bubble lasers have been made from soap solutions to which a few drops of fluorescent Dye laser, laser dye have been added. The fluorescent dye acts as the gain medium. When a pump laser is shone onto the bubble, the dye molecules a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as carbon tet for short and tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC), is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a non-flammable, dense, colourless liquid with a "sweet" chloroform-like odour that can be detected at low levels. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, an anthelmintic and a cleaning agent, but has since been phased out because of environmental and safety concerns. Exposure to high concentrations of carbon tetrachloride can affect the central nervous system and degenerate the liver and kidneys. Prolonged exposure can be fatal. Properties In the carbon tetrachloride molecule, four chlorine atoms are positioned symmetrically as corners in a tetrahedron, tetrahedral configuration joined to a central carbon atom by single covalent bonds. Because of this symmetric geometry, CCl4 is non-polar. methane, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...-insoluble liquid with the odor associated with paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, consisting of a methyl group (CH3) attached to a phenyl group by a single bond. As such, its systematic IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry, IUPAC name is methylbenzene. Toluene is predominantly used as an industrial feedstock and a solvent. As the solvent in some types of paint thinner, permanent markers, contact cement and certain types of glue, toluene is sometimes used as a recreational inhalant and has the potential of causin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Nonlinearity
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic (QEO) effect, is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change for the Kerr effect is directly proportional to the ''square'' of the electric field instead of varying linearly with it. All materials show a Kerr effect, but certain liquids display it more strongly than others. The Kerr effect was discovered in 1875 by Scottish physicist John Kerr. Two special cases of the Kerr effect are normally considered, these being the Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, and the optical Kerr effect, or AC Kerr effect. Kerr electro-optic effect The Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, is the special case in which a slowly varying external electric field is applied by, for instance, a voltage on electrodes across the sample material. Under this influence, the sample becomes birefringent, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step-index Profile
For an optical fiber, a step-index profile is a refractive index profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core- cladding interface so that the cladding is of a lower refractive index. The step-index profile corresponds to a power-law index profile with the profile parameter approaching infinity. The step-index profile is used in most single-mode fibers and some multimode fibers. A step-index fiber is characterized by the core and cladding refractive indices ''n1'' and ''n2'' and the core and cladding radii a and b. Examples of standard core and cladding diameters 2a/2b are 8/125, 50/125, 62.5/125, 85/125, or 100/140 (units of μm). The fractional refractive-index change \triangle \, = \frac \ll \ 1. The value of n1 is typically between 1.44 and 1.46, and \triangle is typically between 0.001 and 0.02. Step-index optical fiber is generally made by doping high-purity fused silica glass (SiO2) with di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |