Optofluidics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Optofluidics is a research and technology area that combines the advantages of
 Optofluidic
Optofluidic  Viewig et al. used microfluidic technology to selectively fill sections of photonic crystal fibers with fluids that exhibit a high degree of
Viewig et al. used microfluidic technology to selectively fill sections of photonic crystal fibers with fluids that exhibit a high degree of
fluidics
Fluidics, or fluidic logic, is the use of a fluid to perform analog signal, analog or Digital data, digital operations similar to those performed with electronics.
The physical basis of fluidics is pneumatics and hydraulics, based on the theore ...
(in particular microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to a system that manipulates a small amount of fluids (10−9 to 10−18 liters) using small channels with sizes of ten to hundreds of micrometres. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves molecular analysis, molecular bi ...
) and optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
. Applications of the technology include displays, biosensors, lab-on-chip devices, lenses, and molecular imaging tools and energy.
History
The idea of fluid-optical devices can be traced back at least as far as the 18th century, when spinning pools of mercury were proposed (and eventually developed) as liquid-mirror telescopes. In the 20th century new technologies such asdye laser
A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as the lasing medium, usually as a liquid solution. Compared to gases and most solid state lasing media, a dye can usually be used for a much wider range of wavelengths, often spanning 50 to 100 n ...
s and liquid-core waveguides were developed that took advantage of the tunability and physical adaptability that liquids provided to these newly emerging photonic systems. The field of optofluidics formally began to emerge in the mid-2000s as the fields of microfluidics and nanophotonics were maturing and researchers began to look for synergies between these two areas. One of the primary applications of the field is for lab-on-a-chip
A lab-on-a-chip (LOC) is a device that integrates one or several laboratory functions on a single integrated circuit (commonly called a "chip") of only millimeters to a few square centimeters to achieve automation and high-throughput screening. ...
and biophotonic products.
Companies and technology transfer
Optofluidic and related research has led to the formation of a number of new products and start-up companies. Varioptic specializes in the development of electrowetting based lenses for numerous applications. Optofluidics, Inc. was launched in 2011 fromCornell University
Cornell University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university based in Ithaca, New York, United States. The university was co-founded by American philanthropist Ezra Cornell and historian and educator Andrew Dickson W ...
in order to develop tools for molecular trapping and disease diagnosis based on photonic resonator technology. Liquilume from UC Santa Cruz specializes in molecular diagnostics based on arrow waveguides.
In 2012, the European Commission has launched a new COST
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it i ...
framework that is concerned solely with optofluidic technology and their application.
Examples of specific applications
Given the broad range of technologies that have already been developed in the field of microfluidics and the many potential applications of integrating optical components into these systems, the range of applications for optofluidic technology is vast.Laminar flow-based optofluidic waveguides
Optofluidic waveguides are based on principles of traditionaloptical waveguide
An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic waves in the optical spectrum. Common types of optical waveguides include optical fiber waveguides, transparent dielectric waveguides made of plastic and glass, liquid ligh ...
s and microfluidic techniques used to maintain gradients or boundaries between flowing fluids. Yang et al. used microfluidic techniques based on laminar flow
Laminar flow () is the property of fluid particles in fluid dynamics to follow smooth paths in layers, with each layer moving smoothly past the adjacent layers with little or no mixing. At low velocities, the fluid tends to flow without lateral m ...
to generate fluid-based gradient-indices of refraction. This was implemented by flowing two cladding layers of deionized water () around a core layer of ethylene glycol (). Using traditional microfluidic techniques to generate and maintain gradients of fluids, Yang et al. were able maintain refractive index profiles ranging from step-index profile
For an optical fiber, a step-index profile is a refractive index profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core- cladding interface so that the cladding is of a lower refr ...
s to depth-varying gradient-index profiles. This allowed for the novel and dynamic generation of complex waveguides.
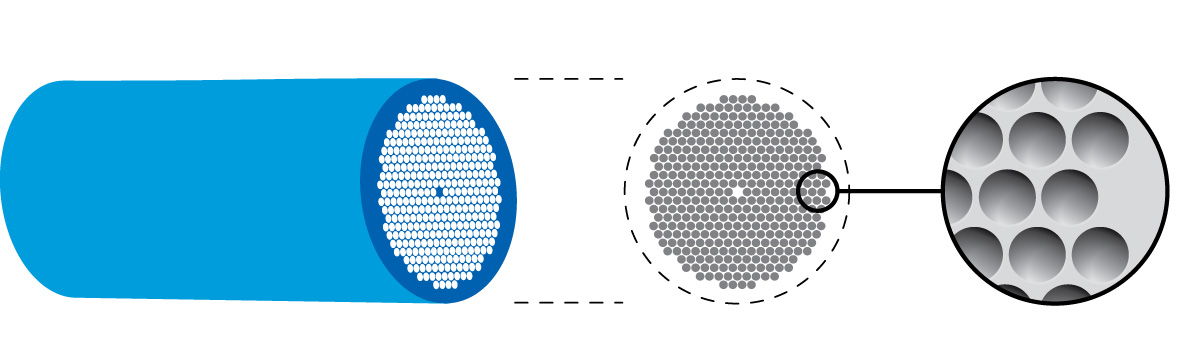
Optofluidic photonic crystal fibers
 Optofluidic
Optofluidic Photonic-crystal fiber
Photonic-crystal fiber (PCF) is a class of optical fiber based on the properties of Photonic crystal, photonic crystals. It was first explored in 1996 at University of Bath, UK. Because of its ability to confine light in hollow cores or with c ...
s (PCFs) are traditional PFCs modified with microfluidic techniques. Photonic-crystal fibers are a type of fiber optic waveguide with cladding layers arranged in a crystalline fashion in their cross-sectional areas. Traditionally, these structured cladding layers are filled with a solid-state material with a different refractive indices
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
or are hollow. Each cladded core then acts as a single mode fiber passing multiple light paths in parallel. Traditional PCFs are also limited to using hollow or solid-state cores that must be filled at the time of construction. This means that the material properties the PCFs were set at the time of construction and were limited to the material properties of solid-state materials.
 Viewig et al. used microfluidic technology to selectively fill sections of photonic crystal fibers with fluids that exhibit a high degree of
Viewig et al. used microfluidic technology to selectively fill sections of photonic crystal fibers with fluids that exhibit a high degree of Kerr nonlinearity
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic (QEO) effect, is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index chan ...
such as toluene
Toluene (), also known as toluol (), is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon with the chemical formula , often abbreviated as , where Ph stands for the phenyl group. It is a colorless, water
Water is an inorganic compound with the c ...
and carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as carbon tet for short and tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC), is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a n ...
. Selectively filling hollow PFCs with fluid allows for control over thermal diffusion via spatial segregation and allows for the ability to pattern multiple different types of fluid. Using non-linear fluids, Vieweg et al. were able to generate a soliton continuum which has many applications for imaging and communications.
Bubble laser
Abubble laser
An ordinary Bubble_(physics), bubble can serve as an optofluidics, optofluidic laser. These bubble lasers have been made of dye-doped soap solutions and Liquid crystal#Smectic_phases, smectic liquid crystal. In a bubble laser, the bubble itself se ...
can be created by add laser dye
file:Coherent 899 dye laser.jpg, Close-up of a table-top dye laser using Rhodamine 6G as active medium.
file:rhodamine 6G.svg, Molecular structure of Rhodamine 6G, perhaps the best known laser dye.
A Laser dye is a dye used as laser medium in a dy ...
and smectic liquid crystal to soapy water and producing foam. The resulting optical cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, ...
varies in resonant frequency depending on size, air pressure, and electric fields.
See also
*List of optofluidics researchers
This is a list of researchers in optofluidics, a research and technology area that combines microfluidics and optics and has applications in Display device, displays, biosensors, lab-on-chip devices, Lens (optics), lenses, and molecular imaging and ...
References
Further reading
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Optofluidics