|
Zurich Model
The Zurich model is the approach by the city of Zurich in Switzerland that permitted its public transportation system to achieve and maintain a high market share. Many other cities have emulated elements of it, especially when new tram systems were introduced. History In the 1970s, Zurich was planning to move many of the Trams in Zurich, tram lines in its central area into tunnels. This project was rejected in a referendum. In the 1970s, a project to create an Zurich Underground Railway, underground railway was similarly rejected. Despite the failures of these attempts to provide Zurich with a different kind of transportation system, public transportation in Zurich has maintained a high modal split, with 65% of people commuting within the city doing so by public transport and only 17% using cars. In his book, ''Status Anxiety'', Alain de Botton has suggested why the model is so effective: Elements of the model *A dense network providing many direct connections and short headways ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zurich
Zurich (; ) is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zurich. It is in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zurich. , the municipality had 448,664 inhabitants. The Urban agglomeration, urban area was home to 1.45 million people (2020), while the Zurich Metropolitan Area, Zurich metropolitan area had a total population of 2.1 million (2020). Zurich is a hub for railways, roads, and air traffic. Both Zurich Airport and Zürich Hauptbahnhof, Zurich's main railway station are the largest and busiest in the country. Permanently settled for over 2,000 years, Zurich was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans, who called it '. However, early settlements have been found dating back more than 6,400 years (although this only indicates human presence in the area and not the presence of a town that early). During the Middle Ages, Zurich gained the independent and privileged status of imperial immediacy and, in 1519 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlsruhe Model
The Karlsruhe model is a tram-train system which consists of tram/light rail trains and commuter/regional rail trains running on the same set of tracks, generally between or outside of urban areas. It was initially developed and implemented in the city of Karlsruhe, Germany, by the local transit authority, ''Karlsruher Verkehrsverbund'' (KVV). Overview Commencing service in 1992, the system in Karlsruhe has provided a connection between the regular railway network and the city's local tram network. The whole system is now called the Karlsruhe Stadtbahn. Passengers may travel from distant towns such as Baden-Baden directly into the city centre of Karlsruhe, bridging the inconvenient distance between the main station and the city centre. For most trips, the number of train transfers has been reduced significantly. This model has led to the creation of similar tram-train systems in other locations. Other examples A similar model has been connecting the city of Vienna with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Transport In Switzerland
Switzerland has a dense network of roads and railways. The Swiss public transport, public transport network has a total length of and has more than 2,600 stations and stops. The crossing of the Alps is an important route for European transportation, as the Alps separate Northern Europe from Southern Europe. Alpine railway routes began in 1882 with the Gotthard Railway, with its central Gotthard Rail Tunnel, followed in 1906 by the Simplon Tunnel and the Lötschberg Tunnel in 1913. As part of the NRLA, New Railway Link through the Alps (NRLA) in 2007, the Lötschberg Base Tunnel opened, followed by the Gotthard Base Tunnel opened in 2016. The Swiss road network is funded by road pricing, road tolls and vehicle taxes. The Swiss motorway system requires the purchase of a Vignette (road tax)#Switzerland, road tax disc—which costs 40 Swiss francs for one calendar year—in order for private cars and commercial trucks to use its roadways. , the Swiss motorway network has a total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
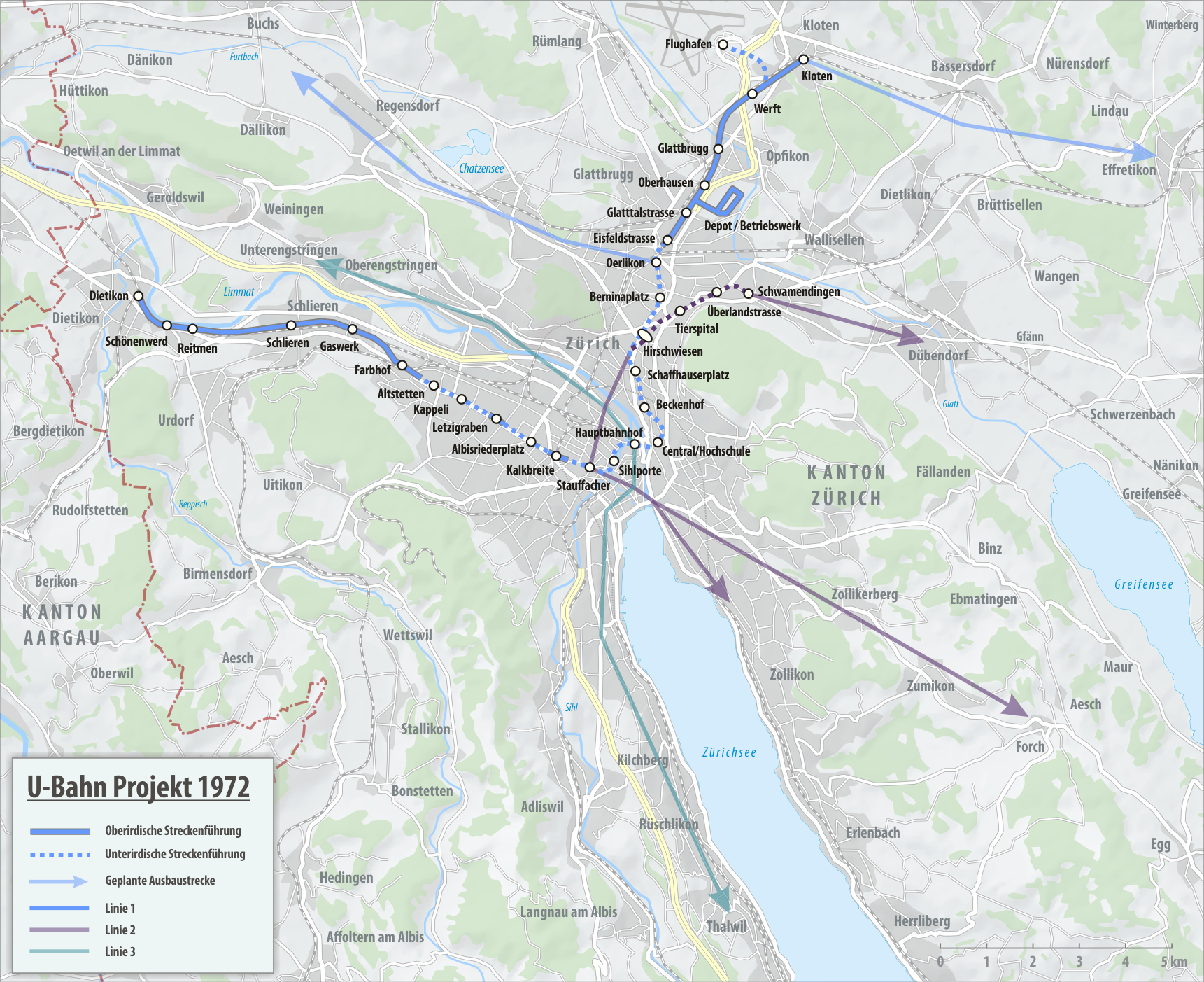
Zurich Underground Railway
The Zurich Underground Railway, or Zurich U-Bahn, was a project started in the 1970s to build a rapid transit network in the Swiss city of Zurich and several bordering municipalities. This project was itself preceded by several earlier plans dating from between 1864 and 1959. In April 1962, the "Tiefbahn" (lit. "deep rail") project was proposed, which would have included placing the Zürich trams underground in the city centre by building 21.15 km of underground lines, this was rejected in a referendum before any construction had been undertaken. In the 1970s "U-Bahn" project, the first line would have led from Dietikon via Schlieren, Zürich HB, Oerlikon and Opfikon to Zurich Airport, including two short branch lines to Schwamendingen and Kloten. The two most important development axes of the agglomeration, Limmattal and Glattal, would have been joined onto the network. The line would have been 27.5 km long, 14.8 km of which would have been underground. At a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zurich S-Bahn
The Zurich S-Bahn () system is a network of rail lines that has been incrementally expanded to cover the ZVV area, which comprises the entire canton of Zurich and portions of neighbouring cantons (Aargau, Glarus, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, St. Gallen, Thurgau and Zug), with a few lines extending into or crossing the territory of southern Germany. The network is one of many commuter rail operations in German speaking countries to be described as an S-Bahn. The lines connect with services of Aargau S-Bahn to the West, Basel S-Bahn (only in ) and Schaffhausen S-Bahn to the North, St. Gallen S-Bahn to the East, and Lucerne S-Bahn/Zug Stadtbahn to the South, as well as with InterCity (Switzerland), InterCity, InterRegio and RegioExpress services at major junction stations. The entire ZVV S-Bahn network went into operation in May 1990, although many of the lines were already in operation. Unusual among rapid transit services, the Zurich S-Bahn provides first class commuter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zürcher Verkehrsverbund
The Zürcher Verkehrsverbund (ZVV), is the largest public transportation network in Switzerland. It covers the canton of Zurich and adjacent areas. All modes of public transportation (rail, light rail, bus, trolleybus, lake passenger liner, funicular, an aerial tram) within a chosen number of fare zones can be used freely with a ticket that is valid for a certain amount of time (e.g., 1 hour, 24 hours) or with monthly/annual subscriptions. History The system was established in May 1990 as a unified fare system with a coordinated local train network. Local train lines were prefixed with the letter S (S-Bahn) to form the Zurich S-Bahn network. A proof-of-payment fare system is in force on all ZVV vehicles. Fare gates are not used, but those caught without a valid ticket during a random inspection face a minimum fine of . Zones The ZVV system uses an integrated ticket network. The zones are numbered 110–184; the numbers 180–184 designates zones outside of the canton's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verkehrsbetriebe Zürich
Verkehrsbetriebe Zürich (VBZ) is a public transport operator in the Swiss city of Zurich, and is wholly owned by the city. Previously known as the Städtische Strassenbahn Zürich (StStZ), the organisation was founded in 1896 and adopted its current name in 1950. The VBZ owns and operates trams, trolleybuses, buses, and a funicular. It also operates, but does not own a further funicular, a rack railway, and the Stadtbahn Glattal light rail system. All of VBZ's passenger services are operated within the tariff and ticketing system provided by the cantonal public transport authority Zürcher Verkehrsverbund (ZVV). The ZVV tariff also covers other passenger transport services in and around the city, including the Zurich S-Bahn, although these are not operated by the VBZ. History The ''Städtische Strassenbahn Zürich'' (StStZ) came into existence in 1896, when the city of Zurich purchased the ''Elektrische Strassenbahn Zürich'' (ESZ). However privately owned tram systems h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trolleybuses In Zurich
The Zurich trolleybus system () is part of the Public transport in Zurich, public transport network of Zurich, Switzerland. Opened in 1939, it integrates with the Zurich S-Bahn, the Trams in Zurich, Zurich tramway network and the city's urban motor bus, motorbus network to form an integrated all-four style scheme. , the system consists of seven lines with a total route length of . It is operated by Verkehrsbetriebe Zürich (VBZ), which also operates the tramway and motorbus networks. Like the other modes of public transport in the region, it is covered by the Zürcher Verkehrsverbund (ZVV). History The Zurich trolleybus system was opened on 27 May 1939, by the then ''Städtische Strassenbahn Zürich'' ("Zurich Municipal Tramway") (''St. St. Z.''). It was the third modern trolleybus system to be opened in Switzerland, after the Trolleybuses in Lausanne, Lausanne system and Trolleybuses in Winterthur, Winterthur system, respectively. Initially, trolleybus lines were created on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Transport In Zurich
Public transport in Zurich is available for four main Mode of transport, modes of transport—boat, bus, train and tram—assisting residents of and visitors to Zurich move around the of List of cities in Switzerland, Switzerland's largest city and Zurich metropolitan area, beyond. In 2015, over 300 million trips were made annually on public transport in Zurich, a city with a population of around 450,000. This figure excludes the Zurich S-Bahn, which had annual ridership of 208 million in 2023. Zürich Hauptbahnhof, Zurich Main Station (''Zürich HB''), meanwhile, is the largest and busiest railway station in the country. Public transport is extremely popular in Zurich, and its inhabitants use it in large numbers. In 2010, a microcensus discovered that 32% of Zurich residents used trams or trolleybuses regularly (of which 60% used at least those two modes), while 26% depended on a personal vehicle. Fewer than half the residents owned a car or a motorcycle. About 70% of the visito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne Principles
The "Melbourne Principles" for Sustainable Cities are ten short statements on how cities can become more sustainable. They were developed in Melbourne (Australia) on 2 April 2002 during an international Charrette, sponsored by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the International Council for Local Environmental Initiatives. Experts at the Charrette were drawn from developing and developed countries. Adoption The Melbourne Principles were adopted at the Local Government Session of the Earth Summit 2002 in Johannesburg, as part of the final communique, known as Local Action 21 or the Johannesburg Call. They consist of ten short statements on how cities can become more sustainable. Each principle has a few paragraphs of elaboration that provides additional information on its meaning and application. The Principles are designed to be read by decision-makers, and provide a starting point on the journey towards sustainability. Additional tools will be needed to opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Impact Of Light Rail Systems
Below are health impacts of light rail systems. Reduction in obesity Research shows that using light rail increases walking. Frank et al. (2004) report that obesity around Atlanta, as measured by body mass index (BMI), is associated positively with time spent in cars and negatively with mixed land-use (such as incorporating Light Rail transit) and with walking. There is also research which suggests that utilizing Light Rail transit increases physical activity even compared to riding the bus. Users of public transit who do not use trains, including light rail, walk an additional six minutes compared with non-users, whereas those who use trains including light rail walk an additional 4.5 minutes, for a total of 10.5 extra minutes per day. Additionally, MacDonald, et al. (2010) used data collected pre and post light rail development in Charlotte, North Carolina to determine that residents who commuted via light rail had 81% reduced odds of becoming obese. Moreover, bicycle access t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Transportation
Public transport (also known as public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) are forms of transport available to the general public. It typically uses a fixed schedule, route and charges a fixed fare. There is no rigid definition of which kinds of transport are included, and air travel is often not thought of when discussing public transport—dictionaries use wording like "buses, trains, etc." Examples of public transport include city buses, trolleybuses, trams (or light rail) and passenger trains, rapid transit (metro/subway/underground, etc.) and ferries. Public transport between cities is dominated by airlines, coaches, and intercity rail. High-speed rail networks are being developed in many parts of the world. Most public transport systems run along fixed routes with set embarkation/disembarkation points to a prearranged timetable, with the most frequent services running to a headway (e.g., "every 15 minutes" as opposed to being scheduled for a specific time of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |