|
Zinterol
Zinterol is a beta-adrenergic agonist. Its structure is based on soterenol (antiarrhythmic Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular ta ...) and phentermine. References Sulfonamides Phenols Phenylethanolamines {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-adrenergic Agonist
Beta adrenergic agonists or beta agonists are medications that relax muscles of the airways, causing widening of the airways and resulting in easier breathing. They are a class of sympathomimetic agents, each acting upon the beta adrenoceptors. In general, pure beta-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of beta blockers: beta-adrenoreceptor agonist ligands mimic the actions of both epinephrine- and norepinephrine- signaling, in the heart and lungs, and in smooth muscle tissue; epinephrine expresses the higher affinity. The activation of β1, β2 and β3 activates the enzyme, adenylate cyclase. This, in turn, leads to the activation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); cAMP then activates protein kinase A (PKA) which phosphorylates target proteins, ultimately inducing smooth muscle relaxation and contraction of the cardiac tissue. Function Activation of β1 receptors induces positive inotropic, chronotropic output of the cardiac muscle, lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms ( tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Vaughan Williams classification The Vaughan Williams classification was introduced in 1970 by Miles Vaughan Williams.Vaughan Williams, EM (1970) "Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs". In ''Symposium on Cardiac Arrhythmias'' (Eds. Sandoe E; Flensted-Jensen E; Olsen KH). Astra, Elsinore. Denmark (1970) Vaughan Williams was a pharmacology tutor at Hertford College, Oxford. One of his students, Bramah N. Singh, contributed to the development of the classification system. The system is therefore sometimes known as the Singh-Vaughan Williams classification. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
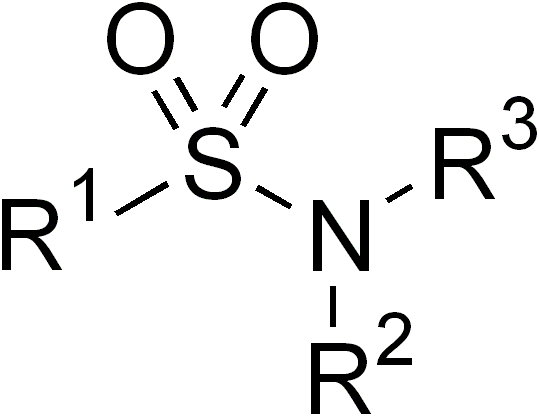
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |