|
Zhang Jiao
Zhang Jue (; died October 184) was a religious leader in ancient China who became a military general and led the Yellow Turban Rebellion during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He had a reputation as a Taoist sorcerer capable of performing miracles, and he became extraordinarily popular. Proclaiming the government as corrupt and oppressive, he and his followers attempted to take over the capital city but was thwarted. His name is sometimes read as Zhang Jiao (), since the Chinese character of Zhang's given name can be read as either "Jiao" or "Jue". "Jue" is the traditional or literary reading, while "Jiao" is the modern or colloquial one. Yellow Turban Rebellion The Yellow Turbans originated as a Taoist movement called the '' Tàipíng Dào'' or "Way of the Great Peace" (太平道), which had started well over a decade prior to the rebellion. Zhang Jue's followers hailed him as being able to cure patients by giving them water blessed by the burning of talismans (fulu). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang (surname)
Zhang (; ) is the List of common Chinese surnames, third most common surname in China and Taiwan (commonly spelled as Chang in Taiwan), and it is one of the most common surnames in the world. It is spoken in the Chinese tones, first tone ''Zhāng''. It is a surname that exists in many languages and cultures, corresponding to the surname 'Archer' in English for example. In the Wade–Giles system of Romanization of Chinese, romanization, it is romanized as Chang, which is commonly used in Taiwan. Cheung is commonly used in Hong Kong as a romanization. It is the 24th name on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem, contained in the verse 何呂施張 ''(Hé Lǚ Shī Zhāng)''. Zhang is also the pinyin romanization of the less-common surnames (''Zhāng''), which is the 40th name on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem, and (''Zhǎng''). Today, it is one of the most common surnames in the world at over 100 million people worldwide. Zhang was listed by the People's Republic of China's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandate Of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven ( zh, t=天命, p=Tiānmìng, w=, l=Heaven's command) is a Chinese ideology#Political ideologies, political ideology that was used in History of China#Ancient China, Ancient China and Chinese Empire, Imperial China to legitimacy (political), legitimize the rule of the King of China, king or emperor of China. According to this doctrine, Heaven (, ''Tian'') bestows its mandate) the sovereign used to fengjian, appoint an aristocratic relative to rule a Ancient Chinese states, regional state. In this sense the relation between Heaven and the sovereign was analogous to the relation between the sovereign and the regional lord. on a virtuous ruler. This ruler, the Son of Heaven, was the supreme Universal monarchy, universal monarch, who ruled ''Tianxia'' (; "all under heaven", the world). If a ruler was overthrown, this was interpreted as an indication that the ruler was unworthy and had lost the mandate. It was also a common belief that natural disasters such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuang Zhou
Zhuang Zhou (), commonly known as Zhuangzi (; ; literally "Master Zhuang"; also rendered in the Wade–Giles romanization as Chuang Tzu), was an influential Chinese philosopher who lived around the 4th century BCE during the Warring States period, a period of great development in Chinese philosophy, the Hundred Schools of Thought. He is credited with writing—in part or in whole—a work known by his name, the '' Zhuangzi'', which is one of two foundational texts of Taoism, alongside the ''Tao Te Ching''. Life The only account of the life of Zhuangzi is a brief sketch in chapter 63 of Sima Qian's ''Records of the Grand Historian'', and most of the information it contains seems to have simply been drawn from anecdotes in the ''Zhuangzi'' itself. In Sima's biography, he is described as a minor official from the town of Meng (in modern Anhui) in the state of Song, living in the time of King Hui of Liang and King Xuan of Qi (late fourth century BC). Sima Qian writes that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xian (Taoism)
A ''xian'' ( zh, s=仙, t=僊, p=xiān, w=hsien) is any manner of immortal or mythical being within the Taoist Pantheon (religion), pantheon or Chinese folklore. has often been translated into English as "immortal" or "wizard". Traditionally, ''xian'' refers to entities who have attained immortality and supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical abilities later in life, with a connection to the heavenly realms inaccessible to mortals. This is often achieved through spiritual Self-cultivation#Taoism and the authentic self, self-cultivation, Chinese alchemy, alchemy, or worship by others. This is different from the Deity, gods (Deity, deities) in Chinese mythology and Taoism. ''Xian'' is also used as a descriptor to refer to often benevolent figures of great historical, spiritual and cultural significance. The Quanzhen School of Taoism, Daoism had a variety of definitions for during its history, including a metaphorical meaning where the term simply means a good, principl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiping Jing
''Taipingjing'' ("Scriptures of the Great Peace") is the name of several different Taoist texts. At least two works were known by this title: :*, 12 Chapters, contents unknown, author: Gan Zhongke :*, 170 Chapters, only 57 of which survive via the Daozang, author: unknown ''Taipingjing'' usually refers to the work which has been preserved in the Daozang. It is considered to be a valuable resource for researching early Taoist beliefs and the society at the end of the Eastern Han dynasty. Zhang Jue (d. 184), the leader of the Yellow Turban Rebellion, taught "Taiping Taoism" () based on this work. The contents of the ''Taipingjing'' are diverse but it primarily deals with subjects such as heaven and earth, the five elements, yin and yang and the sexagenary cycle. Fundamental concepts in the ''Taipingjing'' The ''Taipingjing'' is a guide that reveals the proper methods to bring forward an era of great peace or equality, the "Great Peace", an idea which probably dates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chenopodium Album
''Chenopodium album'' is a fast-growing annual plant in the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae. Though cultivated in some regions, the plant is elsewhere considered a weed. Common names include lamb's quarters, melde, goosefoot, wild spinach and fat-hen, though several are also applied to other species of the genus '' Chenopodium'', for which reason it is often distinguished as white goosefoot. Description It tends to grow upright at first, reaching heights of , rarely to 3 m); it then typically becomes recumbent after flowering (due to the weight of the foliage and seeds) unless supported by other plants. The leaves are alternate and varied in appearance. The first leaves, near the base of the plant, are toothed and roughly diamond-shaped, 3–7 cm long and 3–6 cm broad. The leaves on the upper part of the flowering stems are entire and lanceolate-rhomboid, 1–5 cm long and 0.4–2 cm broad; they are waxy-coated, unwettable and mealy in appearance, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
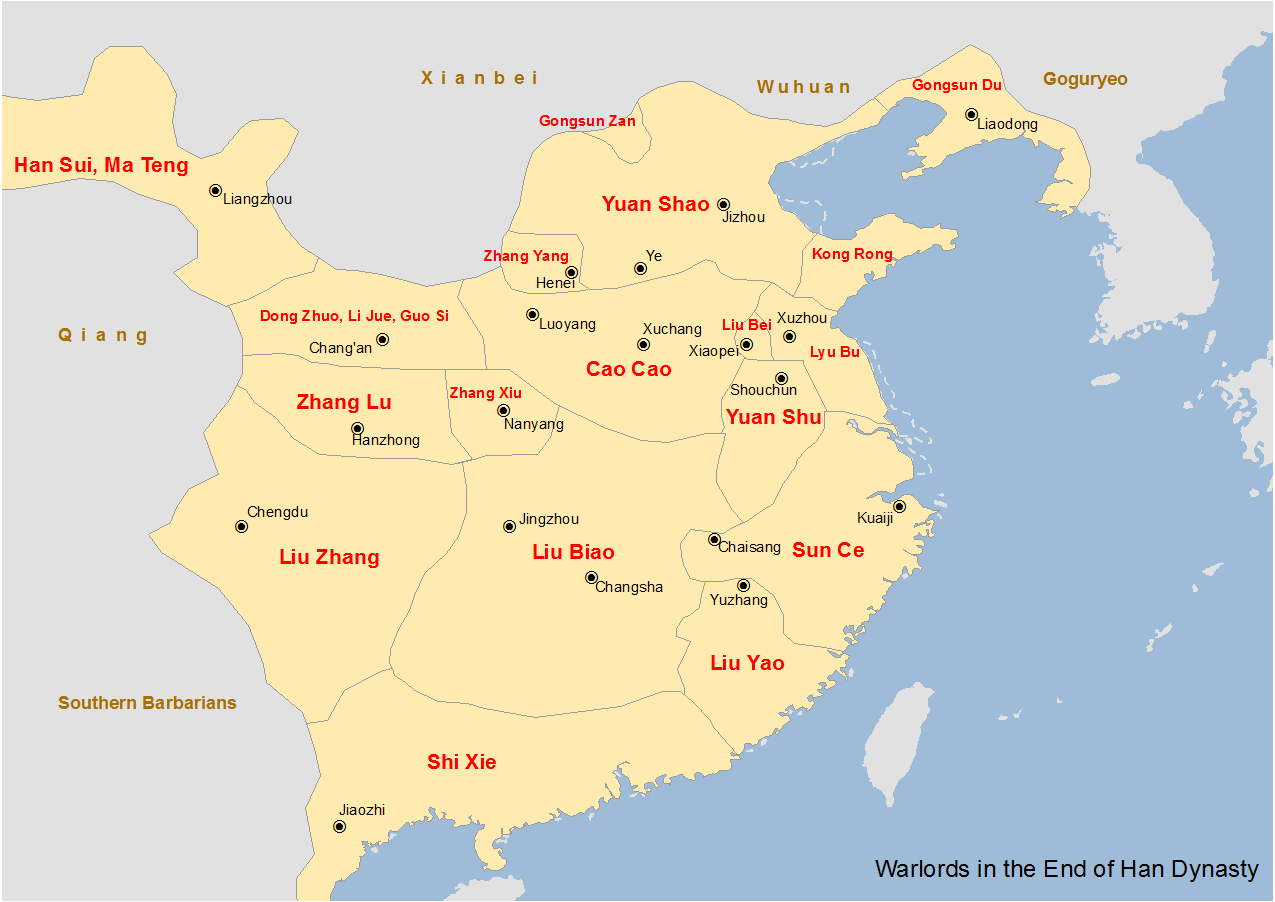
Romance Of The Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ending with the reunification of the land in 280 by the Western Jin. The novel is based primarily on the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', written by Chen Shou in the 3rd century. The story – part historical and part fictional – romanticises and dramatises the lives of feudal lords and their retainers, who tried to supplant the dwindling Han dynasty or restore it. While the novel follows hundreds of characters, the focus is mainly on the three power blocs that emerged from the remnants of the Han dynasty, and would eventually form the three states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The novel deals with the plots, personal and military battles, intrigues, and struggles of these states to achieve dominance for almost 100 years. ''Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Cao
Cao Cao (; ; ; 15 March 220), courtesy name Mengde, was a Chinese statesman, warlord, and poet who rose to power during the end of the Han dynasty (), ultimately taking effective control of the Han central government. He laid the foundation for the state of Cao Wei (220–265), established by his son and successor Cao Pi, who ended the Eastern Han dynasty and inaugurated the Three Kingdoms period (220–280). Beginning in his own lifetime, a corpus of legends developed around Cao Cao which built upon his talent, his cruelty, and his perceived eccentricities. Cao Cao began his career as an official under the Han government and held various appointments including that of a district security chief in the capital and the chancellor of a Jun (country subdivision), principality. He rose to prominence in the 190s during which he recruited his own followers, formed his own army, and set up a base in Yan Province (covering parts of present-day Henan and Shandong). In 196, he received E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jinzhou, Hebei
Jinzhou () is a county-level city of Hebei, Hebei Province, North China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Shijiazhuang, capital of Hebei. Until November 1991, it was known as Jin County (). Jinzhou is located in central Hebei province, east of Shijiazhuang. It covers an area of 619 square kilometers, and census, has a population of about 537,700. It consists of nine towns and one township, as well as 224 villages. Jinzhou has a recorded history of at least 2500 years. It was the hometown of Wei Zheng (), a well-known and well-respected historical figure and official of early Tang dynasty. It is also, according to the Chinese government, the "duck pear town" (). Administrative divisions There are 9 towns and 1 township: *Jinzhou, Jinzhou, Jinzhou () *Zongshizhuang () *Yingli (town), Yingli () *Taoyuan, Jinzhou, Hebei, Taoyuan () *Dongzhuosu () *Mayu, Hebei, Mayu () *Xiaoqiao, Hebei, Xiaoqiao () *Huaishu () *Donglizhuang () *Zhoujiazhuang Townsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhu Jun (Han Dynasty)
Zhu Jun (140s? - April 195), courtesy name Gongwei, was a military general and official who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty of China. Life Zhu Jun was from Shangyu County (), Kuaiji Commandery (), which is present-day Shangyu District, Shaoxing, Zhejiang. His father died when he was still young, so he was raised by his mother, who earned a living by selling fabrics. When he reached adulthood, he served as a scribe in the local county office. Zhu Jun gained a reputation for being very filial towards his mother. Despite this, when an acquaintance Zhou Gui (周规) was unable to repay his debts to the local authorities, Zhu Jun stole fabrics from his mother in order to help Zhou settle the debts. As a result, Zhu Jun's mother lost her property. Greatly angered, she then blamed Zhu Jun. Zhu Jun replied, "Small losses will result in great fortunes later. To be poor first before becoming rich is the natural order." Du Shang (; 117-166), the Chief of Shangyu County, favoured him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huangfu Song
Huangfu Song; pronounced in Mandarin (died April 195), courtesy name Yizhen, was a military general who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is best known for helping to suppress the Yellow Turban Rebellion and Liang Province rebellion. He was one of three imperial commanders when the Yellow Turban Rebellion broke out, along with Zhu Jun and Lu Zhi. He was known to be a modest and generous person. Lu Zhi was removed from command after the eunuch Zuo Feng (左豐) made false accusations against him; Lu Zhi had refused to bribe Zuo Feng. Huangfu Song, who took over command of the imperial troops from Lu Zhi, continued to use Lu as a strategist and reported his contributions to the imperial court. Thus, in the same year, Lu Zhi regained his post as Master of Writing (尚书). Life and background Huangfu Song was a nephew of Huangfu Gui (; 104-174), a military general, and Lady Huangfu. His father Huangfu Jie (Huangfu Gui's elder brother) was the Administrator of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dong Zhuo
Dong Zhuo () (c. 140s – 22 May 192), courtesy name Zhongying, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty. At the end of the reign of the Eastern Han, Dong Zhuo was a general and powerful minister of the imperial government. Originally from Liang Province, Dong Zhuo seized control of the imperial capital Luoyang in 189 when it entered a state of turmoil following the death of Emperor Ling of Han and a massacre of the eunuch faction by the court officials led by General-in-Chief He Jin. Dong Zhuo subsequently deposed Liu Bian (Emperor Shao) and replaced him with his half-brother, the puppet Emperor Xian to make him become the de facto ruler of China in the boy-emperor's name. The Eastern Han dynasty regime survived in name only. Dong Zhuo's rule was brief and characterized by cruelty and tyranny. In the following year, a coalition of regional officials (; ''cishi'') and warlords launched a campaign against him. Failing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |