|
Zhan Catalyst
A Zhan catalyst is a type of ruthenium-based organometallic complex used in olefin metathesis. This class of chemicals is named after the chemist who first synthesized them, Zheng-Yun J. Zhan. These catalysts are ruthenium complexes with functionally substituted alkoxybenzylidene carbene ligands, which can be chemically bonded to the surface of resins, PEG chains, and polymers. Like the structurally similar Grubbs catalyst, Hoveyda-Grubbs catalyst, they contain an isopropoxystyrene moiety, but include an extra electron-withdrawing sulfonamide group attached to the carbon ''para'' to the phenol oxygen. Of the three catalysts, Zhan Catalyst-1B and -1C both contain a dimethylsulfonamide moiety attached to the aryl ring, while Zhan Catalyst-II is connected to a resin via a sulfonamide linker. History The Zhan catalysts were inspired by previous work in the olefin metathesis field. Robert H. Grubbs first reported the first and second generation of Ru catalysts in 1992, with good met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is unreactive to most chemicals. Karl Ernst Claus, a Russian scientist of Baltic-German ancestry, discovered the element in 1844 at Kazan State University and named it in honor of Russia. (He used the Latin name '' Ruthenia'', which can have other meanings, but specifically stated that the element was named in honor of his "motherland".) Ruthenium is usually found as a minor component of platinum ores; the annual production has risen from about 19 tonnes in 2009 to some 35.5 tonnes in 2017. Most ruthenium produced is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and thick-film resistors. A minor application for ruthenium is in platinum alloys and as a chemical catalyst. A new application of ruthenium is as the capping layer for extreme ultraviolet photoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhan Cat Ii
Zhan may refer to: Places * Zhan, Kurdistan, an Iranian village in Kurdistan Province * Zhan Rural District in Lorestan Province, Iran ** Zhan, Lorestan, a village in Zhan Rural District Names * Zhan (surname), several Chinese-language surnames Given name * Zhuge Zhan (227–263), Chinese politician * Zhang Zhan (born 1983), Chinese lawyer and citizen journalist * Gao Zhan (21st century), Chinese smuggler * Zhan Videnov (born 1959), Prime Minister of Bulgaria * Zhan Bush Zhan Viacheslavovich Bush ( born 1 April 1993) is a Russian figure skater. He is the 2013 Cup of Nice bronze medalist, a four-time medalist on the ISU Junior Grand Prix series, and 2011 Russian national senior bronze medalist. He placed 5th at ... (born 1993), Russian/Israeli figure skater See also * Zahn {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
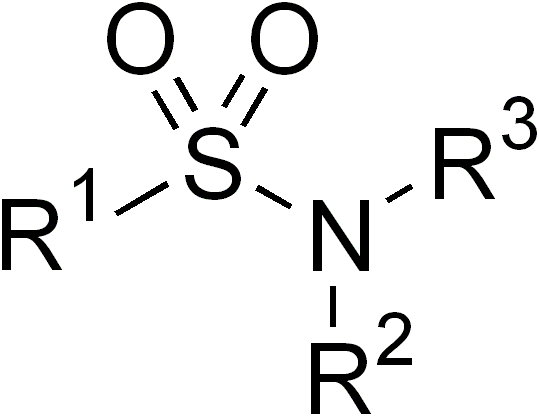
Sulfonamides
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the Chemical structure, structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for Sulfonamide (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysts
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form reaction intermediate, intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous catalysis, homogeneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |