|
Zeldovich Regularization
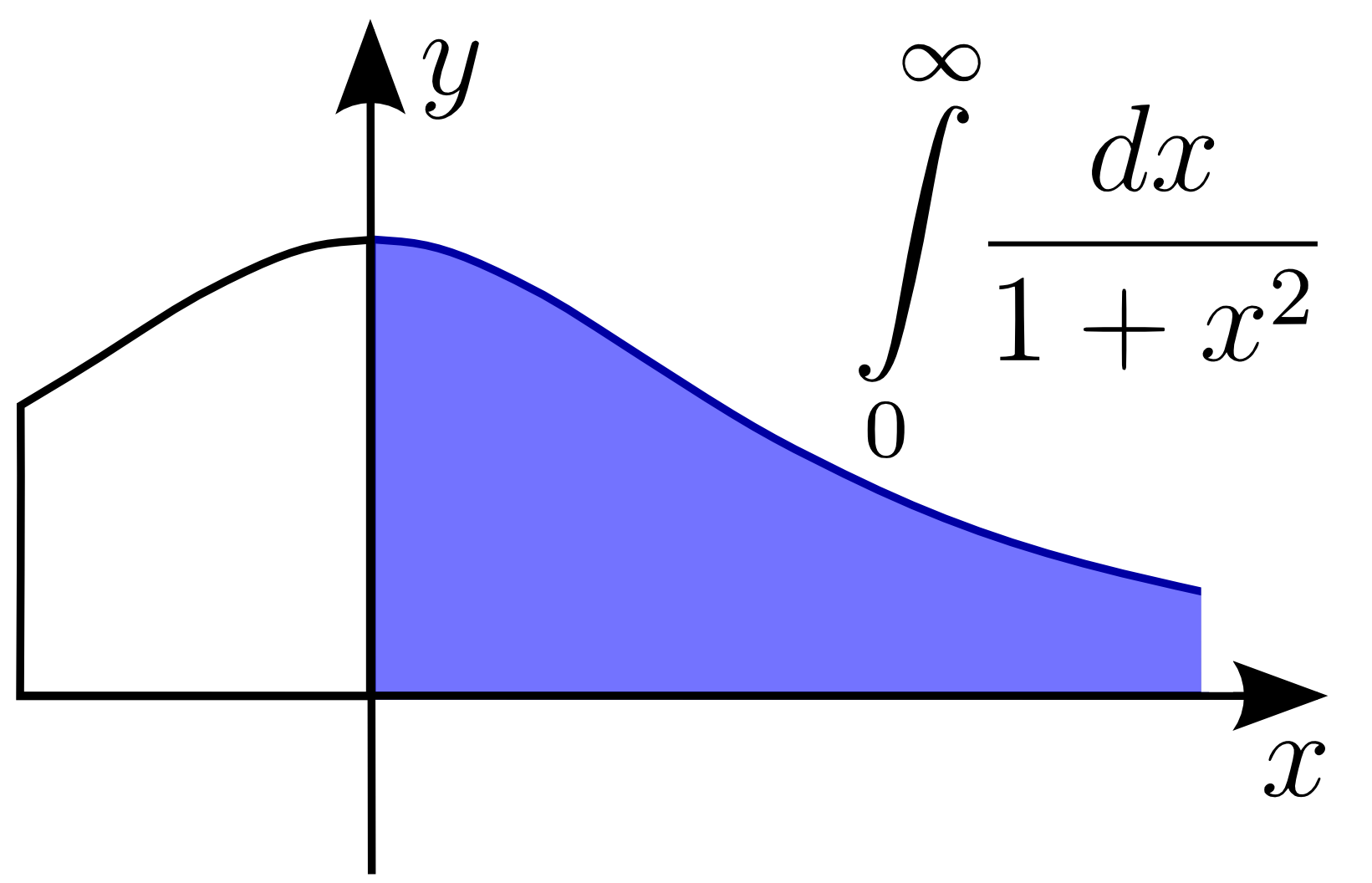
Zeldovich regularization refers to a regularization method to calculate divergent integrals and divergent series, that was first introduced by Yakov Zeldovich Yakov Borisovich Zeldovich (, ; 8 March 1914 – 2 December 1987), also known as YaB, was a leading Soviet people, Soviet Physics, physicist of Belarusians, Belarusian origin, who is known for his prolific contributions in physical Physical c ... in 1961. Zeldovich was originally interested in calculating the norm of the Gamow wave function which is divergent since there is an outgoing spherical wave. Zeldovich regularization uses a Gaussian type-regularization and is defined, for divergent integrals, by : \int_0^\infty f(x) dx \equiv \lim_\int_0^\infty f(x) e^ dx. and, for divergent series, byOrlov, Y. V., & Irgaziev, B. F. (2008). On the normalization of the Gamov resonant wave function in the configuration space. Bulletin of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Physics, 72, 1539-1543. :\sum_n c_n \equiv \lim_\sum_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regularization (physics)
In physics, especially quantum field theory, regularization is a method of modifying observables which have singularities in order to make them finite by the introduction of a suitable parameter called the regulator. The regulator, also known as a "cutoff", models our lack of knowledge about physics at unobserved scales (e.g. scales of small size or large energy levels). It compensates for (and requires) the possibility of separation of scales that "new physics" may be discovered at those scales which the present theory is unable to model, while enabling the current theory to give accurate predictions as an "effective theory" within its intended scale of use. It is distinct from renormalization, another technique to control infinities without assuming new physics, by adjusting for self-interaction feedback. Regularization was for many decades controversial even amongst its inventors, as it combines physical and epistemological claims into the same equations. However, it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improper Integral
In mathematical analysis, an improper integral is an extension of the notion of a definite integral to cases that violate the usual assumptions for that kind of integral. In the context of Riemann integrals (or, equivalently, Darboux integrals), this typically involves unboundedness, either of the set over which the integral is taken or of the integrand (the function being integrated), or both. It may also involve bounded but not closed sets or bounded but not continuous functions. While an improper integral is typically written symbolically just like a standard definite integral, it actually represents a limit of a definite integral or a sum of such limits; thus improper integrals are said to converge or diverge. If a regular definite integral (which may retronymically be called a proper integral) is worked out as if it is improper, the same answer will result. In the simplest case of a real-valued function of a single variable integrated in the sense of Riemann (or Darbou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergent Series
In mathematics, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a finite limit. If a series converges, the individual terms of the series must approach zero. Thus any series in which the individual terms do not approach zero diverges. However, convergence is a stronger condition: not all series whose terms approach zero converge. A counterexample is the harmonic series :1 + \frac + \frac + \frac + \frac + \cdots =\sum_^\infty\frac. The divergence of the harmonic series was proven by the medieval mathematician Nicole Oresme. In specialized mathematical contexts, values can be objectively assigned to certain series whose sequences of partial sums diverge, in order to make meaning of the divergence of the series. A ''summability method'' or ''summation method'' is a partial function from the set of series to values. For example, Cesàro summation assigns Grandi's divergent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakov Zeldovich
Yakov Borisovich Zeldovich (, ; 8 March 1914 – 2 December 1987), also known as YaB, was a leading Soviet people, Soviet Physics, physicist of Belarusians, Belarusian origin, who is known for his prolific contributions in physical Physical cosmology, cosmology, physics of Plasma physics, thermonuclear reactions, combustion, and Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamical phenomena. From 1943, Zeldovich, a self-taught physicist, started his career by playing a crucial role in the development of the former Soviet atomic bomb project, Soviet program of nuclear weapons. In 1963, he returned to academia to embark on pioneering contributions on the fundamental understanding of the Black hole thermodynamics, thermodynamics of black holes and expanding the scope of physical cosmology. Biography Early life and education Yakov Zeldovich was born into a History of the Jews in Belarus, Belarusian Jewish family in his grandfather's house in Minsk. However, in mid-1914, the Zeldovich family moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamow Factor
The Gamow factor, Sommerfeld factor or Gamow–Sommerfeld factor, named after physicists George Gamow or after Arnold Sommerfeld, is a probability factor for two nuclear particles' chance of overcoming the Coulomb barrier in order to undergo nuclear reactions, for example in nuclear fusion. By classical physics, there is almost no possibility for protons to fuse by crossing each other's Coulomb barrier at temperatures commonly observed to cause fusion, such as those found in the Sun. In 1927 it was discovered that there is a significant chance for nuclear fusion due to quantum tunnelling. While the probability of overcoming the Coulomb barrier increases rapidly with increasing particle energy, for a given temperature, the probability of a particle having such an energy falls off very fast, as described by the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution. Gamow found that, taken together, these effects mean that for any given temperature, the particles that fuse are mostly in a temperature-dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function (mathematics), function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real number, real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a function, graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric "Normal distribution, bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian Root mean square, RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normal distribution, normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abel's Theorem
In mathematics, Abel's theorem for power series relates a limit of a power series to the sum of its coefficients. It is named after Norwegian mathematician Niels Henrik Abel, who proved it in 1826. Theorem Let the Taylor series G (x) = \sum_^\infty a_k x^k be a power series with real coefficients a_k with radius of convergence 1. Suppose that the series \sum_^\infty a_k converges. Then G(x) is continuous from the left at x = 1, that is, \lim_ G(x) = \sum_^\infty a_k. The same theorem holds for complex power series G(z) = \sum_^\infty a_k z^k, provided that z \to 1 entirely within a single ''Stolz sector'', that is, a region of the open unit disk where , 1-z, \leq M(1-, z, ) for some fixed finite M > 1. Without this restriction, the limit may fail to exist: for example, the power series \sum_ \frac n converges to 0 at z = 1, but is unbounded near any point of the form e^, so the value at z = 1 is not the limit as z tends to 1 in the whole open disk. Note that G(z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borel Summation
In mathematics, Borel summation is a summation method for divergent series, introduced by . It is particularly useful for summing divergent asymptotic series, and in some sense gives the best possible sum for such series. There are several variations of this method that are also called Borel summation, and a generalization of it called Mittag-Leffler summation. Definition There are (at least) three slightly different methods called Borel summation. They differ in which series they can sum, but are consistent, meaning that if two of the methods sum the same series they give the same answer. Throughout let denote a formal power series :A(z) = \sum_^\infty a_kz^k, and define the Borel transform of to be its corresponding exponential series :\mathcalA(t) \equiv \sum_^\infty \fract^k. Borel's exponential summation method Let denote the partial sum :A_n(z) = \sum_^n a_k z^k. A weak form of Borel's summation method defines the Borel sum of to be : \lim_ e^\sum_^\infty \f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summability Methods
In mathematics, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a finite limit. If a series converges, the individual terms of the series must approach zero. Thus any series in which the individual terms do not approach zero diverges. However, convergence is a stronger condition: not all series whose terms approach zero converge. A counterexample is the harmonic series :1 + \frac + \frac + \frac + \frac + \cdots =\sum_^\infty\frac. The divergence of the harmonic series was proven by the medieval mathematician Nicole Oresme. In specialized mathematical contexts, values can be objectively assigned to certain series whose sequences of partial sums diverge, in order to make meaning of the divergence of the series. A ''summability method'' or ''summation method'' is a partial function from the set of series to values. For example, Cesàro summation assigns Grandi's divergen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |