|
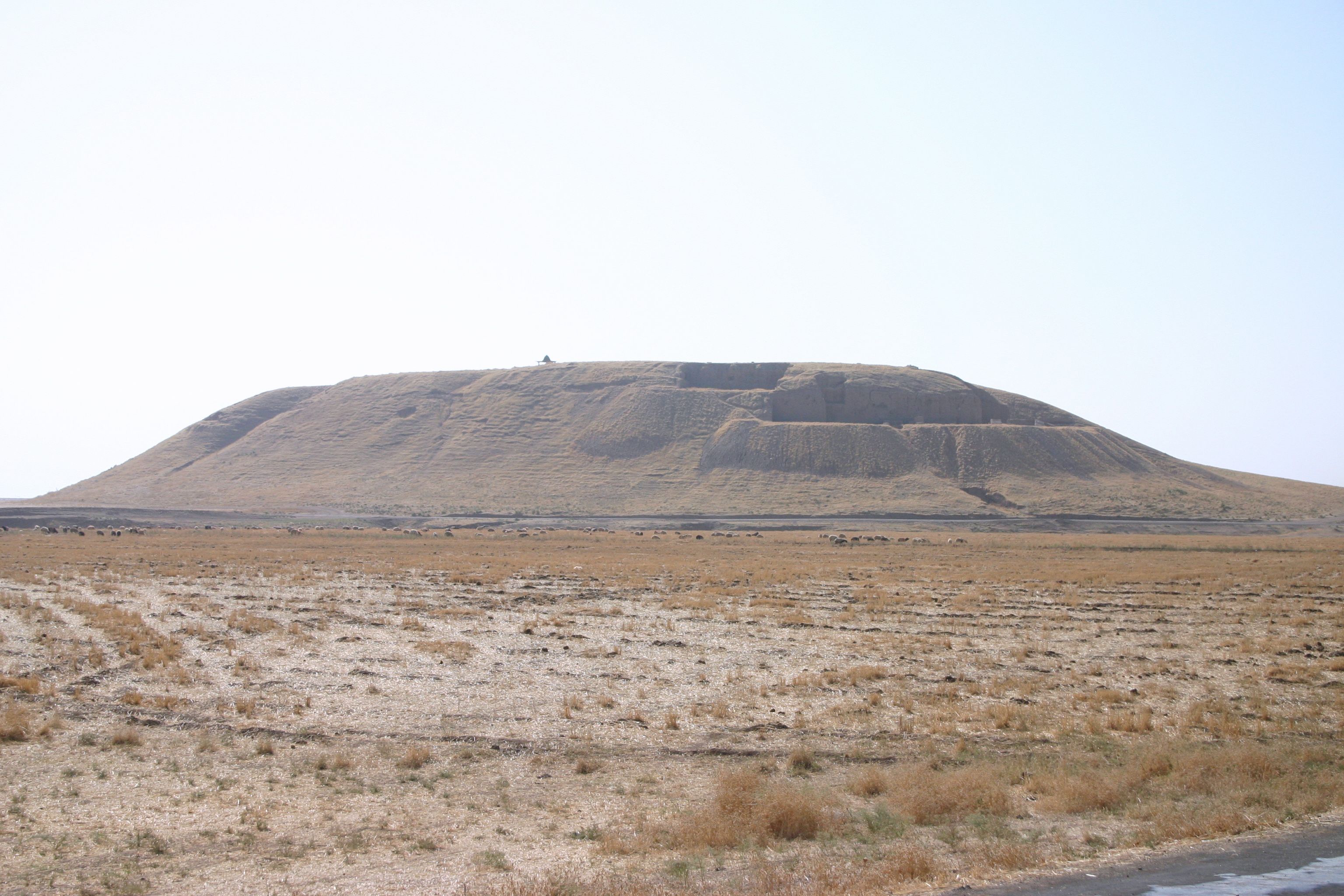
Zahiran
Zahiran also known as Sahiri or Sa-hi-ri, also known as Zahiran was an Iron Age city of the ancient near east. It was a city in what is today Syria. During the Mari–Ebla war (2300 BC) Zahiran was the site of a battle between Igrish-Halam King of Ebla, and Iblul-il, King of Mari. About a decade later it would be absorbed into the empire of Sargon of Akkad. The town was sacked in the Battle of Nineveh (612 BC). The chronicle of Aššur-uballit II, known as Chronicle 3, states of the Battle of Nineveh between Babylonian and Assyrian armies that "''in the month Âbu the king of Akkad and his army went upstream to Mane, Sahiri and Bali-hu. He plundered them, sacked them extensively and abducted their gods.''"Bill T. Arnold, Bryan E. Beyer, Readings from the Ancient Near East: Primary Sources for Old Testament The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nineveh (612 BC)
The Battle of Nineveh, also called the fall of Nineveh is conventionally dated between 613 and 611 BC, with 612 BC being the most supported date. After Assyrian defeat at the battle of Assur, an allied army which combined the forces of Medes and the Babylonians besieged Nineveh and sacked 750 hectares of what was, at that time, one of the greatest cities in the world. The fall of Nineveh led to the destruction of the Neo-Assyrian Empire as the dominant state in the Ancient Near East over the following three years. Archeological records show that the capital of the once mighty Assyrian Empire was extensively de-urbanized and depopulated in the decades and centuries following the battle. A garbled account of the fall of the city later led to the story of the legendary king Sardanapalus. Babylon became the imperial center of Mesopotamia for the first time in over a thousand years, leading to the Neo-Babylonian Empire, claiming imperial continuity as a new dynasty. Background Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
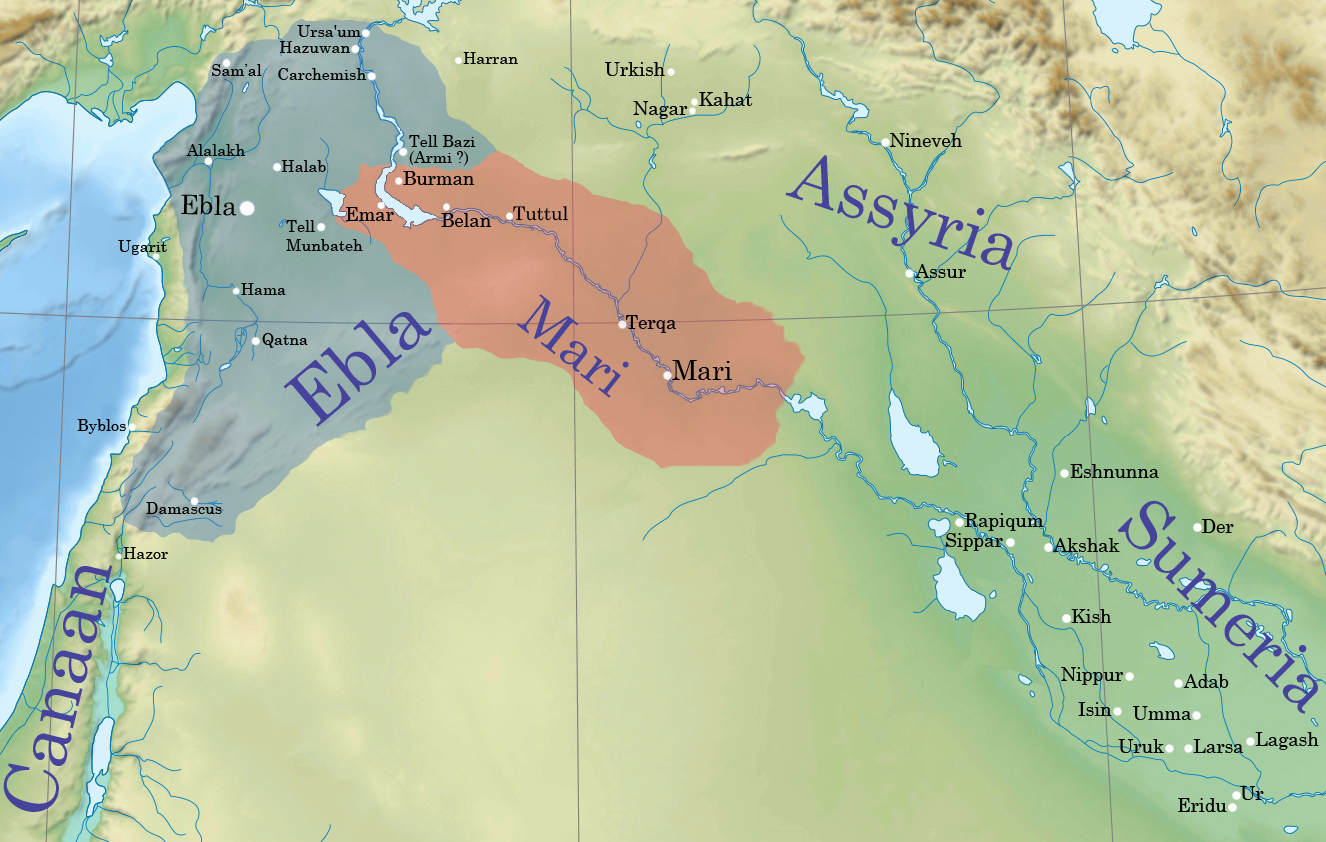
Amorite Cities
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Egypt from the 21st century BC to the late 17th century BC. The Amorites established several prominent city-states in various locations, such as Isin, Kurda, Larsa, Mari, and Ebla, and later founded Babylon and the Old Babylonian Empire. They also founded the Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the fragmented era of the Second Intermediate Period in the Nile Delta, which was characterized by rulers bearing Amorite names such as Yakbim Sekhaenre, and were likely part of the later Hyksos. The term in Akkadian and Sumerian texts refers to the Amorites, their principal deity, and an Amorite kingdom. The Amorites are mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as inhabitants of Canaan both before and after the conquest of the land under Joshua.van Seters, John, "The Terms 'Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iblul-Il
Iblul-Il (died 2380 BC) was the most energetic king (Lugal) of the second Mari, Syria#The second kingdom, Mariote kingdom, noted for his extensive campaigns in the middle Euphrates valley against the Ebla#Archive period, Eblaites, and in the upper Tigris region against various opponents, which asserted the Mariote supremacy in the Syrian north. Reign Sources Iblul-Il is attested in Mari, where statues bearing his name were excavated in 1952 from the city's temples. However, the deeds of the king are recorded in a letter sent to Ebla by Enna-Dagan, a successor of Iblul-Il. Campaigns Iblul-Il campaigned extensively against Ebla and its vassals and allies. The offensive was probably due to Ebla's increasing militaristic character, and was meant to block the trade route between Kish (Sumer), Kish, Tell Brak#Kingdom of Nagar, Nagar, and Ebla. Iblul-Il was a contemporary of Ebla's king Igrish-Halam, and is mentioned in the letter of Enna-Dagan campaigning in the middle Euphrates defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, the purpose being the recording of events that occurred, seen from the perspective of the chronicler. A chronicle which traces world history is a universal chronicle. This is in contrast to a narrative or history, in which an author chooses events to interpret and analyze and excludes those the author does not consider important or relevant. The information sources for chronicles vary. Some are written from the chronicler's direct knowledge, others from witnesses or participants in events, still others are accounts passed down from generation to generation by oral tradition.Elisabeth M. C. Van Houts, ''Memory and Gender in Medieval Europe: 900–1200'' (Toronto; Buffalo: University of Toronto Press, 1999), pp. 19–20. Some used writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tells (archaeology)
In archaeology, a tell (from , ', 'mound' or 'small hill') is an artificial topographical feature, a mound consisting of the accumulated and stratified debris of a succession of consecutive settlements at the same site, the refuse of generations of people who built and inhabited them and natural sediment. Tells are most commonly associated with the ancient Near East but are also found elsewhere, such as in Southern and parts of Central Europe, from Greece and Bulgaria to Hungary and Spain,, see map. and in North Africa. Within the Near East they are concentrated in less arid regions, including Upper Mesopotamia, the Southern Levant, Anatolia and Iran, which had more continuous settlement. Eurasian tells date to the Neolithic, the Chalcolithic and the Bronze and Iron Ages. In the Southern Levant the time of the tells ended with the conquest by Alexander the Great, which ushered in the Hellenistic period with its own, different settlement-building patterns. Many tells across the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Syria
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek. The Old Testament consists of many distinct books by various authors produced over a period of centuries. Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections: the first five books or Pentateuch (which corresponds to the Jewish Torah); the history books telling the history of the Israelites, from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon; the poetic and wisdom literature, which explore themes of human experience, morality, and divine justice; and the books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God. The Old Testament canon differs among Christian denominations. The Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as an Akkadian-populated but Amorites, Amorite-ruled state . During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was retrospectively called "the country of Akkad" ( in Akkadian), a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire. It was often involved in rivalry with the older ethno-linguistically related state of Assyria in the north of Mesopotamia and Elam to the east in Ancient Iran. Babylonia briefly became the major power in the region after Hammurabi (floruit, fl. –1752 BC middle chronology, or –1654 BC, short chronology timeline, short chronology) created a short-lived empire, succeeding the earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mane (ancient City)
Mane was an ancient city in what is today Syria and northern Iraq. Its exact location remains unknown, though it was north of Nineveh. During the Battle of Nineveh (612 BC), it was besieged. The chronicle of Aššur-uballit II, known as Chronicle 3, states of the Battle of Nineveh between Babylonian and Assyrian armies that "''in the month Âbu the king of Akkad and his army went upstream to Mane, Sahiri and Bali-hu. He plundered them, sacked them extensively and abducted their gods.''"Bill T. Arnold, Bryan E. Beyer, Readings from the Ancient Near East: Primary Sources for Old Testament The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ... Study (Baker Academic, 2002) p. 156. References {{reflist Ancient cities of the Middle East Former populated places in Syria Tells (archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkad (region)
Akkad (; also spelt Accad, Akkade, a-ka₃-de₂ki or Agade, Akkadian: , also URI KI in Sumerian during the Ur III period) was the capital of the Akkadian Empire, which was the dominant political force in Mesopotamia during a period of about 150 years in the last third of the 3rd millennium BC. Its location is unknown. In the early days of research various unidentified mounds were considered as the location of Akkad. In modern times most of the attention has focused on an area roughly defined by 1) near Eshnunna, 2) near Sippar, 3) not far from Kish and Babylon, 4) near the Tigris River, and 5) not far from the Diyala River – all within roughly 30 kilometers of modern Baghdad in central Iraq. There are also location proposals as far afield as the Mosul area in northern Iraq. The main goddess of Akkad was Ishtar-Annunitum or ''‘Aštar-annunîtum'' (Warlike Ishtar), though it may have been a different aspect, Istar- Ulmašītum. Her husband Ilaba was also revered. Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Calendar
The Babylonian calendar was a lunisolar calendar used in Mesopotamia from around the 2nd millennium BC until the Seleucid Era ( 294 BC), and it was specifically used in Babylon from the Old Babylonian Period ( 1780s BC) until the Seleucid Era. In the Seleucid Era it was reformed as "Greek time", Anno Graecorum was introduced and used in the Middle East and Egypt until the middle of the first millennium when the First Council of Nicaea AD 325 defined the Church year based on the Roman early Julian calendar. As Anno Graecorum formed the basis for time references in the Bible and spread westward, it rather increased the Babylonian calendars importance. The Babylonian calendar is also partly reflected in calendars in South and East Asia and the Islamic calendar as well as Iranian calendars. The Julian calendar inherited the definitions of the 12 month system, week, hour etc. from the Babylonian calendar and the current Jewish calendar can be seen as a slightly modified Baby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |