Zahiran on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
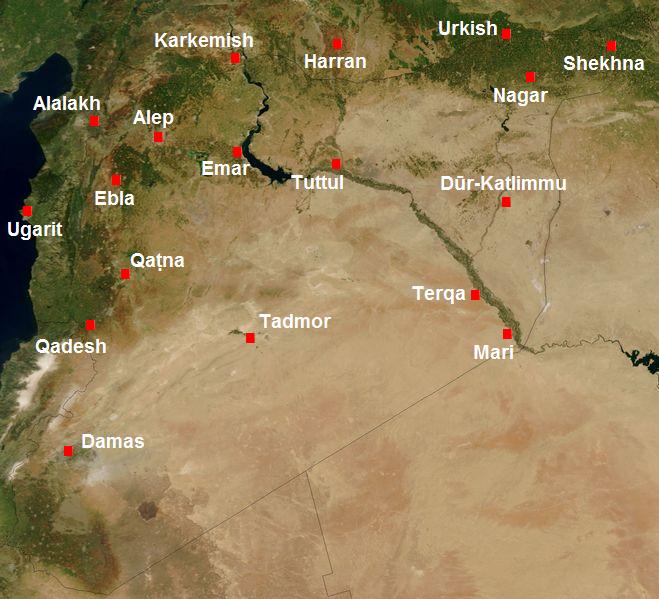 Zahiran also known as Sahiri or Sa-hi-ri, also known as Zahiran was an
Zahiran also known as Sahiri or Sa-hi-ri, also known as Zahiran was an
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
city of the ancient near east
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
. It was a city in what is today Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
.
During the Mari–Ebla war (2300 BC) Zahiran was the site of a battle between Igrish-Halam
Igrish-Halam or Igriš-Halab () was a king of the ancient city state of Ebla. His name means "(The god of) Halab has driven away (the opponent)", hence, the name might be a commemoration of an Eblaite victory that led to the incorporation of lan ...
King of Ebla, and Iblul-il
Iblul-Il (died 2380 BC) was the most energetic king (Lugal) of the second Mari, Syria#The second kingdom, Mariote kingdom, noted for his extensive campaigns in the middle Euphrates valley against the Ebla#Archive period, Eblaites, and in the uppe ...
, King of Mari.
About a decade
A decade (from , , ) is a period of 10 years. Decades may describe any 10-year period, such as those of a person's life, or refer to specific groupings of calendar years.
Usage
Any period of ten years is a "decade". For example, the statement ...
later it would be absorbed into the empire of Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; ; died 2279 BC), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly unc ...
.
The town was sacked in the Battle of Nineveh (612 BC)
The Battle of Nineveh, also called the fall of Nineveh is conventionally dated between 613 and 611 BC, with 612 BC being the most supported date. After Assyrian defeat at the battle of Assur, an allied army which combined the forces of Medes and ...
. The chronicle
A chronicle (, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events ...
of Aššur-uballit II, known as Chronicle 3, states of the Battle of Nineveh between Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
ian and Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n armies that "''in the month Âbu the king of Akkad and his army went upstream to Mane, Sahiri and Bali-hu. He plundered them, sacked them extensively and abducted their gods.''"Bill T. Arnold, Bryan E. Beyer, Readings from the Ancient Near East: Primary Sources for Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
Study (Baker Academic, 2002) p. 156.
References
{{reflist, 2 Amorite cities Former populated places in Syria Tells (archaeology) Bronze Age sites in Syria 7th century BC