|
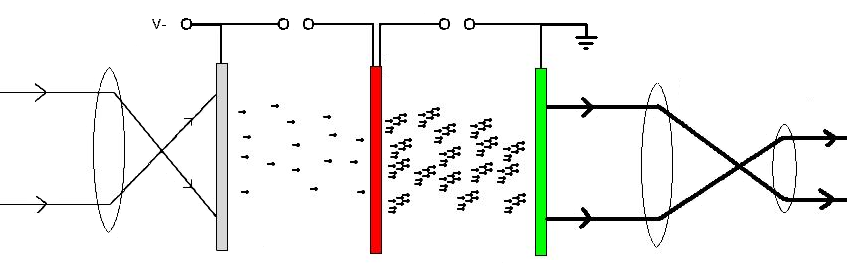
ZCam
ZCam is a brand of time-of-flight camera products for video applications by Israeli developer 3DV Systems. The ZCam supplements full-color video camera imaging with real-time range imaging information, allowing for the capture of video in 3D. The original ZCam, released in 2000, was an ENG video camera add-on used for digital video compositing. Before agreeing in March 2009 to sell its assets to Microsoft, 3DV had planned to release a ranging video webcam (previously called the Z-Sense), also under the name ZCam. The ZCam webcam was one of several competing real-time range imaging camera products in development that target home game controller applications. Technology The ZCam's time-of-flight camera system features a near-infrared (NIR) pulse illumination component, as well as an image sensor with a fast gating mechanism. Based on the known speed of light, ZCam coordinates the timing of NIR pulse wave emissions from the illuminator with the gating of the image sensor, so that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-of-flight Camera
A time-of-flight camera (ToF camera), also known as time-of-flight sensor (ToF sensor), is a range imaging camera system for measuring distances between the camera and the subject for each point of the image based on time-of-flight, the round trip time of an artificial light signal, as provided by a laser or an LED. Laser-based time-of-flight cameras are part of a broader class of scannerless LIDAR, in which the entire scene is captured with each laser pulse, as opposed to point-by-point with a laser beam such as in scanning LIDAR systems. Time-of-flight camera products for civil applications began to emerge around 2000, as the semiconductor processes allowed the production of components fast enough for such devices. The systems cover ranges of a few centimeters up to several kilometers. Types of devices Several different technologies for time-of-flight cameras have been developed. RF-modulated light sources with phase detectors Photonic Mixer Devices (PMD), the Swiss Ranger, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z CAM
This is a list of digital camera brands. Former and current brands are included in this list. With some of the brands, the name is licensed from another company, or acquired after the bankruptcy of an older photographic equipment company. The actual manufacture of a camera model is performed by a different company in many cases. In many cases brands are limited to certain countries. Not all brands of devices that can take digital images are listed here, including many industrial digital camera brands, some webcam brands, brands of cell phones that feature cameras, and brands of video cameras that can take digital stills. Defunct brands are listed separately. Active consumer camera brands , these brands offer some combination of compact digital cameras, bridge camera, digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), and mirrorless interchangeable lens cameras (MILCs): Other active brands These brands offer only non-camera digital imaging devices, or non-consumer digital ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Business Media
UBM plc was a British business-to-business (B2B) events organiser headquartered in London, England, before its acquisition by Informa in 2018. It had a long history as a Multinational corporation, multinational media company. Its main focus was on B2B events, but its principal operations included live media and business-to-business communications, marketing services and data provision, and it principally served the technology, healthcare, trade and transport, ingredients and fashion industries. UBM was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index. History Newspaper interests The history of the companies that made up UBM stretches back almost two hundred years. Up until its acquisition UBM businesses published many titles that were launched in the 19th century, including ''Building'' magazine, launched in 1843 by Joseph Hansom, as well as ''Chemist & Druggist''. The company was founded in 1918 as United Newspapers by David Lloyd George to acqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid State (electronics)
Solid-state electronics are semiconductor electronics: electronic equipment that use semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used as an adjective for devices in which semiconductor electronics that have no moving parts replace devices with moving parts, such as the solid-state relay, in which transistor switches are used in place of a moving-arm electromechanical relay, or the solid-state drive (SSD), a type of semiconductor memory used in computers to replace hard disk drives, which store data on a rotating disk. History The term ''solid-state'' became popular at the beginning of the semiconductor era in the 1960s to distinguish this new technology. A semiconductor device works by controlling an electric current consisting of electrons or electron hole, holes moving within a solid crystalline piece of semiconductor, semiconducting material such as silicon, while the thermionic vacuum tubes it replaced worked by controll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Intensifier
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light processes, such as fluorescence of materials in X-rays or gamma rays ( X-ray image intensifier), or for conversion of non-visible light sources, such as near-infrared or short wave infrared to visible. They operate by converting photons of light into electrons, amplifying the electrons (usually with a microchannel plate), and then converting the amplified electrons back into photons for viewing. They are used in devices such as night-vision goggles. Introduction Image intensifier tubes (IITs) are optoelectronic devices that allow many devices, such as night vision devices and medical imaging devices, to function. They convert low levels of light from various wavelengths into visible quantities of light at a single wavelength. Operation Im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanosecond
A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, of a second, or seconds. The term combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e.g. nanogram, nanometre, etc.) and ''second'', the primary unit of time in the SI. A nanosecond is to one second, as one second is to approximately 31.69 years. A nanosecond is equal to 1000 picoseconds or microsecond. Time units ranging between 10 and 10 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of nanoseconds. Time units of this granularity are commonly found in telecommunications, pulsed lasers, and related aspects of electronics. Common measurements * 0.001 nanoseconds – one picosecond * 0.96 nanoseconds – 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 96 nanoseconds – Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 1.0 nanosecond – cycle time of an electromagnetic wave with a frequency of 1 GHz (). * 1.0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Time
In electronics, fall time (pulse decay time) t_f is the time taken for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease (fall) from a specified value (usually 90% of the peak value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot) to another specified value (usually 10% of the maximum value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot). Limits on undershoot and oscillation (also known as ringing and hunting) are sometimes additionally stated when specifying fall time limits. See also *Rise time *Transition time Transition or transitional may refer to: Mathematics, science, and technology Biology * Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ ... References *{{FS1037C MS188 Transient response characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rise Time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratiosSee for example , and . or, equivalently, as percentages with respect to a given reference value. In analog electronics and digital electronics, these percentages are commonly the 10% and 90% (or equivalently and ) of the output step height: however, other values are commonly used. For applications in control theory, according to , rise time is defined as "''the time required for the response to rise from to of its final value''", with 0% to 100% rise time common for underdamped second order systems, 5% to 95% for critically damped and 10% to 90% for overdamped ones.Precisely, states: "''The rise time is the time required for the response to rise from x% to y% of its final value. For overdamped second order systems, the 0% to 100% rise time is normally used, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driver Circuit
In electronics, a driver is a electrical circuit, circuit or electronic component, component used to control another circuit or component, such as a high-power transistor, liquid crystal display (LCD), stepper motors, Static random-access memory, SRAM memory, and numerous others. They are usually used to regulate current flowing through a circuit or to control other factors such as other components and some other devices in the circuit. The term is often used, for example, for a specialized integrated circuit that controls high-power switches in Switched-mode power supply, switched-mode power converters. An amplifier can also be considered a driver for loudspeakers, or a voltage regulator that keeps an attached component operating within a broad range of input voltages. Typically the driver stage(s) of a circuit requires different characteristics to other circuit stages. For example, in a transistor power amplifier circuit, typically the driver circuit requires current gain, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Lens
A camera lens, photographic lens or photographic objective is an optical lens (optics), lens or assembly of lenses (compound lens) used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to Imaging, make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image Photosensitivity, chemically or Image sensor, electronically. There is no major difference in principle between a lens used for a still camera, a video camera, a telescope, a microscope, or other apparatus, but the details of design and construction are different. A lens might be permanently fixed to a camera, or it might be interchangeable lens camera, interchangeable with lenses of different focal lengths, apertures, and other properties. While in principle a simple lens, simple convex lens will suffice, in practice a compound lens made up of a number of optical lens elements is required to correct (as much as possible) the many optical aberrations that arise. Some aberrations will be prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Diodes
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation is generated in the form of an emitted photon. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence, and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet (UV) spectra. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Wave
A pulse wave or pulse train or rectangular wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform that is the periodic version of the rectangular function. It is held high a percent each cycle ( period) called the duty cycle and for the remainder of each cycle is low. A duty cycle of 50% produces a square wave, a specific case of a rectangular wave. The average level of a rectangular wave is also given by the duty cycle. A pulse wave is used as a basis for other waveforms that modulate an aspect of the pulse wave. In pulse-width modulation (PWM) information is encoded by varying the duty cycle of a pulse wave. Pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM) encodes information by varying the amplitude. Frequency-domain representation The Fourier series expansion for a rectangular pulse wave with period T, amplitude A and pulse length \tau is x(t) = A \frac + \frac \sum_^ \left(\frac \sin\left(\pi n\frac\right) \cos\left(2\pi nft\right)\right) where f = \frac. Equivalently, if duty cycle d = \frac is used, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |