|
Photographic Lens
A camera lens, photographic lens or photographic objective is an optical lens (optics), lens or assembly of lenses (compound lens) used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to Imaging, make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image Photosensitivity, chemically or Image sensor, electronically. There is no major difference in principle between a lens used for a still camera, a video camera, a telescope, a microscope, or other apparatus, but the details of design and construction are different. A lens might be permanently fixed to a camera, or it might be interchangeable lens camera, interchangeable with lenses of different focal lengths, apertures, and other properties. While in principle a simple lens, simple convex lens will suffice, in practice a compound lens made up of a number of optical lens elements is required to correct (as much as possible) the many optical aberrations that arise. Some aberrations will be prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Lenses Front View
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication. A person who operates a camera to capture or take Photograph, photographs is called a photographer, while the captured image, also known as a photograph, is the result produced by the camera. Typically, a lens is used to focus (optics), focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed Exposure (photography), exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an Charge-coupled device, electrical charge at each pixel, which is Image processing, electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinhole Camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens but with a tiny aperture (the so-called ''Pinhole (optics), pinhole'')—effectively a light-proof box with a small hole in one side. Light from a scene passes through the aperture and projects an inverted image on the opposite side of the box, which is known as the camera obscura effect. The size of the images depends on the distance between the object and the pinhole. A Worldwide Pinhole Photography Day is observed on the last Sunday of April, every year. History Camera obscura The camera obscura or pinhole image is a natural optical phenomenon. Early known descriptions are found in the Chinese Mozi (book), Mozi writings (circa 500 BCE) and the Aristotelian ''Problems (Aristotle), Problems'' (circa 300 BCE – 600 CE). Ibn al-Haytham (965–1039), an Physics in the medieval Islamic world, Arab physicist also known as Alhazen, described the camera obscura effect. Over the centuries others started to experiment with it, main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Incidence (optics)
The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular (at 90 degree angle) to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as optical, acoustic, microwave, and X-ray. In the figure below, the line representing a ray makes an angle θ with the normal (dotted line). The angle of incidence at which light is first totally internally reflected is known as the critical angle. The angle of reflection and angle of refraction are other angles related to beams. In computer graphics and geography, the angle of incidence is also known as the illumination angle of a surface with a light source, such as the Earth's surface and the Sun. It can also be equivalently described as the angle between the tangent plane of the surface and another plane at right angles to the light rays. This means that the illumination angle of a certain point on Earth's surface is 0° if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-reflective Coating
An antireflective, antiglare or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lens (optics), lenses, other optical elements, and photovoltaic cells to reduce reflection (physics), reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost due to reflection. In complex systems such as cameras, binoculars, telescopes, and optical microscope, microscopes the reduction in reflections also improves the Contrast (vision), contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on glasses, eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight. Many coatings consist of transparent thin-film optics, thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens Flare
A lens flare happens when light is scattered, or ''flared'', in a lens system, often in response to a bright light, producing a sometimes undesirable artifact in the image. This happens through light scattered by the imaging mechanism itself, for example through internal reflection and forward scatter from material imperfections in the lens. Lenses with large numbers of elements such as zooms tend to have more lens flare, as they contain a relatively large number of interfaces at which internal scattering may occur. These mechanisms differ from the focused image generation mechanism, which depends on rays from the refraction of light from the subject itself. There are two types of flare: visible artifacts and glare across the image. The glare makes the image look "washed out" by reducing contrast and color saturation (adding light to dark image regions, and adding white to saturated regions, reducing their saturation). Visible artifacts, usually in the shape of the apert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brownie (camera)
The Brownie was a series of camera models made by Eastman Kodak and first released in 1900. It introduced the Snapshot (photography), snapshot to the masses by addressing the cost factor which had meant that amateur photography remained beyond the means of many people; the Pocket Kodak, for example, would cost most families in Britain nearly a whole month's wages. The Brownie was a basic Paperboard, cardboard box camera with a simple Lens (optics)#Types of simple lenses, convex-concave lens that took -inch square pictures on No. 117 roll film. It was conceived and marketed for sales of Kodak roll films. Because of its simple controls and initial price of US$1 (equivalent to $ in ) along with the low price of Kodak roll film and processing, the Brownie camera surpassed its marketing goal. Invention and etymology The Brownie was invented by Frank A. Brownell for the Eastman Kodak Company. Named after The Brownies, the Brownie characters popularised by the Canadian writer Palmer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephoto
A telephoto lens, also known as telelens, is a specific type of a long-focus lens used in photography and cinematography, in which the physical length of the lens is shorter than the focal length. This is achieved by incorporating a special lens group known as a ''telephoto group'' that extends the light path to create a long-focus lens in a much shorter overall design. The angle of view and other effects of long-focus lenses are the same for telephoto lenses of the same specified focal length. Long-focal-length lenses are often informally referred to as ''telephoto lenses'', although this is technically incorrect: a telephoto lens specifically incorporates the telephoto group. Construction A simple photographic lens may be constructed using one lens element of a given focal length; to focus on an object at infinity, the distance from this single lens to focal plane of the camera (where the sensor or film is) has to be adjusted to the focal length of that lens. For example, gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
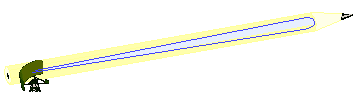
Pencil Beam
In optics, a pencil or pencil of rays, also known as a pencil beam or narrow beam, is a geometric construct (pencil of half-lines) used to describe a Light beam, beam or portion of a beam of electromagnetic radiation or charged subatomic particle, particles, typically in the form of a Cone (geometry), cone or Cylinder (geometry), cylinder. Antennas which strongly bundle in azimuth and elevation are often described as "pencil-beam" antennas. For example, a phased array antenna can send out a beam that is extremely thin. Such antennas are used for tracking radar, and the process is known as beamforming. In optics Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ..., the focus (optics), focusing action of a lens (optics), lens is often described in terms of pencils of ray (optics), ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exit Pupil
In optics, the exit pupil is a virtual aperture in an optical system. Only ray (optics), rays which pass through this virtual aperture can exit the system. The exit pupil is the image of the aperture stop in the optics that follow it. In a optical telescope, telescope or compound microscope, this image is the image of the Objective (optics), objective element(s) as produced by the eyepiece. The size and shape of this disc is crucial to the instrument's performance, because the observer's eye can see light only if it passes through the aperture. The term ''exit pupil'' is also sometimes used to refer to the diameter of the virtual aperture. Older literature on optics sometimes refers to the exit pupil as the ''Ramsden disc'', named after English instrument-maker Jesse Ramsden. Visual instruments To use an optical instrument, the entrance pupil of the viewer's eye (the image of the pupil, anatomical pupil as seen through the cornea) must be aligned with and be of similar size to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Projector
A projector or image projector is an optical device that projects an image (or moving images) onto a surface, commonly a projection screen. Most projectors create an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens, but some newer types of projectors can project the image directly, by using lasers. A virtual retinal display, or retinal projector, is a projector that projects an image directly on the retina instead of using an external projection screen. The most common type of projector used today is called a video projector. Video projectors are digital replacements for earlier types of projectors such as slide projectors and overhead projectors. These earlier types of projectors were mostly replaced with digital video projectors throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, but old analog projectors are still used at some places. The newest types of projectors are handheld projectors that use lasers or LEDs to project images. Movie theaters used a type of projector called a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entrance Pupil
In an optical system, the entrance pupil is the optical image of the physical aperture stop, as 'seen' through the optical elements in front of the stop. The corresponding image of the aperture stop as seen through the optical elements behind it is called the ''exit pupil''. The entrance pupil defines the cone of rays that can enter and pass through the optical system. Rays that fall outside of the entrance pupil will not pass through the system. If there is no lens in front of the aperture (as in a pinhole camera), the entrance pupil's location and size are identical to those of the aperture. Optical elements in front of the aperture will produce a magnified or diminished image of the aperture that is displaced from the aperture location. The entrance pupil is usually a virtual image: it lies behind the first optical surface of the system. The entrance pupil is a useful concept for determining the size of the cone of rays that an optical system will accept. Once the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Image
In optics, the ''image'' of an object is defined as the collection of Focus (optics), focus points of Ray (optics), light rays coming from the object. A ''real image'' is the collection of focus points made by Vergence (optics), converging rays, while a virtual image is the collection of focus points made by backward extensions of Beam divergence, diverging rays. In other words, a virtual image is found by tracing real rays that emerge from an optical device (lens, mirror, or some combination) backward to perceived or apparent origins of ray divergences. There is a concept ''virtual object'' that is similarly defined; an object is virtual when forward extensions of rays converge toward it. This is observed in ray tracing for a multi-lenses system or a diverging lens. For the diverging lens, forward extension of converging rays toward the lens will meet the converging point, so the point is a virtual object. For a (refracting) lens, the real image of an object is formed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |