|
Yotvingians
Yotvingians, also called Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians, were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prussians. The linguist Petras Būtėnas asserts that they were closest to the Lithuanians. The Yotvingians contributed to the formation of the Lithuanian state. Culture Etymology According to Vytautas Mažiulis, the name Sūduva derives from a local hydronym ''*Sūd(a)vā'', derived from a Baltic verbal root, ''*sū-'': to flow, pour. Language Numerous linguists consider the Yotvingian language as a dialect of the Old Prussian language. The Lithuanian linguist Petras Būtėnas states that such an opinion is incorrect, because the Lithuanian predominates in Yotvingian toponymy instead of the Old Prussian . The Lithuanian professor Zigmas Zinkevičius wrote that the Yotvingians spoke a dialect of Western Baltic that was closer to Lithuanian than Prussian. The only known written source of the Yotvingian language is the manuscript "". Geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yotvingia
Yotvingia, or Sudovia, was a region where the Balts, Baltic tribe known as Yotvingians lived. It was located in the area of Suvalkija, Sudovia and Dzūkija, Dainava; south west from the upper Nemunas, between Marijampolė, Merkinė (Lithuania), Slonim, Kobryn (Belarus), Białystok, and Ełk, Poland, Ełk (Poland). Today this area corresponds mostly to the Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland, Marijampolė County of Lithuania and a part of Grodno Region, Hrodna Province and Brest Province of Belarus. History The treaty of 944 between Kievan prince Igor of Kiev, Igor and the Byzantine Empire has the names of many Rus' ambassadors, one of which was Jatviag Gunarev. It is also the first written documentation of the term ''Jatviag'', or ''Yatviag''. The southern part of the Yotvingian lands, Sudovia and Galindia, were subdued by an army of Kievan Rus', led by Vladimir I of Kiev in 983. :LT:Netimeras, Netimeras, a ruler of the Yotvingians (part of Lithuanian kingdom), was converted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudovian Language
Sudovian (also known as Yotvingian, or Jatvingian) was a West Baltic language of Northeastern Europe. Sudovian was closely related to Old Prussian. It was formerly spoken southwest of the Neman river in what is now Lithuania, east of Galindia and in the north of Yotvingia, and by exiles in East Prussia. Name The language is referred to as Yotvingian, Jatvingian or Sudovian. Those names are derived from the southern- and northernmost tribes living in the area. When the Germans learnt the name "Sudovian" from the Prussians, they got to know the name of the northernmost tribe only, while Poles in the south met a tribe calling itself Yatvingian. Both Germans and Poles generalized the terms for all the Baltic inhabitants of the area. The territory they lived in is referred to as Sudovia underland Jotva ettwen Dainavia, or Pollexia. Classification Sudovian was an Indo-European language belonging to the Baltic branch. There are several proposals for the classification of the Sudov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanians (tribe)
The Lithuanians or Old East Lithuanians (Latin: ''Letwini''; Baranauskas, Tomas (2006). ''Aukštaitija XIII–XV amžiuje'' 'Aukštaitija in the 13th–15th centuries''(in Lithuanian). Kaunas: Žiemgalos leidykla. p. 33. Low German: ''Lettowen''; Old East Slavic: ''Литъва'', ''Литва''; Old Swedish: ''lättugha''; modern Lithuanian: ''rytiniai senlietuviai, senlietuviai'') were one of the largest East Baltic tribes, inhabiting present-day Eastern Lithuania in the 5th–13th centuries. Following the Northern Crusades, the ancient Lithuanians began gradually assimilating other neighbouring Baltic tribes, becoming the primary progenitor group of modern Lithuanians. History Origin and trade It is believed that ancient Lithuania covered around 80,000 km2 and was home to around 300,000 inhabitants, most of them living as farmers. Traditionally historians divide the area into six attested lands – Nalšia, Deltuva, Upytė, Lietuva, Neris and Deremela, with Lietuva ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Balts
The Western Baltic culture (; also known as (West Baltic circle), ) was the Western Baltic languages, westernmost branch of the Balts, representing a distinct archaeological culture of the Bronze Age and Iron Age, along the southern coast of the Baltic Sea. It is a zone of several small archaeological cultures that were ethnically Baltic and had similar cultural features (e.g. similar monuments or some features of the funeral rite). They included tribes such as the Old Prussians, Galindians, Yotvingians (or Sudovians) and Skalvians, in addition to the little-known Pomeranian Balts or Western Balts proper, in the area now known as Pomerania. History Most of the Western Balts arose from the dating back to the early Iron Age. The Western Baltic culture includes: * (from the end of to the end of the 4th c. A.D., possibly even the end of the 5th c.) * (from the mid-2nd c. A.D. to the end of the 6th c.) * (from the end of the 1st c. A.D. to the beginning of the 6th c.) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
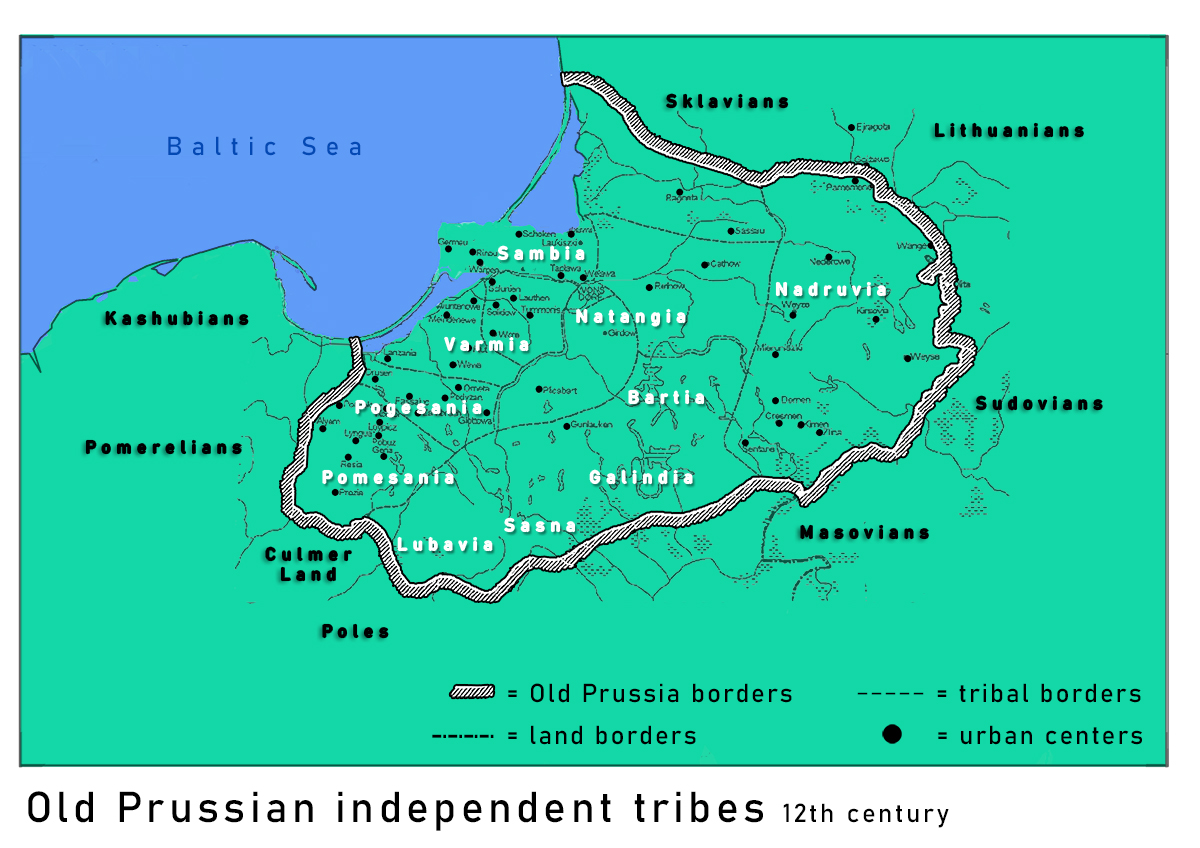
Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. As Balts, they spoke an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language of the Baltic languages, Baltic branch now known as Old Prussian language, Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian Prussian mythology, deities. Their ethnonym was later adopted by predominantly Low German language, Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Duchy of Poland (c. 960–1025), Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the State of the Teuton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puńsk
Puńsk (; ) is a village in the Podlaskie Voivodeship in northeastern Poland, seat of the Gmina Puńsk in the Sejny County. It is located only from the border with Lithuania. History Early history The oldest traces of humans in Puńsk territory date back to about 10,000 years BC. Middle Ages In the early medieval ages it was inhabited by the Baltic Yotvingians. Lithuanian Crusade In the 13th century, the Teutonic Knights mostly exterminated the local Balts with only few of them surviving. Nowadays only some castle hills (e.g. in Šiurpilis), mounds (e.g. in Eglinė), cemeteries (e.g. in Szwajcaria), village names (e.g. Zervynai, Krosna) and archaeological excavations remind us about their existence. Later on the Suwałki Region became overgrown with forests. Lithuanian Grand Dukes hunted there. In the early 15th century the people from Merkinė and Punia started to colonize this territory again. The lake was named ''Punia'', from which the village derived its name. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
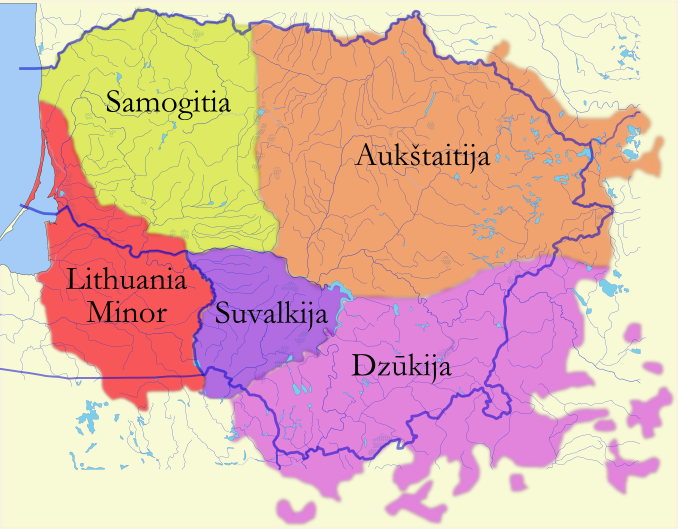
Dzūkija
Dzūkija () or Dainava is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. Dzūkija is a cultural region defined by traditional lifestyles and dialects of the local Lithuanian population (mostly rural farmers) and has never been defined as a political or administrative unit. Traditionally, Alytus is regarded as the capital of the region and largest city. Although Vilnius is surrounded by Dzūkija, the city itself is not considered as a part of any ethnographic region in most cases. Geography Dzūkija is situated in southeastern Lithuania, and consists of Alytus County and southern Vilnius County. Historically, it extended into what is now northeastern Poland (Podlaskie Voivodeship) and northwestern Belarus ( Grodno Region). Large parts of Dzūkija have light sandy soil, unsuited for agriculture. Therefore, the region is densely covered with pine forests, one of which is Dainava Forest, the largest in Lithuania. The Čepkeliai Marsh, the largest swamp in Lithuania, is situated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ełk
Ełk is a city in northeastern Poland with 61,677 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is the seat of Ełk County in the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship. It lies on the shore of Ełk Lake, which was formed by a glacier, and is surrounded by extensive forests. It is the largest city and unofficial capital of historical Masuria. Founded in medieval times, Ełk, became a notable regional printing and publishing centre and home to the leading Polish school in Masuria since the early modern period, and in the late modern period it was a center of resistance to preserve Polish language in Masuria against Germanisation of Poles during the Partitions, Germanisation policies. It is an important rail and road junction and food industry hub in north-eastern Poland, and the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Ełk. One of the principal attractions in the area is legal hunting. History Middle Ages The area where the town of Ełk is located was originally inhabited by Yotvingians, Jatvingians, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of with a population of . The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into Regions of Belarus, six regions. Minsk is the capital and List of cities and largest towns in Belarus, largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status. For most of the medieval period, the lands of modern-day Belarus was ruled by independent city-states such as the Principality of Polotsk. Around 1300 these lands came fully under the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth; this period lasted for 500 years until the Partitions of Poland, 1792-1795 partitions of Poland-Lithuania placed Belarus within the Belarusian history in the Russian Empire, Russian Empire for the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marijampolė
Marijampolė (; also known by Marijampolė#Names, several other names) is the Capital city, capital of Marijampolė County in the south of Lithuania, bordering Poland and Russian Kaliningrad Oblast, and Lake Vištytis. The city's population stood at approximately 48,700 in 2003. Marijampolė is the List of cities in Lithuania, seventh-largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, sixteenth-largest city in the Baltic States. It is the cultural centre and largest settlement of the historical region of Suvalkija (Sudovia). Marijampolė has been a regional center since 1994. The city covers an area equal to . The Šešupė River divides the city into two parts, which are connected by six bridges. The city is known for the international art and architecture symposium ''Malonny'', an event which focuses on street art, murals, and public installations, transforming Marijampolė's urban spaces into an open-air art gallery. Names The city has also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |