|
Yotvingia
Yotvingia, or Sudovia, was a region where the Balts, Baltic tribe known as Yotvingians lived. It was located in the area of Suvalkija, Sudovia and Dzūkija, Dainava; south west from the upper Nemunas, between Marijampolė, Merkinė (Lithuania), Slonim, Kobryn (Belarus), Białystok, and Ełk, Poland, Ełk (Poland). Today this area corresponds mostly to the Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland, Marijampolė County of Lithuania and a part of Grodno Region, Hrodna Province and Brest Province of Belarus. History The treaty of 944 between Kievan prince Igor of Kiev, Igor and the Byzantine Empire has the names of many Rus' ambassadors, one of which was Jatviag Gunarev. It is also the first written documentation of the term ''Jatviag'', or ''Yatviag''. The southern part of the Yotvingian lands, Sudovia and Galindia, were subdued by an army of Kievan Rus', led by Vladimir I of Kiev in 983. :LT:Netimeras, Netimeras, a ruler of the Yotvingians (part of Lithuanian kingdom), was converted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yotvingians
Yotvingians, also called Sudovians, Jatvians, or Jatvingians, were a Western Baltic people who were closely tied to the Old Prussians. The linguist Petras Būtėnas asserts that they were closest to the Lithuanians. The Yotvingians contributed to the formation of the Lithuanian state. Culture Etymology According to Vytautas Mažiulis, the name Sūduva derives from a local hydronym ''*Sūd(a)vā'', derived from a Baltic verbal root, ''*sū-'': to flow, pour. Language Numerous linguists consider the Yotvingian language as a dialect of the Old Prussian language. The Lithuanian linguist Petras Būtėnas states that such an opinion is incorrect, because the Lithuanian predominates in Yotvingian toponymy instead of the Old Prussian . The Lithuanian professor Zigmas Zinkevičius wrote that the Yotvingians spoke a dialect of Western Baltic that was closer to Lithuanian than Prussian. The only known written source of the Yotvingian language is the manuscript "". Geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudovian Language
Sudovian (also known as Yotvingian, or Jatvingian) was a West Baltic language of Northeastern Europe. Sudovian was closely related to Old Prussian. It was formerly spoken southwest of the Neman river in what is now Lithuania, east of Galindia and in the north of Yotvingia, and by exiles in East Prussia. Name The language is referred to as Yotvingian, Jatvingian or Sudovian. Those names are derived from the southern- and northernmost tribes living in the area. When the Germans learnt the name "Sudovian" from the Prussians, they got to know the name of the northernmost tribe only, while Poles in the south met a tribe calling itself Yatvingian. Both Germans and Poles generalized the terms for all the Baltic inhabitants of the area. The territory they lived in is referred to as Sudovia underland Jotva ettwen Dainavia, or Pollexia. Classification Sudovian was an Indo-European language belonging to the Baltic branch. There are several proposals for the classification of the Sudov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
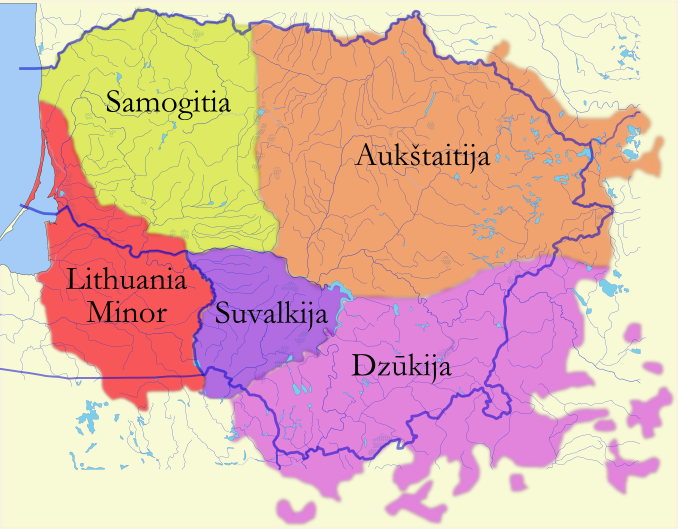
Suvalkija
Suvalkija or Sudovia ( or ''Sūduva'') is the smallest of the five cultural regions of Lithuania. Its unofficial capital is Marijampolė. People from Suvalkija (Suvalkijans) are called (plural) or (singular) in Lithuanian. It is located south of the Nemunas River, Neman River, in the former territory of Vilkaviškis bishopric. Historically, it is the newest ethnographic region, as its most distinct characteristics and separate regional identity formed during the 19th century when the territory was part of Congress Poland. It was never a separate political entity, and even today, it has no official status in the administrative division of Lithuania. However, it continues to be the subject of studies focusing on Lithuanian folk culture of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Most of Lithuania's cultural differences blended or disappeared during the Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet occupation (1944–1990), remaining the longest in southeastern Lithuania. The concept r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians (modern), Latgalians) — all East Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Curonians, Sudovians, Skalvians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the West Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct, but made a large influence on the living branches, especially on literary Lithuanian language. The Balts are descended from a group of Proto-Indo-Europeans, Proto-Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the lower Vistula and southeast shore of the Baltic Sea and upper Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and which over time became differentiated into West and East Balts. In the fifth century CE, parts of the eastern Baltic coast began to be settled by the ancestors of the Western Balts, whereas the East Balts lived in modern-day Belarus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Of Querfurt
Bruno of Querfurt, O.S.B. Cam., (; 974 – 14 February or 9/14 March 1009), also known as Brun, was a Christian missionary bishop, Camaldolese monk and martyr, who was beheaded near the border of Kievan Rus and Lithuania for trying to spread Christianity. He is also called the second "Apostle of the Prussians". Biography Early life Bruno was from a noble family of Querfurt (now in Saxony-Anhalt). He is rumoured to have been a relative of the Holy Roman Emperor Otto III. At the age of six, he was sent to be educated at the cathedral school in Magdeburg, the seat of Adalbert of Magdeburg, the teacher and namesake of Adalbert of Prague. While still a youth, he was made a canon of the Cathedral of Magdeburg. The fifteen-year-old Otto III made Bruno a part of his royal court. In 995 Otto III appointed Bruno as his court chaplain. While in Rome for Otto's imperial coronation, Bruno met Adalbert of Prague, the first "Apostle of the Prussians", killed a year later, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galindia
Galindians were two distinct, and now extinct, tribes of the Balts. Most commonly, Galindians refers to the Western Galindians who lived in the southeast part of Prussia. Less commonly, it is used for a tribe that lived in the area of what is today Moscow (). Etymology Johannes Voigt (supported by many others) suggested that name is derived from the Baltic word *''galas'' ("the end", probably synonymous to "located farthest", "located near the border of the territory or area"), alluding to the fact that they settled for some time further west and further east than any other Baltic tribe. Polish historian suggested another etymology: the name ''Galind''- may be derived from the hydronym of in the province of Olsztyn, in what was the very center of ancient ''Galindia''. J. Nalepa (1971) suggested the root *''gal''- was originally a different ablaut grade of the same root found in Lithuanian "''gilus''" – deep, and "''gelmė''" – depth. The original meaning referred to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkinė
Merkinė (also known by #Etymology, several other names) is a small town in Alytus County, which is located at the confluence of the Neman and Merkys rivers. The town belongs to the Varėna District Municipality and is located about 26 kilometers west of Varėna and 28 kilometers south of Alytus. As of 2021, the town had 963 residents. Merkinė is one of the oldest settlements in Lithuania. The Merkinė Castle was first mentioned in written sources in 1359. The first settlers inhabited the confluence of Merkys and Nemunas in the 9th-10th century BC, at the end of the Paleolithic. On top of Merkinė hillfort#Lithuania, hill-fort stood one of the most important Lithuanian castles, built in the 13th century, which guarded against invasions of the Teutonic Order. Merkinė was a part of a strategic triangle - Kaunas - Vilnius - Merkinė, protected with the chains of hillforts and castles. The center of Merkinė town is a state-protected urbanistic monument. Merkinė is an important poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the List of cities and towns in Poland, tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area. Białystok is located in the Białystok Uplands of the Podlachia, Podlachian Plain on the banks of the Biała (Supraśl), Biała River, (124 mi) northeast of Warsaw. It has historically attracted migrants from elsewhere in Poland and beyond, particularly from Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. This is facilitated by the Belarus–Poland border, nearby border with Belarus also being the eastern border of the European Union, as well as the Schengen Area. The city and its adjacent municipalities constitute Metropolitan Białystok. The city has a Humid continental climate#Dfb/Dwb/Dsb: Mild to warm summer subtype, warm summer continental climate, characterized by warm summers and long frosty winters. Forests are an important part of Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of with a population of . The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into Regions of Belarus, six regions. Minsk is the capital and List of cities and largest towns in Belarus, largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status. For most of the medieval period, the lands of modern-day Belarus was ruled by independent city-states such as the Principality of Polotsk. Around 1300 these lands came fully under the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth; this period lasted for 500 years until the Partitions of Poland, 1792-1795 partitions of Poland-Lithuania placed Belarus within the Belarusian history in the Russian Empire, Russian Empire for the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komantas Of Yotvingia
Komantas or Skomantas (known in Ruthenian sources as ''Komat'', in Latin ''Koommat'', in German ''Skomand'' and ''Skumand''; ca. 1225(?) – after 1285) was a powerful duke and pagan priest of the Yotvingians, one of the early Baltic tribes (according to historian S. C. Rowell and some other researchers, this duke of Sudovia seems to be identical to Skalmantas, the supposed progenitor of Gediminas' dynasty, the Gediminids). He was at the height of his power during the 1260s and 1270s. Skomantas is first mentioned by Peter von Dusburg during the Great Prussian Uprising (1260–1274) as a leader of the 1263 raid on Chełmno, a stronghold of the Teutonic Knights. He also led campaigns against Pinsk and other Slavic territories and therefore could not fully support the uprising. After the uprising Skomantas, with help from the Lithuanians, led 4,000 men against the Teutonic Knights. However, the Old Prussians and other Balts were losing their power. Skomantas' estate was devastated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobryn
Kobryn or Kobrin is a town in Brest Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Kobryn District. It is located in the southwestern corner of Belarus, where the Mukhavets river and Dnieper–Bug Canal meet. The town lies about east of the city of Brest, Belarus, Brest. As of 2025, it has a population of 52,432. History In the early times, it was inhabited by the ancient Balts, Baltic Yotvingian tribe. At various times, the city belonged to Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Russian Empire, the Second Polish Republic, the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR, and the Belarus, Republic of Belarus. Middle Ages and early modern era In the 10th century, the area became part of the emerging Civitas Schinesghe, Polish state under first ruler Mieszko I of Poland. Later, the area was part of the Kievan Rus' and the Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia. Kobryn was first mentioned in 1287. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dzūkija
Dzūkija () or Dainava is one of five ethnographic regions of Lithuania. Dzūkija is a cultural region defined by traditional lifestyles and dialects of the local Lithuanian population (mostly rural farmers) and has never been defined as a political or administrative unit. Traditionally, Alytus is regarded as the capital of the region and largest city. Although Vilnius is surrounded by Dzūkija, the city itself is not considered as a part of any ethnographic region in most cases. Geography Dzūkija is situated in southeastern Lithuania, and consists of Alytus County and southern Vilnius County. Historically, it extended into what is now northeastern Poland (Podlaskie Voivodeship) and northwestern Belarus ( Grodno Region). Large parts of Dzūkija have light sandy soil, unsuited for agriculture. Therefore, the region is densely covered with pine forests, one of which is Dainava Forest, the largest in Lithuania. The Čepkeliai Marsh, the largest swamp in Lithuania, is situated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |