|
Yotvingian
Sudovian (also known as Yotvingian, or Jatvingian) was a West Baltic language of Northeastern Europe. Sudovian was closely related to Old Prussian. It was formerly spoken southwest of the Neman river in what is now Lithuania, east of Galindia and in the north of Yotvingia, and by exiles in East Prussia. Name The language is referred to as Yotvingian, Jatvingian or Sudovian. Those names are derived from the southern- and northernmost tribes living in the area. When the Germans learnt the name "Sudovian" from the Prussians, they got to know the name of the northernmost tribe only, while Poles in the south met a tribe calling itself Yatvingian. Both Germans and Poles generalized the terms for all the Baltic inhabitants of the area. The territory they lived in is referred to as Sudovia underland Jotva ettwen Dainavia, or Pollexia. Classification Sudovian was an Indo-European language belonging to the Baltic branch. There are several proposals for the classification of the Sudovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yotvingia
Yotvingia, or Sudovia, was a region where the Balts, Baltic tribe known as Yotvingians lived. It was located in the area of Suvalkija, Sudovia and Dzūkija, Dainava; south west from the upper Nemunas, between Marijampolė, Merkinė (Lithuania), Slonim, Kobryn (Belarus), Białystok, and Ełk, Poland, Ełk (Poland). Today this area corresponds mostly to the Podlaskie Voivodeship of Poland, Marijampolė County of Lithuania and a part of Grodno Region, Hrodna Province and Brest Province of Belarus. History The treaty of 944 between Kievan prince Igor of Kiev, Igor and the Byzantine Empire has the names of many Rus' ambassadors, one of which was Jatviag Gunarev. It is also the first written documentation of the term ''Jatviag'', or ''Yatviag''. The southern part of the Yotvingian lands, Sudovia and Galindia, were subdued by an army of Kievan Rus', led by Vladimir I of Kiev in 983. :LT:Netimeras, Netimeras, a ruler of the Yotvingians (part of Lithuanian kingdom), was converted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curonian Language
The Curonian language (; ; ), or Old Curonian, was a Baltic language spoken by the Curonians, a Baltic tribe who inhabited Courland (now western Latvia and northwestern Lithuania). Classification Curonian was an Indo-European language of the Baltic branch, as proven by Jānis Endzelīns. Curonian's relation to other Baltic languages is unclear: *Some scholars consider it to have been an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language, intermediate between Lithuanian language, Lithuanian and Latvian language, Latvian. * Others, like Vytautas Mažiulis, classify it as a West Baltic languages, West Baltic language that became closer to the Eastern branch due to extensive contact. * Linguist Eduard Vääri argues that it is possible that Curonians were Baltic Finns. History Old Curonian disappeared in the course of the 16th century. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Baltic states saw a revival of scientific and cultural interest in extinct Baltic languages and tribes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
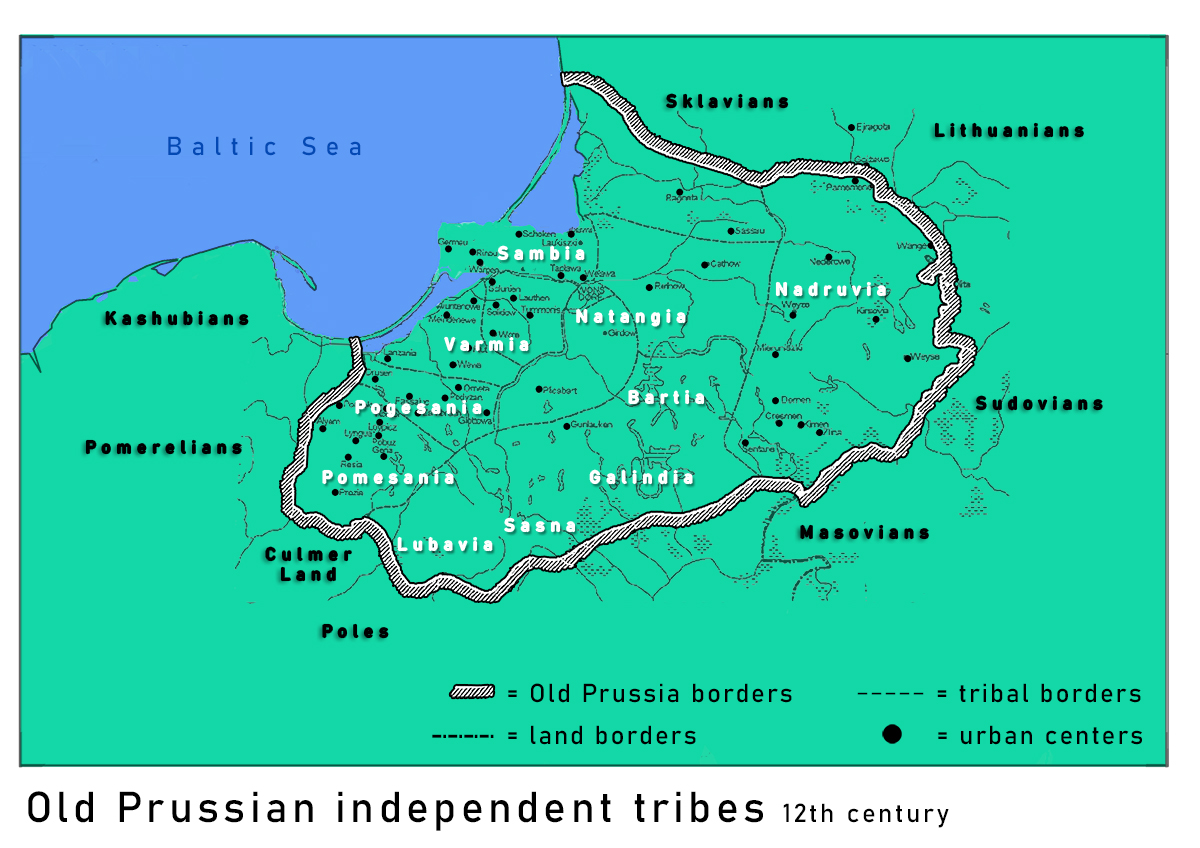
Galindia
Galindians were two distinct, and now extinct, tribes of the Balts. Most commonly, Galindians refers to the Western Galindians who lived in the southeast part of Prussia. Less commonly, it is used for a tribe that lived in the area of what is today Moscow (). Etymology Johannes Voigt (supported by many others) suggested that name is derived from the Baltic word *''galas'' ("the end", probably synonymous to "located farthest", "located near the border of the territory or area"), alluding to the fact that they settled for some time further west and further east than any other Baltic tribe. Polish historian suggested another etymology: the name ''Galind''- may be derived from the hydronym of in the province of Olsztyn, in what was the very center of ancient ''Galindia''. J. Nalepa (1971) suggested the root *''gal''- was originally a different ablaut grade of the same root found in Lithuanian "''gilus''" – deep, and "''gelmė''" – depth. The original meaning referred to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia (Baltic)
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Baltic people that inhabited the region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon to the east. As Balts, they spoke an Indo-European language of the Baltic branch now known as Old Prussian and worshipped pre-Christian deities. Their ethnonym was later adopted by predominantly Low German-speaking inhabitants of the region. The duchy of the Polans under Mieszko I, which was the predecessor of the Kingdom of Poland, first attempted to conquer and baptize the Baltic tribes during the 10th century, but repeatedly encountered strong resistance. Not until the 13th century were the Old Prussians subjugated and their lands conquered by the Teutonic Order. The remaining Old Prussians were assimilated during the following two centuries. The Old Prussian language, documented only in a limited way, was effectively extinct by the 18th century. The origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skalvian Language
The Scalovians (; ), also known as the Skalvians, ''Schalwen'' and ''Schalmen'', were a Baltic tribe related to the Prussians. According to the '' Chronicon terrae Prussiae'' of Peter of Dusburg, the now extinct Scalovians inhabited the land of Scalovia south of the Curonians and Samogitians, by the lower Neman River ca. 1240. Geography This region is located at both sides of the river Memel north of Nadruvians and south of Samogitia. In the North-East it stretched to rivers Šešupė, Ežeruona and Jūra. In the East it bordered on Sudovia, in the North-West on river Minija, in the West on the Curonian Lagoon and in the South-West on river Gilija. The center were the towns of Rusnė, Ragainė and Tilžė. Name The meaning is uncertain: ''skalwa'' "splinter (living split off)" or ''skalauti'' "between waters". According to Prussian legends, the tribe's name is derived from one of the sons of King Widewuto named Schalauo. History The inhabitants can be traced back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. The two common labial articulations are bilabials, articulated using both lips, and labiodentals, articulated with the lower lip against the upper teeth, both of which are present in English. A third labial articulation is dentolabials, articulated with the upper lip against the lower teeth (the reverse of labiodental), normally only found in pathological speech. Generally precluded are linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue contacts the posterior side of the upper lip, making them coronals, though sometimes, they behave as labial consonants. The most common distribution between bilabials and labiodentals is the English one, in which the nasal and the stops, , , and , are bilabial and the fricatives, , and , are labiodental. The voiceless bilabial fricative, voiced bilabial fricative, and the bilabial approximant do not exist as the primary realizations of any sounds in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem is in and in Latin . Thus the term "T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Poliander
Johann Gramann or Graumann (5 July 1487 – 29 April 1541), also known by his pen name Johannes Poliander, was a German pastor, theologian, teacher, humanist, reformer, and Lutheran leader. Life Gramann was born in Neustadt an der Aisch, Middle Franconia. He worked as rector of the Thomasschule in Leipzig. Poliander was Johann Eck's secretary at the 1519 Leipzig Debate, where he met Martin Luther and joined the Protestant Reformation. Poliander became pastor of Altstadt Church in 1525 in Königsberg (Kaliningrad), capital of the new Duchy of Prussia (a fief of the Crown of Poland), succeeding the fiery Johannes Amandus. The humanist was well-regarded by his peers, including the Catholic Johannes Dantiscus. He wrote secular and religious poetry in German and Latin. He was a strong advocate with Albert, Duke of Prussia, for the creation of the University of Königsberg. He donated his personal collection of 1,000 books to Altstadt's council; this became the foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Hartknoch
Christoph Hartknoch (1644–1687) was a Prussian historian and educator. Biography Hartknoch was born in Jablonken (Jabłonka) near Ortelsburg (Szczytno) in the Duchy of Prussia. In 1650 the family moved to Passenheim (Pasym) and there witnessed the brutality and horrors of the Tatar attacks, fighting for the Kingdom of Poland, in southern Prussia. His life was saved by his teacher, who shoved him out the window. Numerous villages in the region were destroyed, but Hartknoch made it to the ducal capital of Königsberg. In Königsberg Hartknoch started studying theology at a Protestant institute. Soon after his parents died and he had to take on jobs. He became a private teacher in Kaunas and then a rector in the Protestant school in Vilnius. He soon returned to Königsberg where books and records interested him in history. In 1679 Hartknoch published a book about Prussian history, ''Old and New Prussia'', first in Latin and then in German, as well as a history of the chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Consonant
Alveolar consonants (; UK also ) are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli (the sockets) of the upper teeth. Alveolar consonants may be articulated with the tip of the tongue (the apical consonants), as in English, or with the flat of the tongue just above the tip (the "blade" of the tongue; called laminal consonants), as in French and Spanish. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) does not have separate symbols for the alveolar consonants. Rather, the same symbol is used for all coronal places of articulation that are not palatalized like English palato-alveolar ''sh'', or retroflex. To disambiguate, the ''bridge'' (, ''etc.'') may be used for a dental consonant, or the under-bar (, ''etc.'') may be used for the postalveolars. differs from dental in that the former is a sibilant and the latter is not. differs from postalveolar in being unpalatalized. The bare letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Consonant
A dental consonant is a consonant articulated with the tongue against the upper teeth, such as , . In some languages, dentals are distinguished from other groups, such as alveolar consonants, in which the tongue contacts the gum ridge. Dental consonants share acoustic similarity and in the Latin script are generally written with consistent symbols (e.g. ''t'', ''d'', ''n''). In the International Phonetic Alphabet, the diacritic for dental consonant is . When there is no room under the letter, it may be placed above, using the character , such as in / p͆/. Cross-linguistically Languages, such as Albanian, Irish and Russian, velarization is generally associated with more dental articulations of coronal consonants. Thus, velarized consonants, such as Albanian , tend to be dental or denti-alveolar, and non-velarized consonants tend to be retracted to an alveolar position. Sanskrit, Hindustani and all other Indo-Aryan languages have an entire set of dental stops that occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicon Terrae Prussiae
''Chronicon terræ Prussiæ'' () is a chronicle of the Teutonic Knights, by Peter of Dusburg, finished in 1326. The manuscript is the first major chronicle of the Teutonic Order in Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, completed some 100 years after the conquest of the crusaders into the Baltic region. It is a major source for information on the Order's battles with Old Prussians and Lithuanians. Contents and reliability The chronicle is written in Latin and consists of four volumes. The first volume gives the background of the Order and its crusades in Outremer. The second volume narrates how the Order arrived to the Prussian land, while the third volume details wars with Old Prussians and other Baltic tribes. The fourth volume provides a historical context of other contemporary events in the world. The chronicle has an addendum of another 20 chapters dealing with events of 1326-1330, which may also have been written by Peter of Dusburg. The chronicle is based on local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |