|
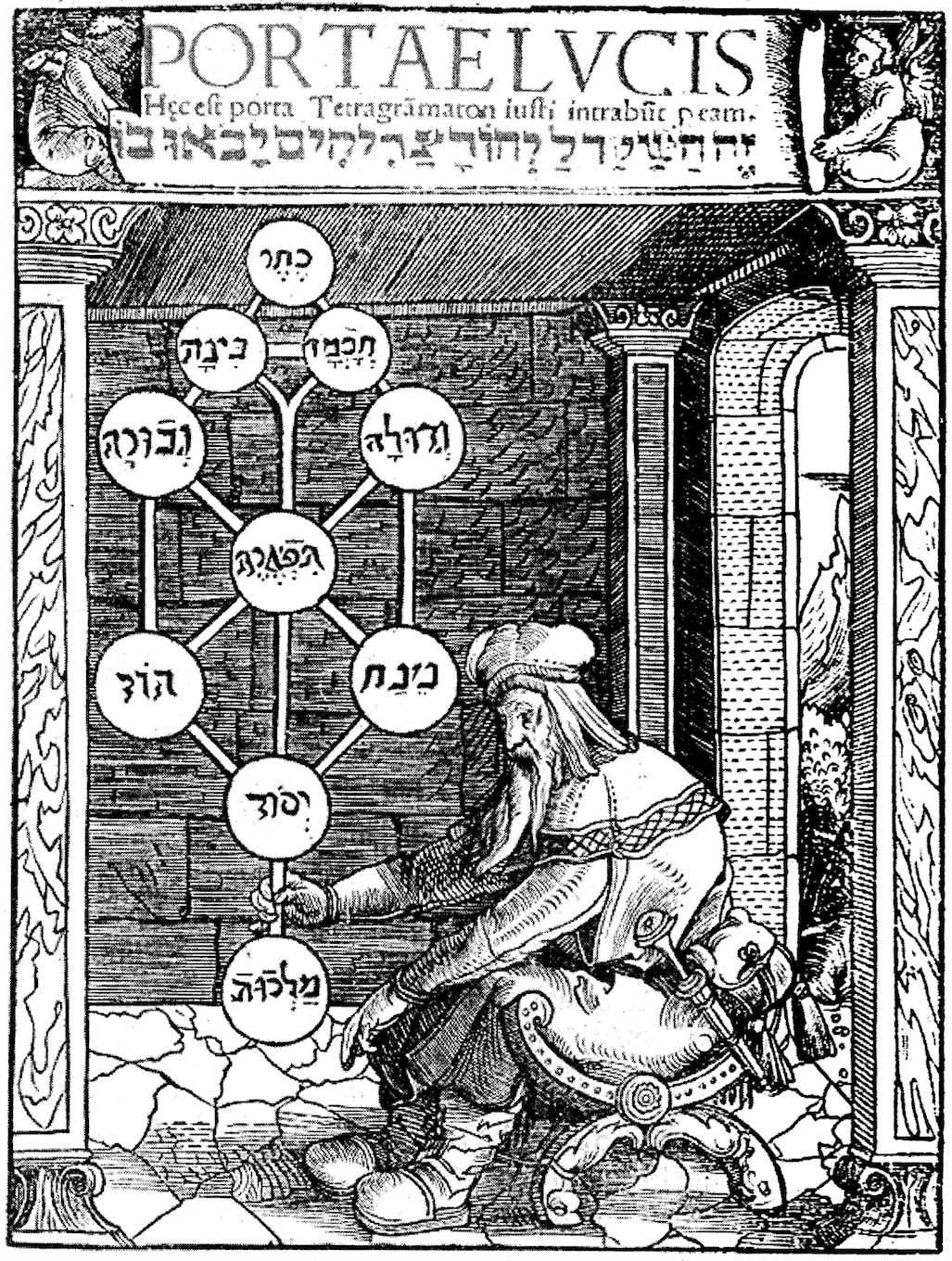
Yesod (Kabbalah)
Yesod (Hebrew: יְסוֹד ''Yəsōḏ'', Tiberian: ''Yăsōḏ'', "foundation") is a sephirah or node in the kabbalistic Tree of Life, a system of Jewish philosophy. Yesod, located near the base of the Tree, is the sephirah below Hod and Netzach, and above Malkuth (the kingdom). It is seen as a vehicle allowing movement from one thing or condition to another (the power of connection). Yesod, Kabbalah, and the Tree of Life are Jewish concepts adopted by various philosophical systems including Christianity, New Age Eastern-based mysticism, and Western esoteric practices. Jewish Kabbalah According to Jewish Kabbalah, Yesod is the foundation upon which God has built the world. It also serves as a transmitter between the sephirot above, and the reality below. The light of the upper sephirot gather in Yesod and are channelled to Malkuth below. In this manner, Yesod is associated with the sexual organs. The masculine Yesod collects the vital forces of the sephirot above, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in folklore, mythology, religion, occultism, and literature; these beliefs are reflected in Media (communication), media including fiction, comics, film, television series, television, and video games. Belief in demons probably goes back to the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age, stemming from humanity's fear of the unknown, the strange and the horrific.. In Religions of the ancient Near East, ancient Near Eastern religions and in the Abrahamic religions, including History of Judaism, early Judaism and ancient-medieval Christian demonology, a demon is considered a harmful spiritual entity that may cause Spirit possession, demonic possession, calling for an exorcism. Large portions of Jewish demonology, a key influence on Christianity and Islam, originated from a later form of Zoroastrianism, and was transferred to Judaism during the Achaemenid Empire, Persian era. Demons may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Kabbalah
Christian Kabbalah arose during the Renaissance due to Christian scholars' interest in the mysticism of Kabbalah, Jewish Kabbalah, which they interpreted according to Christian theology. Often spelled Cabala to distinguish it from the Jewish form and from Hermetic Qabalah, it sought to link Kabbalistic concepts with Christian doctrines, particularly the Trinity. Early proponents included Giovanni Pico della Mirandola and Johann Reuchlin, who adapted Kabbalistic ideas to Christian beliefs, sometimes using them as a tool for conversion. The movement drew from earlier Christian interest in Jewish mysticism, including the work of Spanish ''conversos'' and scholars like Ramon Llull, though it gained prominence in the 15th and 16th centuries. Christian Kabbalists proposed interpretations that linked Jesus and Mary to the Sefirot and saw hidden Christian messages in Kabbalistic texts. Figures such as Athanasius Kircher and Christian Knorr von Rosenroth further expanded these ideas, infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Symbols
The Hebrew word for 'symbol' is , which, in early Judaism, denoted not only a sign, but also a visible religious token of the relation between God and human. __TOC__ Common iconography Shabbat Shabbat, the day of rest, is described in the Tanakh as God's sign ("ot") between Him and the Jewish people. The priests The Torah provides detailed instructions () for the garments worn by the priests in the Temple. These details became the subject of later symbolic interpretations. According to Philo: The priest's upper garment symbolized the ether, the blossoms represented the earth, the pomegranates typified running water, and the bells denoted the music of the water. The ephod corresponded to heaven, and the stones on both shoulders to the two hemispheres, one above and the other below the earth. The six names on each of the stones were the six signs of the zodiac, which were denoted also by the twelve names on the breastplate. The miter was the sign of the crown, which exalted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalistic Words And Phrases
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefirot
Sefirot (; , plural of ), meaning '' emanations'', are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah, through which Ein Sof ("infinite space") reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the seder hishtalshelut (the chained descent of the metaphysical Four Worlds). The term is alternatively transliterated into English as ''sephirot/sephiroth'', singular ''sefira/sephirah''. As revelations of the creator's will (, ''rāṣon''), the sefirot should not be understood as ten gods, but rather as ten different channels through which the one God reveals His will. In later Jewish literature, the ten sefirot refer either to the ten manifestations of God; the ten powers or faculties of the soul; or the ten structural forces of nature. Alternative configurations of the sefirot are interpreted by various schools in the historical evolution of Kabbalah, with each articulating differing spiritual aspects. The tradition of enumerating 10 is stated in the ''Sefer Yetzirah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya (illusion)
''Maya'' (; Devanagari: , IAST: ), literally "illusion" or "magic", has multiple meanings in Indian philosophy, Indian philosophies depending on the context. In later Vedic Sanskrit, Vedic texts, connotes a "magic show, an illusion where things appear to be present but are not what they seem"; the principle which shows "attributeless Absolute" as having "attributes". also connotes that which "is constantly changing and thus is spiritually unreal" (in opposition to an unchanging absolute (philosophy), Absolute, or Brahman), and therefore "conceals the true character of spiritual reality".Lynn Foulston and Stuart Abbott (2009), ''Hindu Goddesses: Beliefs and Practices'', Sussex Academic Press, , pp. 14-16. In the Advaita Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy, , "appearance", is "the powerful force that creates the cosmic illusion that the phenomenon (philosophy), phenomenal world is real". In this nondualist school, at the individual level appears as the lack of knowledge () of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dion Fortune
Dion Fortune (born Violet Mary Firth, 6 December 1890 – 6 or 8 January 1946) was a British occultist, ceremonial magician, and writer. She was a co-founder of the Fraternity of the Inner Light, an occult organisation that promoted philosophies which she claimed had been taught to her by spiritual entities known as the Ascended master, Ascended Masters. A prolific writer, she produced a large number of articles and books on her occult ideas and also authored seven novels, several of which expound occult themes. Fortune was born in Llandudno, Caernarfonshire, North Wales, to a wealthy upper middle-class English family, although little is known of her early life. By her teenage years she was living in England's West Country, where she wrote two books of poetry. After time spent at a horticultural college she began studying psychology and psychoanalysis at the University of London before working as a counsellor in a psychotherapy clinic. During the First World War she joined t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Esotericism
Western esotericism, also known as the Western mystery tradition, is a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas and currents are united since they are largely distinct both from orthodox Judeo-Christian, Judeo-Christian religion and Age of Enlightenment rationalism. It has influenced, or contributed to, various forms of Western philosophy, mysticism, Western religions, religion, science, pseudoscience, Western art history, art, Western literature, literature, and Western culture#Music, music. The idea of grouping a wide range of Western traditions and philosophies together under the term ''esotericism'' developed in 17th-century Europe. Various academics have debated numerous definitions of Western esotericism. One view adopts a definition from certain esotericist schools of thought themselves, treating "esotericism" as a perennial philosophy, perennial hidden inner tradition. A second perspective sees esotericism as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qlippoth
In the ''Zohar'', Lurianic Kabbalah, and Hermetic Qabalah, the ''qlippoth'' (, originally , plural of ''qəlippā''; literally "peels", "shells", or "husks"), are the representation of evil or impure spiritual forces in Jewish mysticism, the opposites of the sefirot. The realm of evil is called ''Sitra Achra'' () in Kabbalistic texts. In the Zohar The qlippoth are first mentioned in the ''Zohar'', where they are described as being created by God to function as a nutshell for holiness. The text subsequently relays an esoteric interpretation of the text of Genesis creation narrative in Genesis 1:14, which describes God creating the moon and sun to act as "luminaries" in the sky. The verse "Let there be luminaries ( ''məʾoroṯ'')," uses a defective spelling of the Hebrew plural form for "luminous body, light source" (), resulting in a written form identical to the Hebrew word for "curses." In the context of the ''Zohar'', interpreting the verse as calling the moon and sun " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Christian traditions – including Eastern Orthodoxy, Catholicism, Lutheranism, and Anglicanism – revere Gabriel as a saint. In the Hebrew Bible, Gabriel appears to the prophet Daniel (biblical figure), Daniel to explain his visions (Daniel 8:15–26, Daniel 9, 9:21–27). The archangel also appears in the Book of Enoch and other ancient Jewish writings not preserved in Hebrew. Alongside the archangel Michael (archangel), Michael, Gabriel is described as the guardian angel of the Israelites, people of History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel, defending it against the angels of the other peoples. In the New Testament, the Gospel of Luke relates the Annunciation, in which the angel Gabriel appears to Zechariah (New Testament figur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |