|
Yasodaman II
Yasodhaman II (317–332) was a son and probably sub-king of king Rudrasimha II of the Western Satraps. He declared on his coins to be the son of Rudrasimha II. Yasodaman was succeeded by another of Rudrasimha II's sons Rudradaman II (332–348). During his rule, a Saka ruler inscribed the Kanakerha inscription,Marshall, The Monuments of Sanchp.392/ref> on the hill of Sanchi mentioning the construction of a well by the Saka chief and "righteous conqueror" (''dharmaviyagi mahadandanayaka'') Sridharavarman (339-368 CE).Buddhist Landscapes in Central India: Sanchi Hill and Archaeologies of Religious and Social Change, c. Third Century BC to Fifth Century AD, Julia Shaw, Routledge, 201p58-59/ref> Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman with his military commander is known from Eran. These inscription point to the extent of Saka rule as the time of Rudrasimha II and Yasodhaman II. References {{Western Satraps Western Satraps 4th-century monarchs in Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Satrap
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra (region), Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering modern-day Sindh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states), between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushan Empire, Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the "Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE. The power of the Western Satraps started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty. After this, the Saka kingdom re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudrasimha II
Rudrasimha II (304–348) was a ruler of the Western Satraps He declared on his coins to be the son of a Lord (Svami) named Jivadaman. His coinage is coeval with that of other rulers, who may have been sub-kings and were his sons: Yasodaman II (317–332) and Rudradaman II (332–348). During his rule, a Saka ruler inscribed the Kanakerha inscription,Marshall, The Monuments of Sanchp.392/ref> on the hill of Sanchi mentioning the construction of a well by the Saka chief and "righteous conqueror" (''dharmaviyagi mahadandanayaka'') Sridharavarman (339-368 CE).Buddhist Landscapes in Central India: Sanchi Hill and Archaeologies of Religious and Social Change, c. Third Century BC to Fifth Century AD, Julia Shaw, Routledge, 201p58-59/ref> Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman with his military commander is known from Eran. These inscription point to the extent of Saka rule as the time of Rudrasimha II. Coins of Rudrasimha were found inside the Buddhist stupa of Devnimori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudradaman II
Rudradāman I (r. 130–150) was a Śaka ruler from the Western Kshatrapas dynasty. He was the grandson of the king Caṣṭana. Rudradāman I was instrumental in the decline of the Sātavāhana Empire. Rudradāman I took up the title of ''Maha-kshtrapa'' ("Great Satrap"), after he became the king and then strengthened his kingdom. Reign As a result of his victories, Rudradāman regained all the former territories previously held by Nahapana, except for the southern territory of Poona and Nasik. The indigenous Nagas also were aggressive toward Śaka kshatrapas. Sātavāhana dominions were limited to their original base in the Deccan and eastern central India around Amaravati: War with the Yaudheyas Rudradāman conquered the Yaudheya tribes in present day Haryana, as described in the Girnar rock inscription of Rudradaman. Rudradaman refers to the Yaudheyas as a militant republic of kshatriyas that confronted him as opposed to submitting: However, the Yaudheyas soon rees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
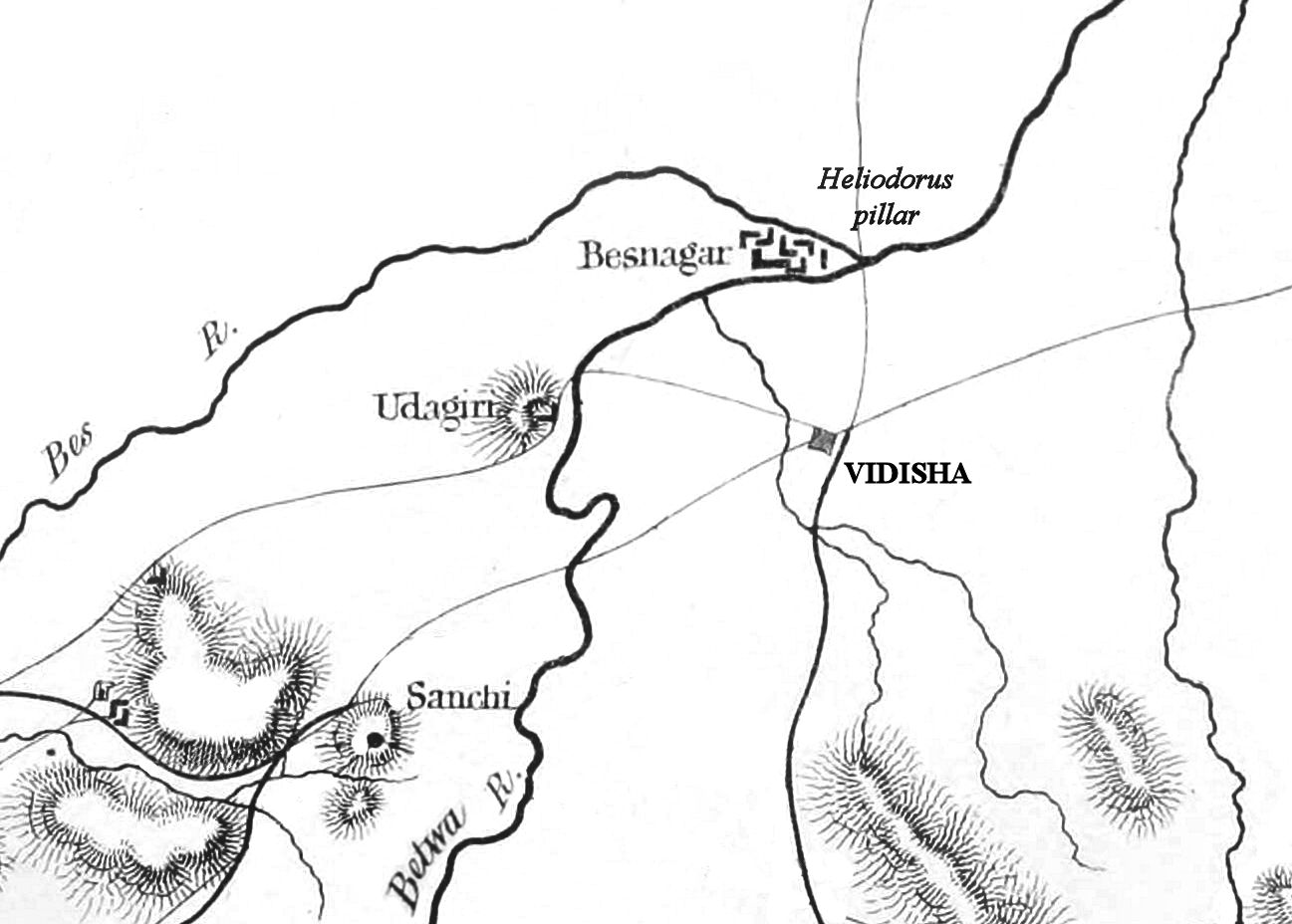
Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar and Bhaddilpur in ancient times) is a city in Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of Vidisha district. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Towards the seventh or eighth century, Bhadravati was ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanchi
Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist art, Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the States and territories of India, State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen, Raisen town, district headquarter and north-east of Bhopal, capital of Madhya Pradesh. The Great Stupa at Sanchi is one of the oldest stone structures in India, and an important monument to the historical architecture of India. It was originally commissioned by the Maurya Empire, Mauryan emperor Ashoka the Great, Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE. Its nucleus was a simple hemispherical brick structure built over the relics of the Gautama Buddha, Buddha. It was crowned by the Chatra (umbrella), chatra, a parasol-like structure symbolising high rank, which was intended to honour and shelter the relics. The original construction work of this stupa was overseen by Ashoka, whose wife Devi was the daughter of a merchant of nearby Vidisha. Sanchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eran
Eran is an ancient town and archaeological site in the Sagar district of Madhya Pradesh, India. It was one of the ancient mints for Indian dynasties as evidenced by the diverse coins excavated here. The site has 5th and 6th-century Gupta era temples and monuments, particularly the colossal stone boar with sages and scholars depicted on the body of the sculpture. The inscription stones found at Eran are important to reconstructing the chronology of Gupta Empire history. Eran or Erakina was the capital of ''Erakina (Airikina) Pradesha'' or ''Airkina Vishaya'', an administrative division of the Gupta Empire. Etymology The ancient name of Eran (), ''Erakaina'', ''Erakanya'' or ''Erakina'' (as mentioned in the inscriptions); ''Airikina'' (, as mentioned in the inscription of Samudragupta) or ''Erikina'' (as mentioned in the inscription of Toramana) is derived from ''Eraka''. The word ''erakā'' probably refers to a tall grass commonly called the Elephant cattail, botanical name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudrasena II
Rudrasena II () was a ruler of the Pravarapura-Nandivardhana branch of the Vakataka dynasty. While his reign was short, he notably married Prabhavatigupta, the daughter of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta II. His early death led to Prabhavatigupta ruling as regent for an extended period of time as his sons Divakarasena, Damodarasena, and Pravarasena II were all minors. Rudrasena's brief reign was also notable for religious changes which were likely brought about by increased Gupta influence. Unlike his ancestors who were all devout Shaivites (worshippers of Shiva), Rudrasena became a devotee of Chakrapani or Vishnu Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( .... Rudrasena's change of faith was probably encouraged by his powerful father-in-law and his queen, who were both s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayinī is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain division. It is one of the Hindu pilgrimage centres of Sapta Puri famous for the ''Kumbh Mela'' (Simhastha) held there every 12 years. The ancient and world famous temple of Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga is located in the center of the city. The city has been one of the most prominent trade and political centres of the Indian Subcontinent from the time of the ancient Mahājanapadas until the British colonisation of India. An ancient city situated on the eastern bank of the Shipra River, Ujjain was the most prominent city on the Malwa plateau of central India for much of its history. It emerged as the political centre of central India around 600 BCE. It was the capital of the ancient Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharuch
Bharuch () is a city at the mouth of the river Narmada in Gujarat in western India. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District. The city of Bharuch and surroundings have been settled since times of antiquity. It was a ship building centre and sea port in the pre-compass coastal trading routes for trading with the Occident and the East, perhaps as far back as the days of earliest trade connections. The route made use of the regular and predictable monsoon winds or galleys. Many goods from the Far East and Far West (the famed Spices and Silk trade) were shipped there during the annual monsoon winds, making it a terminus for several key land-sea trade routes. Bharuch was known to the Greeks, the Parthian Empire, in the Roman Empire, the Chinese, and in other Western and Eastern centres of civilisation through the end of the European Middle Ages and other the middle ages of the world.Periplus of the Erythraean Sea [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering modern-day Sindh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states), between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the " Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE. The power of the Western Satraps started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty. After this, the Saka kingdom revived, but was ultimately defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanakerha Inscription
The Kanakerha inscription, also spelled Kanakherha inscription, is an inscription found on the side of the hill of Sanchi, dating to the 3rd or 4th century CE. The region of Sanchi-Vidisha was captured from the Satavahanas by the Western Satraps during the rule of Rudrasena II (255-278 CE), as shown by finds of his coinage in the area. The Western Satraps are then known to have remained in the area well into the 4th century, as shown by the Kanakherha inscription,Marshall, The Monuments of Sanchp. 392(Public Domain text) on the hill of Sanchi. The inscription mentions the construction of a well by the Saka (Gupta script: , ''Śaka'') chief and "righteous conqueror" (''dharmaviyagi mahadandanayaka'') Sridharavarman (Gupta script: , ''Sridharavarmmana'').Buddhist Landscapes in Central India: Sanchi Hill and Archaeologies of Religious and Social Change, c. Third Century BC to Fifth Century AD, Julia Shaw, Routledge, 201pp. 58–59/ref> Another inscription of the same Sridhavarman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |