|
Y And Z Holes
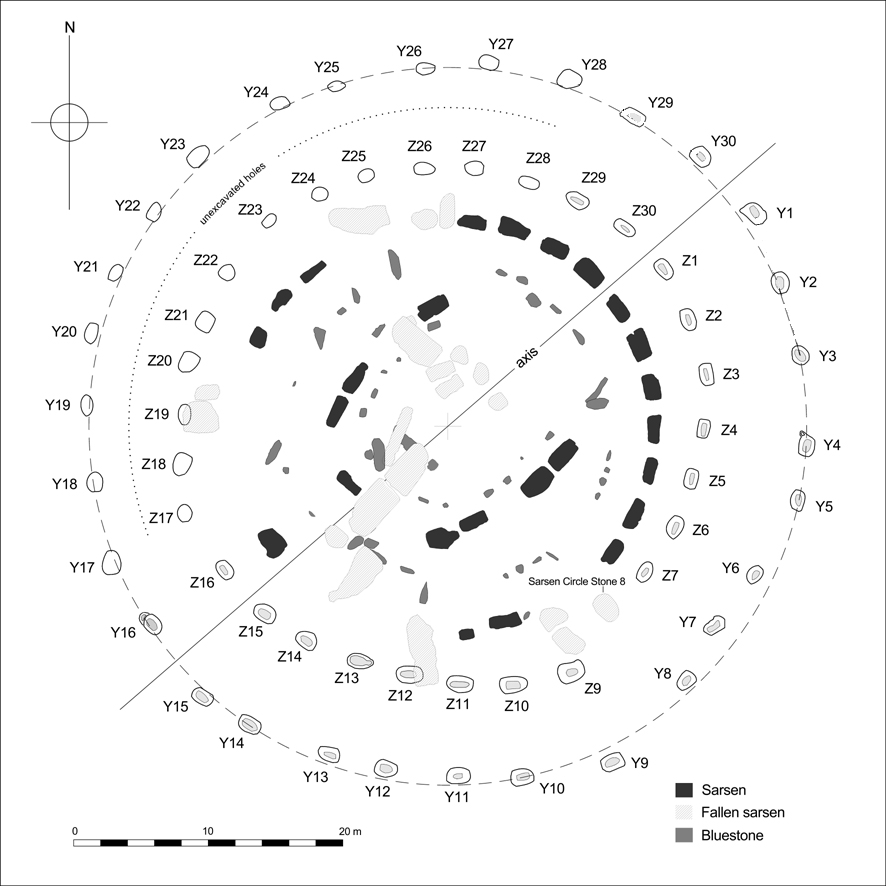
The Y and Z Holes are two rings of concentric (though irregular) circuits of 30 and 29 near-identical pits cut around the outside of the Sarsen Circle at Stonehenge. The current view is that both circuits are contemporary. Radiocarbon dating of antlers deliberately placed in hole Y 30 provided a date of around 1600 BCE, and a slightly earlier date was determined for material retrieved from Z 29. These dates make the Y and Z holes the last known structural activity at Stonehenge. The holes were discovered in 1923 by William Hawley, who, on removing the topsoil over a wide area, noted them as clearly visible patches of "humus" against the chalk substrate. Hawley named them Y and Z because for a short time he had earlier labelled the recently discovered Aubrey Holes as the X holes. 18 of the Y Holes have been excavated, and 16 of the Z Holes. Further evidence of the Y and Z Holes being late in the sequence of events at Stonehenge is demons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
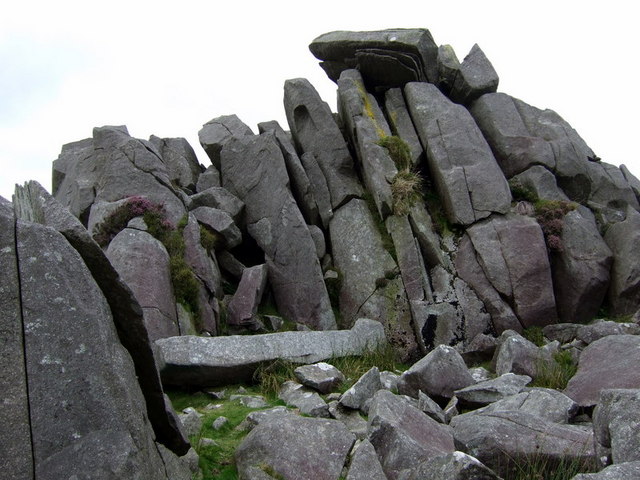
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric Megalith, megalithic structure on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting horizontal lintel stones, held in place with mortise and tenon joints, a feature unique among contemporary monuments. Inside is a ring of smaller bluestones. Inside these are free-standing trilithons, two bulkier vertical sarsens joined by one lintel. The whole monument, now ruinous, is aligned towards the sunrise on the summer solstice and sunset on the winter solstice. The stones are set within Earthwork (archaeology), earthworks in the middle of the densest complex of Neolithic British Isles, Neolithic and Bronze Age Britain, Bronze Age monuments in England, including several hundred ''tumuli'' (burial mounds). Stonehenge was constructed in several phases beginning about 3100 BC and continuing until about 1600 B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotopes of carbon, isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hawley
Lieutenant colonel William Hawley (1851–1941) was a British archaeologist who undertook pioneering excavations at Stonehenge. Military career Hawley joined the Royal Engineers and was a captain of the Portsmouth division of the Royal Engineers Militia from March 1893. In late March 1902, he was seconded for active service in South Africa for the later stages of the Second Boer War, and after the end of this war he was back with his regiment from October 1902. Old Sarum Along with William Henry St John Hope and Duncan Hector Montgomerie, Hawley participated in the first major excavations of the Old Sarum hillfort between 1909 and 1915. These digs were organized by the Society of Antiquaries of London. Stonehenge Work at the Stonehenge prehistoric monument was carried out between 1919 and 1926, largely by Hawley alone, at times assisted by Robert Newall, a draughtsman from the Office of Works. The weather and the confusing stratigraphy of this site made work difficult, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aubrey Holes
The Aubrey holes are a ring of 56 chalk pits at Stonehenge, named after seventeenth-century antiquarian John Aubrey. They date to the earliest phases of Stonehenge in the late fourth and early third millennium BC. Despite decades of argument and analysis, their purpose is still unknown, although an astronomical role has often been suggested. Whilst visiting the monument in 1666, Aubrey noticed five circular cavities in the ground and noted them in his records. These features were ignored or not seen by the later antiquarians to investigate the site, and it was not until the 1920s during the work carried out by Colonel William Hawley that Hawley's assistant Robert Newall identified a ring of pits he named in honour of Aubrey and his early survey. The depressions seen by Aubrey himself are more likely to have been different features from those that now bear his name. Mike Pitts in a 1981 article in ''Nature'' pointed out that the holes had been backfilled thousands of years bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of a second, where the second is defined by a hyperfine transition frequency of caesium. The metre was originally defined in 1791 by the French National Assembly as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a great circle, so the Earth's polar circumference is approximately . In 1799, the metre was redefined in terms of a prototype metre bar. The bar used was changed in 1889, and in 1960 the metre was redefined in terms of a certain number of wavelengths of a certain emission line of krypton-86. The current definition was adopted in 1983 and modified slightly in 2002 to clarify that the metre is a measure of proper length. From 1983 until 2019, the metre was formally defined as the length of the pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard J
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick (nickname), Dick", "Dickon", "Dickie (name), Dickie", "Rich (given name), Rich", "Rick (given name), Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", "Ricky (given name), Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English (the name was introduced into England by the Normans), German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Portuguese and Spanish "Ricardo" and the Italian "Riccardo" (see comprehensive variant list belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluestones
Bluestone is a cultural or commercial name for a number of natural dimension or building stone varieties, including: * basalt in Victoria, Australia, and in New Zealand * dolerites in Tasmania, Australia; and in Britain (including Stonehenge) * feldspathic sandstone in the US and Canada * limestone in the Shenandoah Valley in the US, from the Hainaut quarries in Soignies, Belgium, and from quarries in County Carlow, County Galway and County Kilkenny in Ireland * slate in South Australia It is unrelated to human-made blue brick. Stonehenge The term "bluestone" in Britain is used in a loose sense to cover all of the "foreign", not intrinsic, stones and rock debris at Stonehenge. It is a "convenience" label rather than a geological term, since at least 46 different rock types are represented. One of the most common rocks in the assemblage is known as Preseli spotted dolerite—a chemically altered igneous rock containing spots or clusters of secondary minerals replacing p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to History of writing, develop writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumulus
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built for various purposes, may also originally have been a tumulus. Tumuli are often categorised according to their external apparent shape. In this respect, a long barrow is a long tumulus, usually constructed on top of several burials, such as passage graves. A round barrow is a round tumulus, also commonly constructed on top of burials. The internal structure and architecture of both long and round barrows have a broad range; the categorization only refers to the external apparent shape. The method of may involve a dolmen, a cist, a mortuary enclosure, a mortuary house, or a chamber tomb. Examples of barrows include Duggleby Howe and Maeshowe. Etymology The word ''tumulus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |