|
Xylonycteris
''Xylonycteris'' is an extinct genus of archaeonycterid bat that lived during the Eocene epoch. Distribution ''X. stenodon'' fossils are known from the Paris Basin and date back to the Early Eocene In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by th .... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q132731437 Monotypic prehistoric mammal genera Prehistoric bat genera Eocene mammals of Europe Fossil taxa described in 2018 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeonycteridae
Archaeonycteridae (formerly spelled Archaeonycterididae) is a family of extinct bats. It was originally erected by the Swiss naturalist Pierre Revilliod as Archaeonycterididae to hold the genus ''Archaeonycteris''. It was formerly classified under the superfamily Icaronycteroidea (disused) by Kurten and Anderson in 1980. In 2007, the spelling was corrected to Archaeonycteridae and it was reclassified to the unranked clade Microchiropteramorpha by Smith ''et al.''. The family Palaeochiropterygidae was also merged into Archaeonycteridae by Kurten and Anderson, but modern authorities specializing in bat fossils maintain the distinction between the two. They existed from the Ypresian to the Lutetian ages of the Middle Eocene epoch (55.8 to 40.4 million years ago). The family is known to closely resemble modern bat species from the well preserved specimens found in the Messel Pit Fossil Site in Germany. Other discoveries were made in Europe and other areas of the Northern Hemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds ( taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the abs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
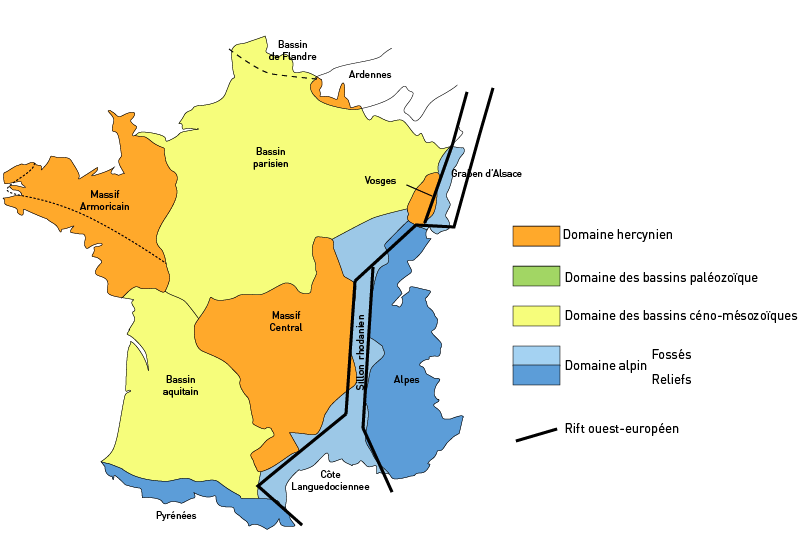
Paris Basin
The Paris Basin is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny (Hercynian orogeny). The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in the craton, bordered by the Armorican Massif to the west, the Ardennes-Brabant axis to the north, the Massif des Vosges to the east, and the Massif Central to the south.Duval, B.C., 1992, Villeperdue Field, In Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade, 1978-1988, AAPG Memoir 54, Halbouty, M.T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Extent The region usually regarded as the Paris Basin is rather smaller than the area formed by the geological structure. The former occupies the centre of the northern half of the country, excluding Eastern France. The latter extends from the hills just south of Calais to Poitiers and from Caen to the brink of the middle Rhine Valley, east of Saarbrücken. Geography The landscape is one of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age or lowest stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the lower Eocene. Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. Stratigraphic definition The Ypresian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1850. The Ypresian is named after the Flemish city of Ypres in Belgium (spelled ''Ieper'' in Dutch). The definitions of the original stage were totally different from the modern ones. The Ypresian shares its name with the Belgian Ieper Group (French: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Biology
''Historical Biology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of paleobiology. It was established in 1988, and is published by Taylor & Francis. The journal is edited by Gareth J. Dyke (National Oceanography Centre). Abstracting & Indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following databases. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.259. References External links * Biology journals Taylor & Francis academic journals Publications established in 1988 Paleontology journals 8 times per year journals {{paleontology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Prehistoric Mammal Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, ''Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Bat Genera
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Mammals Of Europe
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)