
A fossil (from
Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a Literary language, literary standard language, standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It formed parallel to Vulgar Latin around 75 BC out of Old Latin ...
, ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past
geological age. Examples include
bones,
shells,
exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
s, stone imprints of animals or
microbes, objects preserved in
amber,
hair,
petrified wood
Petrified wood (from Ancient Greek meaning 'rock' or 'stone'; literally 'wood turned into stone'), is the name given to a special type of ''fossilized wood'', the fossilized remains of terrestrial plant, terrestrial vegetation. ''Petrifaction ...
and
DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth.
In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''
Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
.
includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and
evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years
to 4.1 billion years old.
[ Early edition, published online before print.] The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock
strata led to the recognition of a
geological timescale and the
relative ages of different fossils. The development of
radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the
absolute ages of rocks and the fossils they host.
There are many processes that lead to
fossilization, including
permineralization, casts and molds,
authigenic mineralization, replacement and recrystallization, adpression,
carbonization, and bioimmuration.
Fossils vary in size from one-
micrometre (1 μm) bacteria to
dinosaurs and trees, many meters long and weighing many tons. The largest presently known is a ''
Sequoia'' sp. measuring in length at Coaldale, Nevada. A fossil normally preserves only a portion of the deceased organism, usually that portion that was partially
mineralized during life, such as the bones and teeth of
vertebrates, or the
chitinous or
calcareous exoskeletons of
invertebrates. Fossils may also consist of the marks left behind by the organism while it was alive, such as
animal tracks or
feces (
coprolites). These types of fossil are called
trace fossils or ''ichnofossils'', as opposed to ''body fossils''. Some fossils are
biochemical and are called ''chemofossils'' or
biosignatures.
History of study
Gathering fossils dates at least to the beginning of recorded history. The fossils themselves are referred to as the fossil record. The fossil record was one of the early sources of data underlying the study of
evolution and continues to be relevant to the
history of life on Earth.
Paleontologists examine the fossil record to understand the process of evolution and the way particular
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
have evolved.
Ancient civilizations
Fossils have been visible and common throughout most of natural history, and so documented human interaction with them goes back as far as recorded history, or earlier.
There are many examples of
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
stone knives in Europe, with fossil
echinoderms set precisely at the hand grip, dating back to ''
Homo heidelbergensis'' and
Neanderthals.
These ancient peoples also drilled holes through the center of those round fossil shells, apparently using them as beads for necklaces.
The ancient Egyptians gathered fossils of species that resembled the bones of modern species they worshipped. The god
Set was associated with the
hippopotamus, therefore fossilized bones of hippo-like species were kept in that deity's temples. Five-rayed fossil sea urchin shells were associated with the deity
Sopdu, the Morning Star, equivalent of
Venus in Roman mythology.
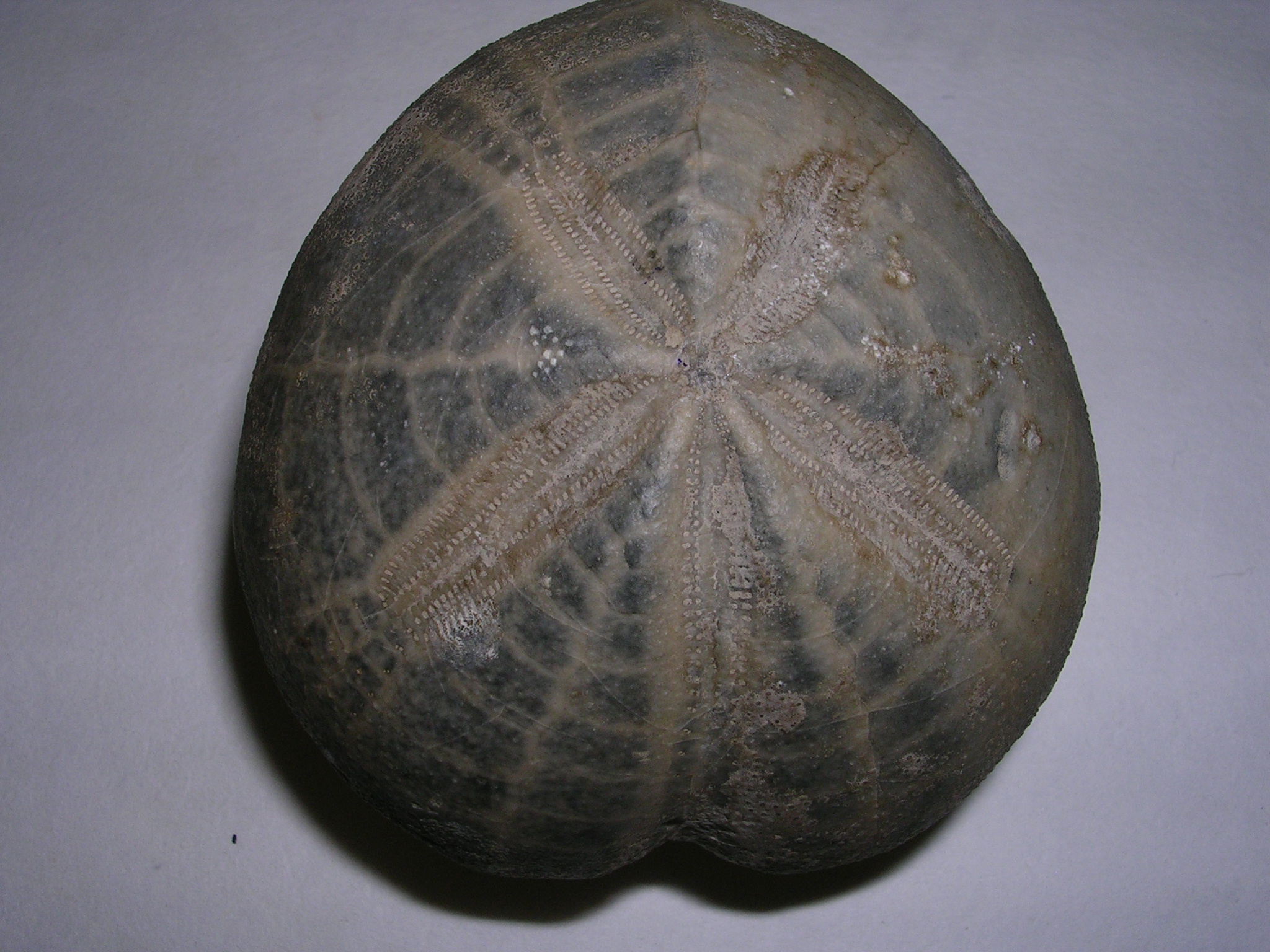

Fossils appear to have directly contributed to the mythology of many civilizations, including the ancient Greeks. Classical Greek historian
Herodotos wrote of an area near
Hyperborea where
gryphons protected golden treasure. There was indeed gold mining
in that approximate region, where beaked ''
Protoceratops'' skulls were common as fossils.
A later
Greek scholar,
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, eventually realized that fossil seashells from rocks were similar to those found on the beach, indicating the fossils were once living animals. He had previously explained them in terms of
vaporous
exhalations, which
Persian polymath
Avicenna modified into the theory of
petrifying fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are M ...
s (). Recognition of fossil seashells as originating in the sea was built upon in the 14th century by
Albert of Saxony, and accepted in some form by most
naturalists by the 16th century.
Roman naturalist
Pliny the Elder wrote of "
tongue stones", which he called
glossopetra. These were fossil shark teeth, thought by some classical cultures to look like the tongues of people or snakes.
He also wrote about the
horns of Ammon, which are fossil
ammonites, whence the group of shelled octopus-cousins ultimately draws its modern name. Pliny also makes one of the earlier known references to
toadstones, thought until the 18th century to be a magical cure for poison originating in the heads of toads, but which are fossil teeth from ''
Lepidotes'', a
Cretaceous ray-finned fish.
The
Plains tribes of North America are thought to have similarly associated fossils, such as the many intact pterosaur fossils naturally exposed in the region, with their own mythology of the
thunderbird.
There is no such direct mythological connection known from prehistoric Africa, but there is considerable evidence of tribes there excavating and moving fossils to ceremonial sites, apparently treating them with some reverence.
In Japan, fossil shark teeth were associated with the mythical
tengu, thought to be the razor-sharp claws of the creature, documented some time after the 8th century AD.
In medieval China, the fossil bones of ancient mammals including ''
Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' were often mistaken for "
dragon bones" and used as medicine and
aphrodisiacs. In addition, some of these fossil bones are collected as "art" by scholars, who left scripts on various artifacts, indicating the time they were added to a collection. One good example is the famous scholar
Huang Tingjian of the
Song dynasty during the 11th century, who kept a specific seashell fossil with his own poem engraved on it. In his ''
Dream Pool Essays'' published in 1088, Song dynasty Chinese
scholar-official Shen Kuo hypothesized that marine fossils found in a
geological stratum of mountains located hundreds of miles from the
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
was evidence that a prehistoric seashore had once existed there and
shifted over centuries of time.
[Needham, Joseph. (1959). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 3, Mathematics and the Sciences of the Heavens and the Earth''. Cambridge University Press. pp. 603–618.] His observation of
petrified bamboos in the dry northern climate zone of what is now
Yan'an,
Shaanxi province, China, led him to advance early ideas of gradual
climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
due to bamboo naturally growing in wetter climate areas.
[Rafferty, John P. (2012). ''Geological Sciences; Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing, p. 6. ]
In medieval
Christendom, fossilized sea creatures on mountainsides were seen as proof of the biblical deluge of
Noah's Ark. After observing the existence of seashells in mountains, the
ancient Greek philosopher Xenophanes (c. 570 – 478 BC) speculated that the world was once inundated in a great flood that buried living creatures in drying mud.
[Rafferty, John P. (2012). ''Geological Sciences; Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing, pp. 5–6. .]
In 1027, the
Persian Avicenna explained fossils' stoniness in ''
The Book of Healing'':
From the 13th century to the present day, scholars pointed out that the fossil skulls of
Deinotherium giganteum, found in
Crete and Greece, might have been interpreted as being the skulls of the
Cyclopes of
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, and are possibly the origin of that Greek myth. Their skulls appear to have a single eye-hole in the front, just like their modern
elephant cousins, though in fact it's actually the opening for their trunk.
In
Norse mythology, echinoderm shells (the round five-part button left over from a sea urchin) were associated with the god
Thor, not only being incorporated in
thunderstones, representations of Thor's hammer and subsequent hammer-shaped crosses as Christianity was adopted, but also kept in houses to garner Thor's protection.
These grew into the
shepherd's crowns of English folklore, used for decoration and as good luck charms, placed by the doorway of homes and churches.
In
Suffolk, a different species was used as a good-luck charm by bakers, who referred to them as
fairy loaves, associating them with the similarly shaped loaves of bread they baked.
Early modern explanations
More scientific views of fossils emerged during the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
.
Leonardo da Vinci concurred with Aristotle's view that fossils were the remains of ancient life. For example, Leonardo noticed discrepancies with the biblical flood narrative as an explanation for fossil origins:
In 1666,
Nicholas Steno examined a shark, and made the association of its teeth with the "tongue stones" of ancient Greco-Roman mythology, concluding that those were not in fact the tongues of venomous snakes, but the teeth of some long-extinct species of shark.
(1635–1703) included
micrographs of fossils in his ''
Micrographia'' and was among the first to observe fossil
forams. His observations on fossils, which he stated to be the petrified remains of creatures some of which no longer existed, were published posthumously in 1705.
William Smith (1769–1839), an English canal engineer, observed that rocks of different ages (based on the
law of superposition) preserved different assemblages of fossils, and that these assemblages succeeded one another in a regular and determinable order. He observed that rocks from distant locations could be correlated based on the fossils they contained. He termed this the principle of ''faunal succession''. This principle became one of Darwin's chief pieces of evidence that biological evolution was real.
Georges Cuvier came to believe that most if not all the animal fossils he examined were remains of extinct species. This led Cuvier to become an active proponent of the geological school of thought called
catastrophism. Near the end of his 1796 paper on living and fossil elephants he said:
Interest in fossils, and geology more generally, expanded during the early nineteenth century. In Britain,
Mary Anning's discoveries of fossils, including the first complete
ichthyosaur and a complete
plesiosaurus skeleton, sparked both public and scholarly interest.
Linnaeus and Darwin
Early
naturalists well understood the similarities and differences of living species leading
Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
to develop a hierarchical classification system still in use today. Darwin and his contemporaries first linked the hierarchical structure of the tree of life with the then very sparse fossil record. Darwin eloquently described a process of descent with modification, or evolution, whereby organisms either adapt to natural and changing environmental pressures, or they perish.
When Darwin wrote ''
On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'', the oldest animal fossils were those from the
Cambrian Period, now known to be about 540 million years old. He worried about the absence of older fossils because of the implications on the validity of his theories, but he expressed hope that such fossils would be found, noting that: "only a small portion of the world is known with accuracy." Darwin also pondered the sudden appearance of many groups (i.e.
phyla) in the oldest known Cambrian fossiliferous strata.
After Darwin
Since Darwin's time, the fossil record has been extended to between 2.3 and 3.5 billion years. Most of these Precambrian fossils are microscopic bacteria or
microfossils. However, macroscopic fossils are now known from the late Proterozoic. The
Ediacara biota (also called Vendian biota) dating from 575 million years ago collectively constitutes a richly diverse assembly of early multicellular
eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s.
The fossil record and faunal succession form the basis of the science of
biostratigraphy or determining the age of rocks based on embedded fossils. For the first 150 years of
geology, biostratigraphy and superposition were the only means for determining the
relative age of rocks. The
geologic time scale was developed based on the relative ages of rock strata as determined by the early paleontologists and
stratigraphers.
Since the early years of the twentieth century,
absolute dating methods, such as
radiometric dating (including
potassium/argon,
argon/argon,
uranium series, and, for very recent fossils,
radiocarbon dating) have been used to verify the relative ages obtained by fossils and to provide absolute ages for many fossils. Radiometric dating has shown that the earliest known stromatolites are over 3.4 billion years old.
Modern era
Paleontology has joined with
evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biolo ...
to share the interdisciplinary task of outlining the tree of life, which inevitably leads backwards in time to Precambrian microscopic life when cell structure and functions evolved. Earth's deep time in the Proterozoic and deeper still in the Archean is only "recounted by microscopic fossils and subtle chemical signals." Molecular biologists, using
phylogenetics, can compare protein
amino acid or
nucleotide sequence homology (i.e., similarity) to evaluate taxonomy and evolutionary distances among organisms, with limited statistical confidence. The study of fossils, on the other hand, can more specifically pinpoint when and in what organism a mutation first appeared. Phylogenetics and paleontology work together in the clarification of science's still dim view of the appearance of life and its evolution.
 Niles Eldredge
Niles Eldredge's study of the ''
Phacops''
trilobite genus supported the hypothesis that modifications to the arrangement of the trilobite's eye lenses proceeded by fits and starts over millions of years during the
Devonian. Eldredge's interpretation of the ''Phacops'' fossil record was that the aftermaths of the lens changes, but not the rapidly occurring evolutionary process, were fossilized. This and other data led
Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge to publish their seminal paper on
punctuated equilibrium in 1971.
Synchrotron X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
tomographic analysis of early Cambrian bilaterian
embryonic microfossils yielded new insights of
metazoan evolution at its earliest stages. The tomography technique provides previously unattainable three-dimensional resolution at the limits of fossilization. Fossils of two enigmatic bilaterians, the worm-like ''
Markuelia'' and a putative, primitive
protostome, ''
Pseudooides'', provide a peek at
germ layer embryonic development. These 543-million-year-old embryos support the emergence of some aspects of
arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
development earlier than previously thought in the late Proterozoic. The preserved embryos from
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and
Siberia underwent rapid
diagenetic phosphatization resulting in exquisite preservation, including cell structures. This research is a notable example of how knowledge encoded by the fossil record continues to contribute otherwise unattainable information on the emergence and development of life on Earth. For example, the research suggests ''Markuelia'' has closest affinity to priapulid worms, and is adjacent to the evolutionary branching of
Priapulida,
Nematoda and
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
a.
Despite significant advances in uncovering and identifying paleontological specimens, it is generally accepted that the fossil record is vastly incomplete.
Approaches for measuring the completeness of the fossil record have been developed for numerous subsets of species, including those grouped taxonomically,
temporally,
environmentally/geographically,
or in sum.
This encompasses the subfield of
taphonomy and the study of biases in the paleontological record.
Dating/Age
Stratigraphy and estimations
Paleontology seeks to map out how life evolved across geologic time. A substantial hurdle is the difficulty of working out fossil ages. Beds that preserve fossils typically lack the radioactive elements needed for
radiometric dating. This technique is our only means of giving rocks greater than about 50 million years old an absolute age, and can be accurate to within 0.5% or better.
Although radiometric dating requires careful laboratory work, its basic principle is simple: the rates at which various radioactive elements
decay are known, and so the ratio of the radioactive element to its decay products shows how long ago the radioactive element was incorporated into the rock. Radioactive elements are common only in rocks with a volcanic origin, and so the only fossil-bearing rocks that can be dated radiometrically are volcanic ash layers, which may provide termini for the intervening sediments.
Consequently, palaeontologists rely on
stratigraphy to date fossils. Stratigraphy is the science of deciphering the "layer-cake" that is the
sedimentary record. Rocks normally form relatively horizontal layers, with each layer younger than the one underneath it. If a fossil is found between two layers whose ages are known, the fossil's age is claimed to lie between the two known ages. Because rock sequences are not continuous, but may be broken up by
faults or periods of
erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
, it is very difficult to match up rock beds that are not directly adjacent. However, fossils of species that survived for a relatively short time can be used to match isolated rocks: this technique is called ''biostratigraphy''. For instance, the conodont ''Eoplacognathus pseudoplanus'' has a short range in the Middle Ordovician period. If rocks of unknown age have traces of ''E. pseudoplanus'', they have a mid-Ordovician age. Such
index fossils must be distinctive, be globally distributed and occupy a short time range to be useful. Misleading results are produced if the index fossils are incorrectly dated.
Stratigraphy and biostratigraphy can in general provide only relative dating (''A'' was before ''B''), which is often sufficient for studying evolution. However, this is difficult for some time periods, because of the problems involved in matching rocks of the same age across
continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
s.
Family-tree relationships also help to narrow down the date when lineages first appeared. For instance, if fossils of B or C date to X million years ago and the calculated "family tree" says A was an ancestor of B and C, then A must have evolved earlier.
It is also possible to estimate how long ago two living clades diverged (i.e., the age of their
last common ancestor) by assuming that
mutations accumulate at a constant rate for a given gene. These "
molecular clocks", however, are fallible, and provide only approximate timing: for example, they are not sufficiently precise and reliable for estimating when the groups that feature in the
Cambrian explosion first evolved, and estimates produced by different techniques may vary by a factor of two.
Limitations
Organisms are only rarely preserved as fossils in the best of circumstances, and only a fraction of such fossils have been discovered. This is illustrated by the fact that the number of species known through the fossil record is less than 5% of the number of known living species, suggesting that the number of species known through fossils must be far less than 1% of all the species that have ever lived.
Because of the specialized and rare circumstances required for a biological structure to fossilize, only a small percentage of life-forms can be expected to be represented in discoveries, and each discovery represents only a snapshot of the process of evolution. The transition itself can only be illustrated and corroborated by transitional fossils, which are never guaranteed to demonstrate a convenient half-way point.
The fossil record is strongly biased toward organisms with hard parts, leaving most groups of
soft-bodied organisms with little to no presence.
It is replete with
mollusks,
vertebrates,
echinoderms,
brachiopods, and some groups of
arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s.
Sites
Lagerstätten
Fossil sites with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues—are known as
Lagerstätten (German for "storage places"). These formations may have resulted from carcass burial in an
anoxic environment with minimal bacteria, thus slowing decomposition. Lagerstätten span geological time from the
Cambrian period to the
present. Worldwide, some of the best examples of near-perfect fossilization are the
Cambrian Maotianshan Shales and
Burgess Shale, the
Devonian Hunsrück Slates, the
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
Solnhofen Limestone, and the
Carboniferous Mazon Creek localities.
Fossilization processes
Recrystallization
A fossil is said to be ''recrystallized'' when the original skeletal compounds are still present but in a different crystal form, such as from
aragonite to
calcite.
File:Calcite-60801.jpg, Calcite-recrystallized fossil shell of '' Mercenaria permagna'' from Fort Drum, Florida
File:Geodized fossil Busycon snail with yellowish calcite crystals (Anastasia Formation, Upper Pleistocene to lower Holocene, 126 to 8 ka; Indrio Pit, northern side of the town of Fort Pierce, southeastern Florida, USA) (15227151971).jpg, Calcite-recrystallized fossil shell of '' Busycon'' sp. from Indrio Pit
File:MatmorScleractinian.JPG, Recrystallized scleractinian coral (aragonite to calcite) from the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
of southern Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
File:Geodized pentamerid brachiopods (Silurian; Swayzee, Indiana, USA) 1.jpg, Calcite-recrystallized fossil shell of pentamerid brachiopods from Indiana
File:GeopetalCarboniferousNV.jpg, Recrystallized bivalve shell with sparry calcite from Bird Spring Formation
Replacement

Replacement occurs when the shell, bone, or other tissue is replaced with another mineral. In some cases mineral replacement of the original shell occurs so gradually and at such fine scales that microstructural features are preserved despite the total loss of original material. Scientists can use such fossils when researching the anatomical structure of ancient species. Several species of saurids have been identified from mineralized dinosaur fossils.
Permineralization
Permineralization is a process of fossilization that occurs when an organism is buried. The empty spaces within an organism (spaces filled with liquid or gas during life) become filled with mineral-rich
groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
. Minerals precipitate from the groundwater, occupying the empty spaces. This process can occur in very small spaces, such as within the
cell wall of a
plant cell
Plant cells are the cells present in Viridiplantae, green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids ...
, and can produce very detailed fossils at small scales. For permineralization to occur, the organism must become covered by sediment soon after death, otherwise the remains are destroyed by scavengers or decomposition. The degree to which the remains are decayed when covered determines the later details of the fossil. Some fossils consist only of skeletal remains or teeth; other fossils contain traces of
skin,
feathers or even soft tissues. This is a form of
diagenesis.
Phosphatization
Phosphatization refers to a process of fossilization where organic matter is replaced by abundant
calcium-
phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s. The produced fossils tend to be particularly dense and have a dark coloration that ranges from dark orange to black.
Pyritization
This fossil preservation involves the elements
sulfur and
iron. Organisms may become pyritized when they are in marine sediments saturated with iron sulfides. As organic matter decays, it releases sulfide which reacts with dissolved iron in the surrounding waters, forming
pyrite. Pyrite replaces carbonate shell material due to an undersaturation of carbonate in the surrounding waters. Some plants become pyritized when they are in a clay terrain, but to a lesser extent than in a marine environment. Some pyritized fossils include
Precambrian microfossils, marine
arthropods, and plants.
File:Pleuroceras solare, Little Switzerland, Bavaria, Germany.jpg, Pyritized ammonoid '' Pleuroceras solare'' fossil specimen
File:Paraspirifer bownockeri.fond.jpg, Pyritized specimen of the brachiopod '' Paraspirifer bownockeri''
File:Triarthrus eatoni (pyritized fossil trilobite with appendages) (Whetstone Gulf Formation, Upper Ordovician; Lewis County, New York State, USA) 3.jpg, Pyritized '' Triarthrus eatoni'' from Whetstone Gulf Formation
File:Furcaster paleozoicus fossil brittle star (Kaub Formation, Hunsrück Slate Group, Lower Devonian; Budenbach area, western Germany) 4 (15302668235).jpg, Pyritized '' Furcaster paleozoicus'' from Hunsrück Slate
File:Tornoceras uniangulare aldenense fossil goniatite (Alden Pyrite Bed, Ludlowville Formation, Middle Devonian; western New York State, USA) 1 (15359943429).jpg, Pyritized '' Tornoceras uniangulare'' from Ludlowville Formation
Silicification
In
silicification, the precipitation of
silica from saturated water bodies is responsible for the fossil's formation and preservation. The mineral-laden water permeates the pores and cells of some dead organism, where it becomes a
gel. Over time, the gel will
dehydrate, forming a
silica-rich crystal structure, which can be expressed in the form of
quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The Atom, atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon–oxygen Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tet ...
,
chalcedony,
agate,
opal, among others, with the shape of the original remain.
File:2017-07-15 22-10-35 (C) DxO.jpg, Chalcedony replaced fossil shells of '' Elimia tenera'' with inclusions of ostracods
File:Chalcedonized fossil gastropods (Cretaceous; possibly from Dakhla, southern Morocco) (15230327942).jpg, Chalcedonized gastropods internal molds
File:Schnecken auflicht small.jpg, Agatized internal molds of gastropods from Deccan Traps
File:Agate Chalcedony GE9323 540424.jpg, Agatized fossil coral from Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
File:Opaleautralie.jpg, Fossil bivalves replaced by opal, from Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
File:Addyman 3.JPG, Rear view of an opalized Addyman Plesiosaur fossil at the South Australian Museum
Casts and molds
In some cases, the original remains of the organism completely dissolve or are otherwise destroyed. The remaining organism-shaped hole in the rock is called an ''external mold''. If this void is later filled with sediment, the resulting ''cast'' resembles what the organism looked like. An
endocast, or ''internal mold'', is the result of sediments filling an organism's interior, such as the inside of a
bivalve or
snail or the hollow of a
skull. Endocasts are sometimes termed , especially when bivalves are preserved this way.
File:Internal mold, Hormotoma, Mollusca, Gastropoda, Murchisonioidea - Iowa, USA.jpg, Internal mold (steinkern) of '' Hormotoma'' sp. from Galena Formation
File:Small-gasteropod-bariloche.jpg, Gastropod internal mold (steinkern) from Ventana Formation
File:Anomalodonta gigantea Waynesville Franklin Co IN.JPG, Shell external mold of '' Anomalodonta gigantea'' from Waynesville Formation
File:Glycymeris alpinus 01.jpg, Internal mold (steinkern) of '' Glycymeris alpinus'', Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
File:Aviculopecten subcardiformis01.JPG, External mold of '' Aviculopecten subcardiformis'' from the Logan Formation, Lower Carboniferous, Ohio
Authigenic mineralization
This is a special form of cast and mold formation. If the chemistry is right, the organism (or fragment of organism) can act as a nucleus for the precipitation of minerals such as
siderite, resulting in a nodule forming around it. If this happens rapidly before significant decay to the organic tissue, very fine three-dimensional morphological detail can be preserved. Nodules from the Carboniferous
Mazon Creek fossil beds of Illinois, US, are among the best documented examples of such mineralization.
Adpression (compression-impression)
Compression fossils, such as those of fossil ferns, are the result of chemical reduction of the complex organic molecules composing the organism's tissues. In this case, the fossil consists of original material, albeit in a geochemically altered state. This chemical change is an example of
diagenesis. What remains is often a
carbonaceous film known as a phytoleim, in which case the fossil is known as a compression. Often, however, the phytoleim is lost and all that remains is an impression of the organism in the rock—an impression fossil. In many cases, however, compressions and impressions occur together. For instance, when the rock is broken open, the phytoleim will often be attached to one part (compression), whereas the counterpart will just be an impression. For this reason, one term covers the two modes of preservation: ''adpression''.
Carbonization and coalification
Fossils that are carbonized or coalified consist of the organic remains which have been reduced primarily to the chemical element carbon. Carbonized fossils consist of a thin film which forms a silhouette of the original organism, and the original organic remains were typically soft tissues. Coalified fossils consist primarily of coal, and the original organic remains were typically woody in composition.
File:Probable leech from the Waukesha Biota.jpg, Carbonized fossil of a cycloneuralian worm that was once misidentified as a leech from the Silurian Waukesha Biota of Wisconsin.
File:Lycopod axis.jpg, Partially coalified axis (branch) of a lycopod from the Devonian of Wisconsin.
Soft tissue, cell and molecular preservation
Because of their antiquity, an unexpected exception to the alteration of an organism's tissues by chemical reduction of the complex organic molecules during fossilization has been the discovery of soft tissue in dinosaur fossils, including blood vessels, and the isolation of proteins and evidence for DNA fragments.
In 2014,
Mary Schweitzer and her colleagues reported the presence of iron particles (
goethite-aFeO(OH)) associated with soft tissues recovered from dinosaur fossils. Based on various experiments that studied the interaction of iron in
haemoglobin with blood vessel tissue they proposed that solution hypoxia coupled with iron
chelation enhances the stability and preservation of soft tissue and provides the basis for an explanation for the unforeseen preservation of fossil soft tissues.
However, a slightly older study based on eight
taxa ranging in time from the
Devonian to the
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
found that reasonably well-preserved fibrils that probably represent
collagen were preserved in all these fossils and that the quality of preservation depended mostly on the arrangement of the collagen fibers, with tight packing favoring good preservation.
There seemed to be no correlation between geological age and quality of preservation, within that timeframe.
Bioimmuration

Bioimmuration occurs when a skeletal organism overgrows or otherwise subsumes another organism, preserving the latter, or an impression of it, within the skeleton.
Usually it is a
sessile skeletal organism, such as a
bryozoan or an
oyster, which grows along a
substrate, covering other sessile
sclerobionts. Sometimes the bioimmured organism is soft-bodied and is then preserved in negative relief as a kind of external mold. There are also cases where an organism settles on top of a living skeletal organism that grows upwards, preserving the settler in its skeleton. Bioimmuration is known in the fossil record from the
Ordovician to the Recent.
Types
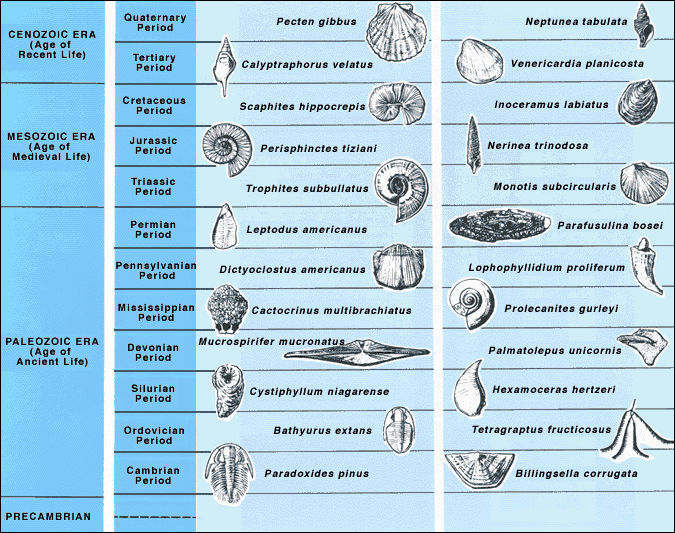
Index
Index fossils (also known as guide fossils, indicator fossils or zone fossils) are fossils used to define and identify
geologic periods (or faunal stages). They work on the premise that, although different
sediments may look different depending on the conditions under which they were deposited, they may include the remains of the same
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
of fossil. The shorter the species' time range, the more precisely different sediments can be correlated, and so rapidly evolving species' fossils are particularly useful as index fossils. The best index fossils are common, easy to identify at species level and have a broad distribution—otherwise the likelihood of finding and recognizing one in the two sediments is poor.
Trace
Trace fossils are fossil records of biological activity by lifeforms but not the preserved remains of the organism itself. They consist mainly of tracks and burrows, but also include
coprolites (fossil
feces) and marks left by feeding.
Trace fossils are particularly significant because they represent a data source that is not limited to animals with easily fossilized hard parts, and they reflect animal behaviours. Many traces date from significantly earlier than the body fossils of animals that are thought to have been capable of making them.
[e.g. ] Whilst exact assignment of trace fossils to their makers is generally impossible, traces may for example provide the earliest physical evidence of the appearance of moderately complex animals (comparable to
earthworms).
Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. They were first described by
William Buckland in 1829. Prior to this they were known as "fossil
fir cones" and "
bezoar stones." They serve a valuable purpose in paleontology because they provide direct evidence of the predation and diet of extinct organisms. Coprolites may range in size from a few millimetres to over 60 centimetres.
File:CambrianRusophycus.jpg, Cambrian trace fossils including '' Rusophycus'', made by a trilobite
File:Coprolite.jpg, A coprolite of a carnivorous dinosaur found in southwestern Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
File:Climactichnites wilsoni, densely packed.jpg, Densely packed, subaerial or nearshore trackways ('' Climactichnites wilsoni'') made by a putative, slug-like mollusk on a Cambrian tidal flat
Transitional
A ''transitional fossil'' is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation.
Microfossils
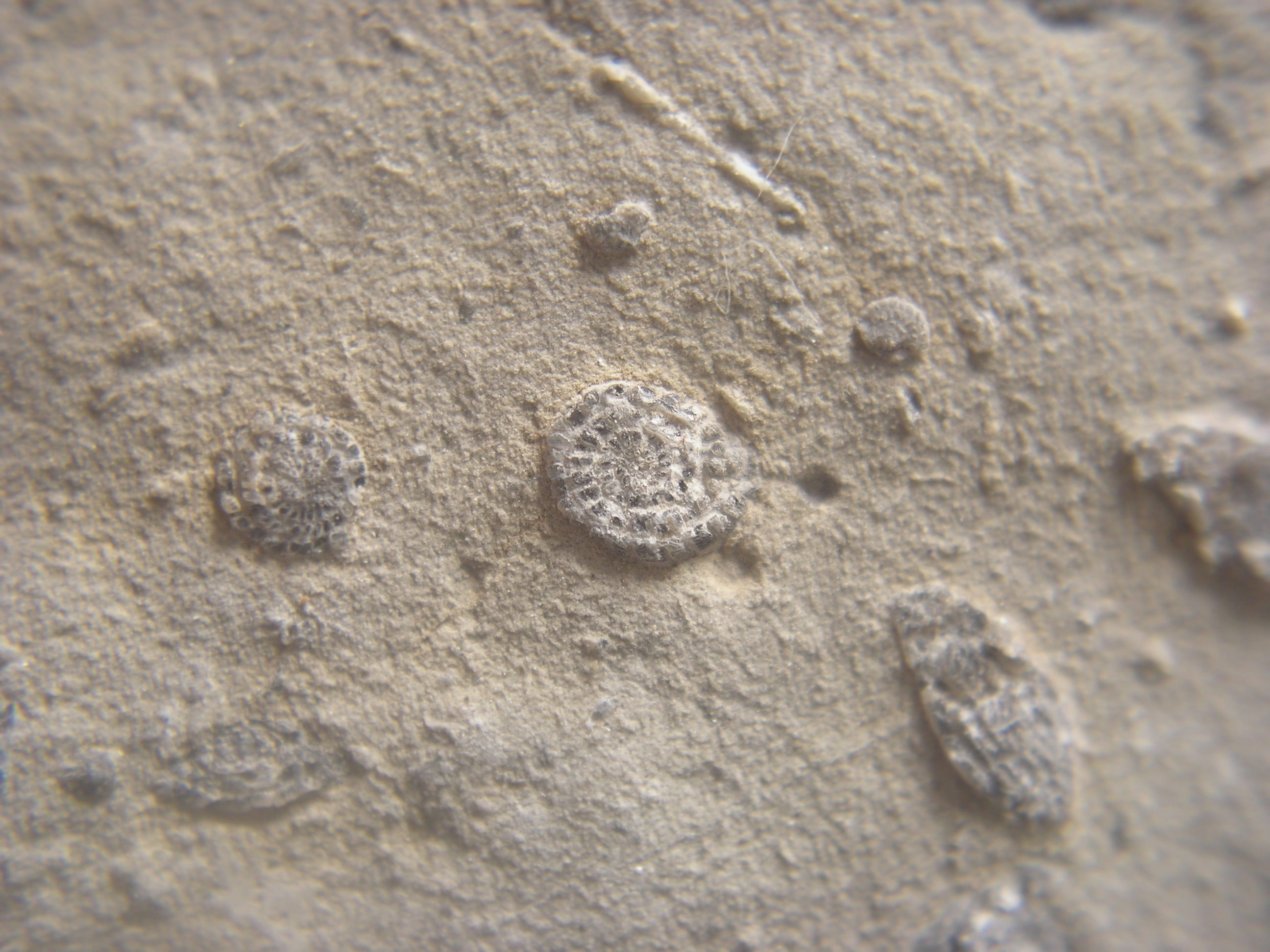 Microfossil
Microfossil is a descriptive term applied to fossilized plants and animals whose size is just at or below the level at which the fossil can be analyzed by the naked eye. A commonly applied cutoff point between "micro" and
"macro" fossils is 1 mm. Microfossils may either be complete (or near-complete) organisms (such as the marine plankters
foraminifera and
coccolithophores) or component parts (such as small teeth or
spores) of larger animals or plants. Microfossils are of critical importance as a reservoir of
paleoclimate information, and are also commonly used by
biostratigraphers to assist in the correlation of rock units.
Resin
Fossil resin (colloquially called
amber) is a natural
polymer found in many types of strata throughout the world, even the
Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
. The oldest fossil resin dates to the
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
, though most dates to the
Cenozoic. The excretion of resin by certain plants is thought to be an evolutionary
adaptation for to protect against insects and to seal wounds. Fossil resin often contains other fossils, called inclusions, that were captured by the sticky resin. These include bacteria, fungi, other plants, and animals. Animal inclusions are usually small
invertebrates, predominantly
arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s such as insects and spiders, and only extremely rarely a
vertebrate such as a small lizard. Preservation of inclusions can be exquisite, including small fragments of
DNA.
Derived or reworked

A ''derived'', ''reworked'' or is a fossil found in rock that accumulated significantly later than when the fossilized animal or plant died. Reworked fossils are created by erosion exhuming (freeing) fossils from the rock formation in which they were originally deposited and redepositing them in a younger sedimentary deposit.
Wood
Fossil wood is wood that is preserved in the fossil record. Wood is usually the part of a plant that is best preserved (and most easily found). Fossil wood may or may not be
petrified. The fossil wood may be the only part of the plant that has been preserved;
therefore such wood may get a special kind of
botanical name. This will usually include "xylon" and a term indicating its presumed affinity, such as ''
Araucarioxylon'' (wood of ''
Araucaria'' or some related genus), ''
Palmoxylon'' (wood of an indeterminate
palm), or ''Castanoxylon'' (wood of an indeterminate
chinkapin).
Subfossil

The term subfossil can be used to refer to remains, such as bones, nests, or
fecal deposits, whose fossilization process is not complete, either because the length of time since the animal involved was living is too short or because the conditions in which the remains were buried were not optimal for fossilization. Subfossils are often found in caves or other shelters where they can be preserved for thousands of years. The main importance of subfossil vs. fossil remains is that the former contain organic material, which can be used for
radiocarbon dating or extraction and
sequencing of DNA,
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
, or other biomolecules. Additionally,
isotope ratios can provide much information about the ecological conditions under which extinct animals lived. Subfossils are useful for studying the evolutionary history of an environment and can be important to studies in
paleoclimatology.
Subfossils are often found in depositionary environments, such as lake sediments, oceanic sediments, and soils. Once deposited, physical and chemical
weathering can alter the state of preservation, and small subfossils can also be ingested by living
organisms. Subfossil remains that date from the
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
are exceptionally rare, are usually in an advanced state of decay, and are consequently much disputed. The vast bulk of subfossil material comes from
Quaternary sediments, including many subfossilized
chironomid head capsules,
ostracod carapaces,
diatoms, and
foraminifera.

For remains such as molluscan
seashells, which frequently do not change their chemical composition over geological time, and may occasionally even retain such features as the original color markings for millions of years, the label 'subfossil' is applied to shells that are understood to be thousands of years old, but are of
Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
age, and therefore are not old enough to be from the
Pleistocene epoch.
Chemical fossils
Chemical fossils, or chemofossils, are chemicals found in rocks and
fossil fuels (petroleum, coal, and natural gas) that provide an organic signature for ancient life.
Molecular fossils and isotope ratios represent two types of chemical fossils. The oldest traces of life on Earth are fossils of this type, including carbon isotope anomalies found in
zircons that imply the existence of life as early as 4.1 billion years ago.
Stromatolites

Stromatolites are layered
accretionary structures formed in shallow water by the trapping, binding and cementation of sedimentary grains by
biofilms of
microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s, especially
cyanobacteria. Stromatolites provide some of the most ancient fossil records of life on Earth, dating back more than 3.5 billion years ago.
Stromatolites were much more abundant in Precambrian times. While older,
Archean fossil remains are presumed to be
colonies of
cyanobacteria, younger (that is,
Proterozoic) fossils may be
primordial forms of the
eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
chlorophytes (that is,
green algae). One
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of stromatolite very common in the
geologic record is ''
Collenia''. The earliest stromatolite of confirmed microbial origin dates to 2.724 billion years ago.
A 2009 discovery provides strong evidence of microbial stromatolites extending as far back as 3.45 billion years ago.
Stromatolites are a major constituent of the fossil record for life's first 3.5 billion years, peaking about 1.25 billion years ago.
They subsequently declined in abundance and diversity, which by the start of the Cambrian had fallen to 20% of their peak. The most widely supported explanation is that stromatolite builders fell victims to grazing creatures (the
Cambrian substrate revolution), implying that sufficiently complex organisms were common over 1 billion years ago.
The connection between grazer and stromatolite abundance is well documented in the younger
Ordovician evolutionary radiation; stromatolite abundance also increased after the
end-Ordovician and
end-Permian extinctions decimated marine animals, falling back to earlier levels as marine animals recovered.
Fluctuations in
metazoan population and diversity may not have been the only factor in the reduction in stromatolite abundance. Factors such as the chemistry of the environment may have been responsible for changes.
While
prokaryotic cyanobacteria themselves reproduce asexually through cell division, they were instrumental in priming the environment for the
evolutionary development of more complex
eukaryotic organisms. Cyanobacteria (as well as
extremophile Gammaproteobacteria) are thought to be largely responsible for increasing the amount of
oxygen in the primeval Earth's
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
through their continuing
photosynthesis. Cyanobacteria use
water,
carbon dioxide and
sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
to create their food. A layer of
mucus often forms over mats of cyanobacterial cells. In modern microbial mats, debris from the surrounding habitat can become trapped within the mucus, which can be cemented by the calcium carbonate to grow thin laminations of
limestone. These laminations can accrete over time, resulting in the banded pattern common to stromatolites. The domal morphology of biological stromatolites is the result of the vertical growth necessary for the continued infiltration of sunlight to the organisms for photosynthesis. Layered spherical growth structures termed
oncolites are similar to stromatolites and are also known from the
fossil record.
Thrombolites are poorly laminated or non-laminated clotted structures formed by cyanobacteria common in the fossil record and in modern sediments.
The Zebra River Canyon area of the Kubis platform in the deeply dissected Zaris Mountains of southwestern
Namibia provides an extremely well exposed example of the thrombolite-stromatolite-metazoan reefs that developed during the Proterozoic period, the stromatolites here being better developed in updip locations under conditions of higher current velocities and greater sediment influx.
Pseudofossils

''Pseudofossils'' are visual patterns in rocks that imitate fossils but are produced by geologic processes rather than biologic processes. Some pseudofossils, such as geological
dendrite crystals, are formed by naturally occurring fissures in the rock that get filled up by percolating minerals. Other types of pseudofossils are kidney ore (round shapes in iron ore) and
moss agates, which look like moss or plant leaves.
Concretions, spherical or ovoid-shaped nodules found in some sedimentary strata, were once thought to be
dinosaur eggs and are often mistaken for fossils as well.
Astrobiology
It has been suggested that
biominerals could be important indicators of
extraterrestrial life and thus could play an important role in the search for past or present life on the planet
Mars. Furthermore,
organic components (
biosignatures) that are often associated with biominerals are believed to play crucial roles in both pre-biotic and
biotic reactions.
On 24 January 2014, NASA reported that current studies by the
''Curiosity'' and
''Opportunity'' rovers on Mars would begin searching for evidence of ancient life, including a
biosphere based on
autotrophic,
chemotrophic and/or
chemolithoautotrophic microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s, as well as ancient water, including
fluvio-lacustrine environments (
plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
s related to ancient
river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s or
lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
s) that may have been
habitable.
The search for evidence of
habitability,
taphonomy (related to fossils), and
organic carbon on the planet
Mars is now a primary
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
objective.
Art
According to one hypothesis, a Corinthian vase from the 6th century BCE (Boston 63.420) is the oldest artistic record of a vertebrate fossil, perhaps a Miocene giraffe combined with elements from other species. However, a later study by
Julián Monge-Nájera using expert evaluations rejects this idea, because mammals do not have the
eye bones shown on the painted monster. Monge-Nájera believes the morphology shown in the vase painting corresponds best to an extant
varanid that would have been known to the Ancient Greeks.
Trading and collecting
Fossil trading is the practice of buying and selling fossils. This is often done illegally with artifacts stolen from research sites, costing many important scientific specimens each year. The problem is quite pronounced in China, where many specimens have been stolen.
Fossil collecting (sometimes, in a non-scientific sense, fossil hunting) is the collection of fossils for scientific study, leisure, or profit. Amateur fossil collecting is the predecessor of modern paleontology and remains a practiced hobby to date. Professionals and amateurs alike collect fossils for their scientific value.
As medicine
The use of fossils to address health issues is rooted in
traditional medicine and include the use of fossils as
talismans. The specific fossil to use to alleviate or cure an illness is often based on its resemblance to the symptoms or affected organ (see
sympathetic magic). The usefulness of fossils as medicine is almost entirely a
placebo effect, though fossil material might conceivably have some
antacid activity or supply some
essential minerals. The use of dinosaur bones as "dragon bones" has persisted in
Traditional Chinese medicine into modern times, with mid-Cretaceous dinosaur bones being consumed in
Ruyang County during the early 21st century.
Gallery
File:Marine fossils found high in the Himalayas. Collection of the Abbot of Dhankar Gompa, HP, India.jpg, Marine fossils found high in the Himalayas. Collection of the Abbot of Dhankar Gompa, HP, India
File:Amonite Cropped.jpg, Three small ammonite fossils, each approximately 1.5 cm across
File:Cockerellites liops Green River Formation.jpg, Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
fossil fish ''Priscacara liops'' from the Green River Formation of Wyoming
File:Trilobite2.jpg, A permineralized trilobite, '' Asaphus kowalewskii''
File:Carcharodontosaurus and Megalodon teeth.jpg, Megalodon and '' Carcharodontosaurus'' teeth. The latter was found in the Sahara Desert.
File:The fossils from Cretaceous age found in Lebanon.jpg, Fossil shrimp ( Cretaceous)
File:PetrifiedWood.jpg, Petrified wood in Petrified Forest National Park, Arizona
File:Petrified Araucaria cone from patagonia-Edit3.jpg, Petrified cone of '' Araucaria mirabilis'' from Patagonia, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
dating from the Jurassic Period (approx. 210 Ma)
File:CyprusPlioceneGastropod.JPG, A fossil gastropod from the Pliocene of Cyprus. A serpulid worm is attached.
File:OrhtocerasNautiloid092313.jpg, Silurian Orthoceras fossil
File:Eocene fossil flower, Clare Family Florissant Fossil Quarry, Florissant, Colorado, USA - 20100807.jpg, Eocene fossil flower from Florissant, Colorado
File:RoyLindmanMicraster.JPG, '' Micraster'' echinoid fossil from England
File:Productid Permian Texas.JPG, Productid brachiopod ventral valve; Roadian, Guadalupian (Middle Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
); Glass Mountains, Texas.
File:Fossil agatized coral Florida.JPG, Agatized coral from the Hawthorn Group (Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
–Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
), Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. An example of preservation by replacement.
File:Fossils from Gotland beaches.jpg, Fossils from beaches of the Baltic Sea island of Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a Provinces of Sweden, province/Counties of Sweden, county (Swedish län), Municipalities of Sweden, municipality, a ...
, placed on paper with 7 mm (0.28 inch) squares
File:Dinosaur footprints in ToroToro Bolivia.jpg, Dinosaur footprints from Torotoro National Park in Bolivia.
See also
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
References
Further reading
"Grand Canyon cliff collapse reveals 313 million-year-old fossil footprints"21 August 2020, ''
CNN''
"Hints of fossil DNA discovered in dinosaur skull"by Michael Greshko, 3 March 2020, ''
National Geographic''
"Fossils for Kids , Learn all about how fossils are formed, the types of fossils and more!"Video (2:23), 27 January 2020, ''Clarendon Learning''
"Fossil & their formation"Video (9:55), 15 November 2019, ''
Khan Academy''
"How are dinosaur fossils formed?by Lisa Hendry, ''
Natural History Museum, London''
"Fossils 101"Video (4:27), 22 August 2019, ''
National Geographic''
"How to Spot the Fossils Hiding in Plain Sight"by Jessica Leigh Hester, 23 February 2018, ''
Atlas Obscura''
"It's extremely hard to become a fossil", by
Olivia Judson, 30 December 2008, ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
''
"Bones Are Not the Only Fossils", by
Olivia Judson, 4 March 2008, ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
''
External links
*
The Virtual Fossil Museum throughout Time and EvolutionPaleoportal, geology and fossils of the United States
The Fossil Record, a complete listing of the families, orders, class and phyla found in the fossil record(archived 3 May 2012)
*
*
{{Authority control
 A fossil (from
A fossil (from  More scientific views of fossils emerged during the
More scientific views of fossils emerged during the  Niles Eldredge's study of the '' Phacops'' trilobite genus supported the hypothesis that modifications to the arrangement of the trilobite's eye lenses proceeded by fits and starts over millions of years during the Devonian. Eldredge's interpretation of the ''Phacops'' fossil record was that the aftermaths of the lens changes, but not the rapidly occurring evolutionary process, were fossilized. This and other data led Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge to publish their seminal paper on punctuated equilibrium in 1971.
Synchrotron
Niles Eldredge's study of the '' Phacops'' trilobite genus supported the hypothesis that modifications to the arrangement of the trilobite's eye lenses proceeded by fits and starts over millions of years during the Devonian. Eldredge's interpretation of the ''Phacops'' fossil record was that the aftermaths of the lens changes, but not the rapidly occurring evolutionary process, were fossilized. This and other data led Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge to publish their seminal paper on punctuated equilibrium in 1971.
Synchrotron  Replacement occurs when the shell, bone, or other tissue is replaced with another mineral. In some cases mineral replacement of the original shell occurs so gradually and at such fine scales that microstructural features are preserved despite the total loss of original material. Scientists can use such fossils when researching the anatomical structure of ancient species. Several species of saurids have been identified from mineralized dinosaur fossils.
Replacement occurs when the shell, bone, or other tissue is replaced with another mineral. In some cases mineral replacement of the original shell occurs so gradually and at such fine scales that microstructural features are preserved despite the total loss of original material. Scientists can use such fossils when researching the anatomical structure of ancient species. Several species of saurids have been identified from mineralized dinosaur fossils.
 Bioimmuration occurs when a skeletal organism overgrows or otherwise subsumes another organism, preserving the latter, or an impression of it, within the skeleton. Usually it is a sessile skeletal organism, such as a bryozoan or an oyster, which grows along a substrate, covering other sessile sclerobionts. Sometimes the bioimmured organism is soft-bodied and is then preserved in negative relief as a kind of external mold. There are also cases where an organism settles on top of a living skeletal organism that grows upwards, preserving the settler in its skeleton. Bioimmuration is known in the fossil record from the Ordovician to the Recent.
Bioimmuration occurs when a skeletal organism overgrows or otherwise subsumes another organism, preserving the latter, or an impression of it, within the skeleton. Usually it is a sessile skeletal organism, such as a bryozoan or an oyster, which grows along a substrate, covering other sessile sclerobionts. Sometimes the bioimmured organism is soft-bodied and is then preserved in negative relief as a kind of external mold. There are also cases where an organism settles on top of a living skeletal organism that grows upwards, preserving the settler in its skeleton. Bioimmuration is known in the fossil record from the Ordovician to the Recent.

 A ''derived'', ''reworked'' or is a fossil found in rock that accumulated significantly later than when the fossilized animal or plant died. Reworked fossils are created by erosion exhuming (freeing) fossils from the rock formation in which they were originally deposited and redepositing them in a younger sedimentary deposit.
A ''derived'', ''reworked'' or is a fossil found in rock that accumulated significantly later than when the fossilized animal or plant died. Reworked fossils are created by erosion exhuming (freeing) fossils from the rock formation in which they were originally deposited and redepositing them in a younger sedimentary deposit.
 The term subfossil can be used to refer to remains, such as bones, nests, or fecal deposits, whose fossilization process is not complete, either because the length of time since the animal involved was living is too short or because the conditions in which the remains were buried were not optimal for fossilization. Subfossils are often found in caves or other shelters where they can be preserved for thousands of years. The main importance of subfossil vs. fossil remains is that the former contain organic material, which can be used for radiocarbon dating or extraction and sequencing of DNA,
The term subfossil can be used to refer to remains, such as bones, nests, or fecal deposits, whose fossilization process is not complete, either because the length of time since the animal involved was living is too short or because the conditions in which the remains were buried were not optimal for fossilization. Subfossils are often found in caves or other shelters where they can be preserved for thousands of years. The main importance of subfossil vs. fossil remains is that the former contain organic material, which can be used for radiocarbon dating or extraction and sequencing of DNA,  Stromatolites are layered accretionary structures formed in shallow water by the trapping, binding and cementation of sedimentary grains by biofilms of
Stromatolites are layered accretionary structures formed in shallow water by the trapping, binding and cementation of sedimentary grains by biofilms of  ''Pseudofossils'' are visual patterns in rocks that imitate fossils but are produced by geologic processes rather than biologic processes. Some pseudofossils, such as geological dendrite crystals, are formed by naturally occurring fissures in the rock that get filled up by percolating minerals. Other types of pseudofossils are kidney ore (round shapes in iron ore) and moss agates, which look like moss or plant leaves. Concretions, spherical or ovoid-shaped nodules found in some sedimentary strata, were once thought to be dinosaur eggs and are often mistaken for fossils as well.
''Pseudofossils'' are visual patterns in rocks that imitate fossils but are produced by geologic processes rather than biologic processes. Some pseudofossils, such as geological dendrite crystals, are formed by naturally occurring fissures in the rock that get filled up by percolating minerals. Other types of pseudofossils are kidney ore (round shapes in iron ore) and moss agates, which look like moss or plant leaves. Concretions, spherical or ovoid-shaped nodules found in some sedimentary strata, were once thought to be dinosaur eggs and are often mistaken for fossils as well.