|
Xingming Observatory
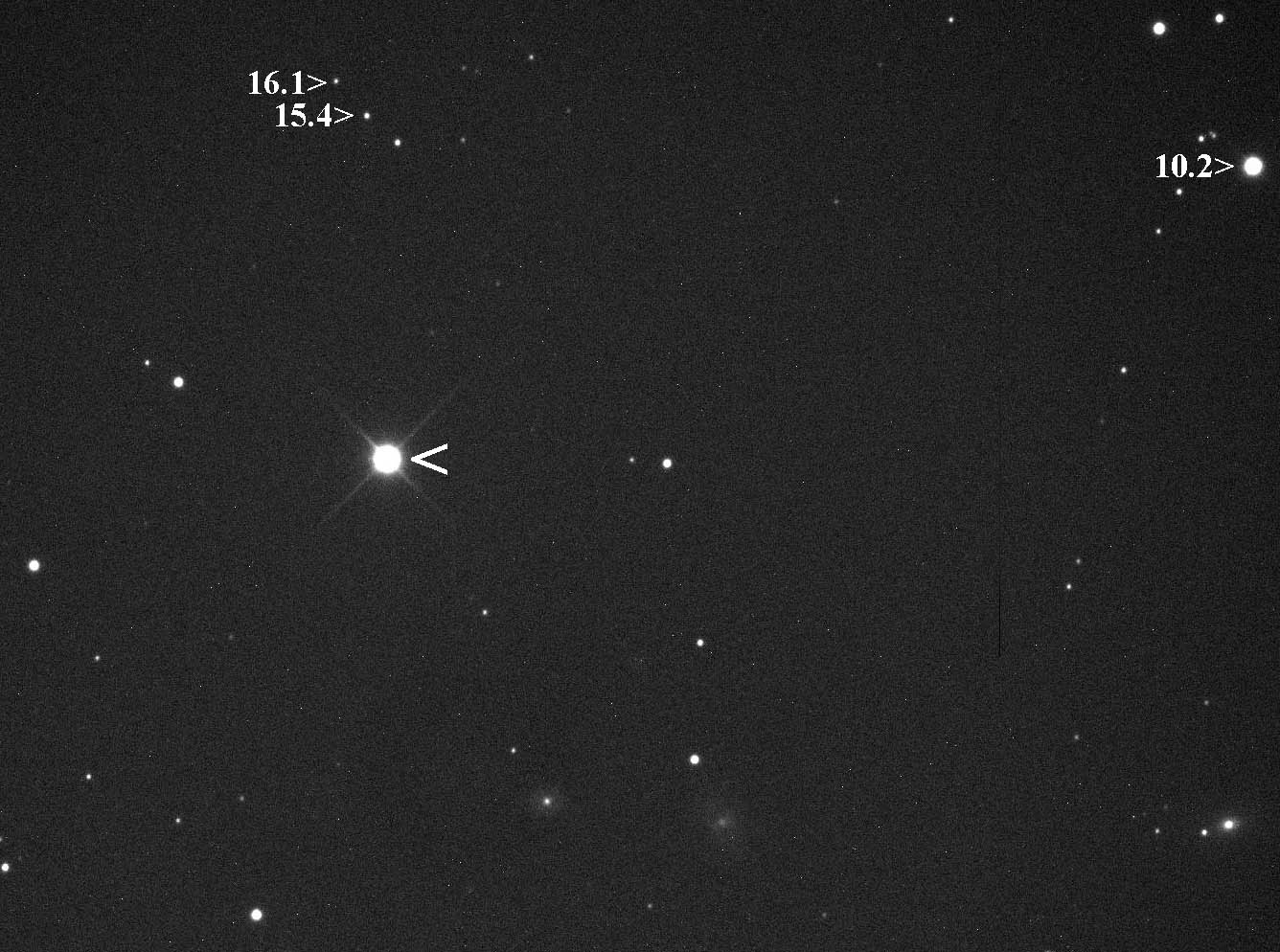
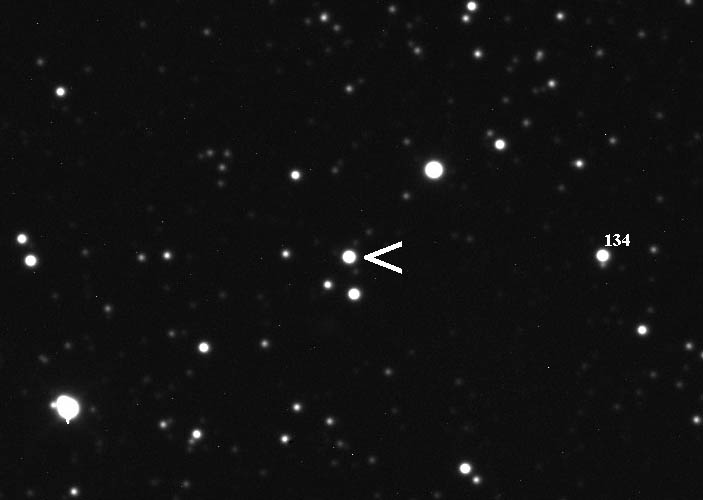
Xingming Observatory () is a private amateur astronomical observatory located in Gangou Township, Ürümqi, Xinjiang, China. The observatory was founded by amateur astronomer Gao Xing in 2007. The name "Xingming" is chosen partly to commemorate Zhou Xingming, a pioneer of amateur astronomy in China. As of 2024, discoveries made by Xingming Observatory include 3 comets, 15 asteroids, 90 supernovae, 63 novae, and 111 dwarf novae. Research Programs The observatory conducts research in time-domain astronomy and solar system observations in collaboration with professional astronomers. It hosts XOSS (Xingming Observatory Sky Survey), an amateur sky survey that searches for transients, asteroids and comets. Observational data from Xingming Observatory contributed to published astronomy research since 2011. Public Outreach The observatory shares a number of telescopes with the public through the XPRO (Xingming Public Remote Observatory) program. It also operates PSP (Popular Superno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. The term ''observatoire'' has been used in French since at least 1976 to denote any institution that compiles and presents data on a particular subject (such as public health observatory) or for a particular geographic area (European Audiovisual Observatory). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Historically, ground-based observatories were as simple as containing a mural instrument (for measuring the angle between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
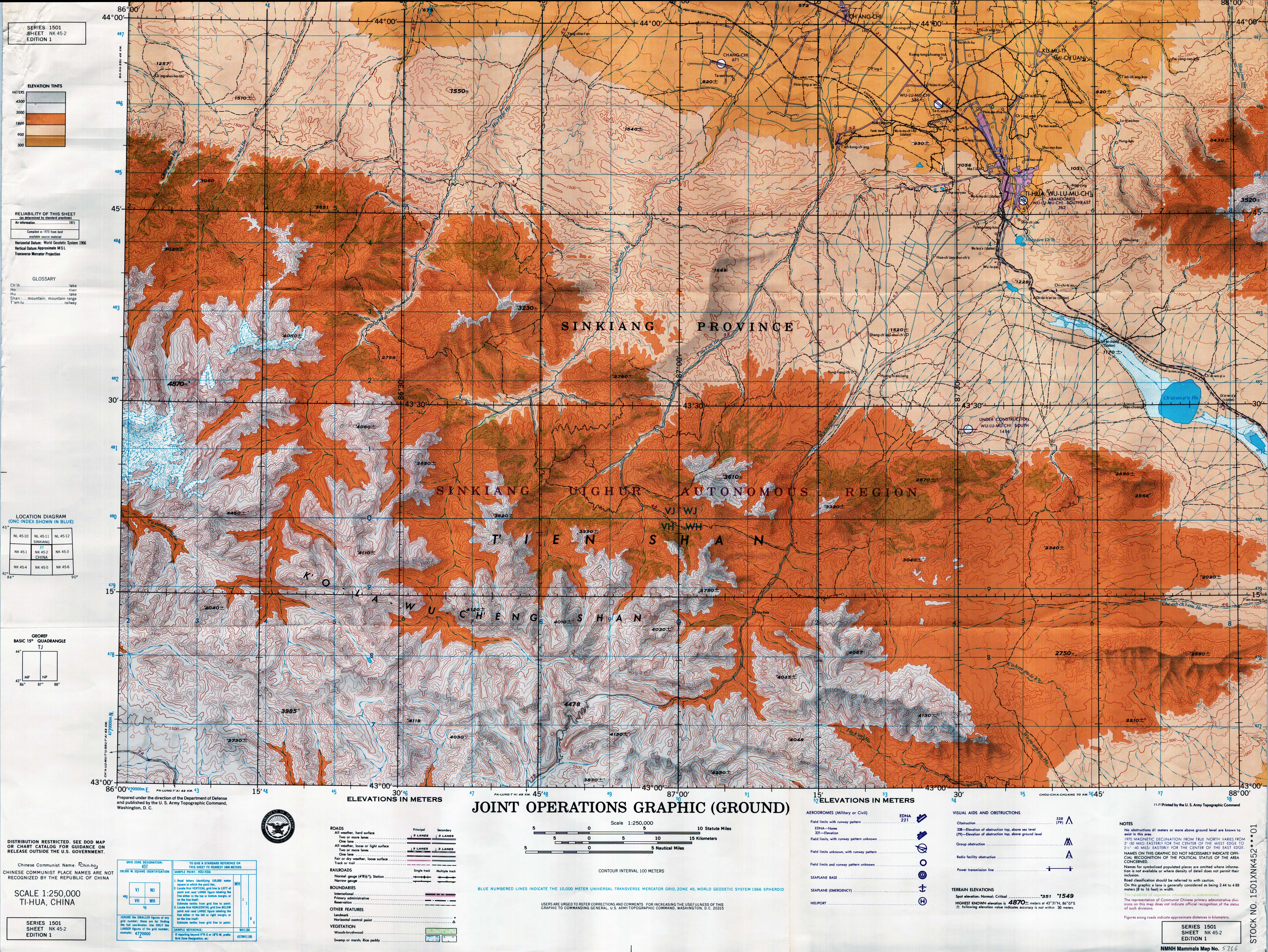
Ürümqi
Ürümqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, Ürümqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the second-largest in Central Asia in terms of population, right after Kabul, Afghanistan. Ürümqi has seen significant economic development since the 1990s and currently serves as a List of transport topics#Nodes, regional transport node and a cultural, political and commercial center. Etymology The name Ürümqi comes from the Mongolic languages, Mongolic Oirat language and means "beautiful pasture" (, ). It was originally the name of a small town founded by the Mongolic peoples, Mongolic, Oirat-speaking Dzungar people, Dzungars. The Qing dynasty took Ürümqi by force in 1755, during Dzungar–Qing Wars, its conquest of the Dzungar Khanate. Qing forces expanded the town into a walled city from 1763 to 1767, and upon completing the expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinjiang
Xinjiang,; , SASM/GNC romanization, SASM/GNC: Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Sinkiang, officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an Autonomous regions of China, autonomous region of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the Northwest China, northwest of the country at the crossroads of Central Asia and East Asia. Being the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, largest province-level division of China by area and the List of the largest country subdivisions by area, 8th-largest country subdivision in the world, Xinjiang spans over and has about 25 million inhabitants. Xinjiang Borders of China, borders the countries of Afghanistan, India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, Pakistan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The rugged Karakoram, Kunlun Mountains, Kunlun and Tian Shan mountain ranges occupy much of Xinjiang's borders, as well as its western and southern regions. The Aksai Chin and Trans-Karakoram Tract regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gao Xing
Gao Xing (; born 1974) is a Chinese amateur astronomer from Ürümqi, Xinjiang, China. (Astronomers name: Gaoxing) He built Xingming Observatory (星明天文台) in 2006 and discovered Comet C/2008 C1 (Chen-Gao) on February 1, 2008 with Chen Tao from Jiangsu and Comet P/2009 L2 (Yang-Gao) on June 15, 2009 with Yang Rui from Hangzhou, Zhejiang and Comet C/2015 F5 (SWAN-Xingming) on April 4, 2015 with Guoyou Sun from Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China (...?) and hence won the Edgar Wilson Award for 2008. (He won Edgar Wilson Award unter that for 2015 3 times.) In the night on February 26, 2009, he discovered a nova in Sagittarius in the Galaxy's central part at night with his partner Sun Guoyou from Wenzhou. Gao reported his new discovery to the International Astronomical Union on May 29 and acquired the identification. On the night of October 3, 2010, he discovered a new supernova in NGC5430 at night with his partner Sun Guoyou. He also discovered several SOHO comets and NEAT astero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a Comet tail, tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can Subtended angle, subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). Asteroids are rocky, metallic, or icy bodies with no atmosphere, and are broadly classified into C-type asteroid, C-type (carbonaceous), M-type asteroid, M-type (metallic), or S-type asteroid, S-type (silicaceous). The size and shape of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from small rubble piles under a kilometer across to Ceres (dwarf planet), Ceres, a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter. A body is classified as a comet, not an asteroid, if it shows a coma (tail) when warmed by solar radiation, although recent observations suggest a continuum between these types of bodies. Of the roughly one million known asteroids, the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 astronomical unit, AU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The supernova remnant, remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems, but causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. This type is usually created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. If the orbital period of the system is a few days or less, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to draw accreted matter onto its surface, creating a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmosphere, mostly consisting of hydrogen, is heated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Nova
A dwarf nova (pl. wiktionary:nova, novae), or U Geminorum variable, is one of several types of cataclysmic variable star, consisting of a close binary star system in which one of the components is a white dwarf that accretion disk, accretes matter from its companion. Dwarf novae are dimmer and repeat more often than "classical" novae. Overview The first one to be observed was U Geminorum in 1855; however, the mechanism was not known until 1974, when Brian Warner (astronomer), Brian Warner showed that the nova is due to the increase of the luminosity of the accretion disk. They are similar to classical novae in that the white dwarf is involved in periodic outbursts, but the mechanisms are different. nova, Classical novae result from the fusion and detonation of accreted hydrogen on the primary's surface. Current theory suggests that dwarf novae result from instability in the accretion disk, when gas in the disk reaches a critical temperature that causes a change in viscosity, result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citizen Science
The term citizen science (synonymous to terms like community science, crowd science, crowd-sourced science, civic science, participatory monitoring, or volunteer monitoring) is research conducted with participation from the general public, or amateur/nonprofessional researchers or participants of science, social science and many other disciplines. There are variations in the exact definition of citizen science, with different individuals and organizations having their own specific interpretations of what citizen science encompasses. Citizen science is used in a wide range of areas of study including ecology, biology and conservation, health and medical research, astronomy, media and communications and information science. There are different applications and functions of "citizen science" in research projects. Citizen science can be used as a methodology where public volunteers help in collecting and classifying data, improving the scientific community's capacity. Citizen sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Astronomical Observatories Of China
The National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC, ) is an astronomical research institute operated by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, Purple Mountain Observatory and National Time Service Center. History and introduction Founded on April 25, 2001, NAOC was formed through the merging of four Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) observatories, three CAS observing stations and one CAS research centre. The Headquarters of the NAOC are situated in the northern Chaoyang District of Beijing on the site of the former Beijing Astronomical Observatory (BAO), and take responsibility for all matters relating to the former BAO. Currently, NAOC has 7 astronomical research departments listed follows: * Optical Astronomy Research Department (光学天文研究部) * Radio Astronomy Research Department (射电天文研究部) * Galactic Astronomy & Cosmology Research Department (星系宇宙学研究部) * Moon & Deep Space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |