|
Xiang Rong (painter)
Xiang Rong (; 18019August 1856) was a Chinese military general and politician. He was born in Wuxi County, Chongqing, and was promoted from the rank of a foot soldier during the later years of the Qing dynasty (16441912). He was involved in early military operations against the Taiping Rebellion in Henan from 1850 onwards. From then he was a Senior Colonel, after one year the military promoted him be the ''tidu'' (提督) of Guangxi, even though he failed, he made the Taiping believers flee Guangxi. Continuing after Guangxi, Xiang Rong never gave up and tracked the Taiping rebels across three province to Jiangnan in southern China. His Jiangnan Battalion (part of the Green Standard Army) was constantly defeated by the Taiping rebel army outside Nanjing. The Taiping rebel army broke through his various encirclements and occupied Wuhan and Nanjing, giving rise to a huge civil war. Death He and his vice commander Zhang Guoliang commanded a 90,000 man force together from April 1853 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuxi County
Wuxi County () is a county of Chongqing Municipality, People's Republic of China, bordering Shaanxi to the north and Hubei to the northeast and east. Sitting at the upper reaches of Daning River and the southern slopes of the central Daba Mountains. It is best known for its scenic views and its preserved witchcraft culture. Wuxi County is noted as a major tourism site of Chongqing. Administrative divisions Wuxi County has 2 subdistricts and numerous towns and townships: Former township: * Zhonggang () Geography The vast majority of Wuxi's land area is mountainous. With a wet abundant precipitation, Wuxi County is suitable for many plants to grow, the local products are medicine nectar, starch, bacon, dried fruit, vegetables and antler. Climate Economy Total economy performance in 2013 is good and growth rate is accelerating. Total GDP is 9.01 billion yuan in 2013. Farming in Wuxi County Major products include rice, maize, potato, sweet potato, cotton, broccoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidu
The provincial military commander () was the highest military official in the Chinese provinces of the Green Standards (綠營 ''lǜyíng'') in Qing dynasty (1644–1911). There was usually one in each province, but sometimes there were two in a province which one in charge of the army and another on in charge of the navy (like Fujian). Under the jurisdiction of the provincial governor (巡撫 ''xúnfǔ'') and sometimes a governor-general (總督), he was in charge of the Chinese military forces known as the Green Standards (綠營 ''lǜyíng''), but had no control over the Eight Banners. The provincial military commander is also known as provincial commander-in-chief and general-in-chief. See also * Taqibu Taqibu (, ; 1816–1855), courtesy name Zhiting, member of the Tao Jia clan, a native of Manchuria's Bordered Yellow Banner, was promoted to the rank of Retainers in early China, retainer in his early years as an officer of the guards. Thereafte ... References {{China- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generals From Chongqing
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently granted posthumously to George Washington and Ulysses S. Grant * (" general admiral") ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1856 Deaths
Events January–March * January 8 – Borax deposits are discovered in large quantities by John Veatch in California. * January 23 – The American sidewheel steamer SS ''Pacific'' leaves Liverpool (England) for a transatlantic voyage on which she will be lost with all 186 on board. * January 24 – U.S. President Franklin Pierce declares the new Free-State Topeka government in " Bleeding Kansas" to be in rebellion. * January 26 – First Battle of Seattle: Marines from the suppress an indigenous uprising, in response to Governor Stevens' declaration of a "war of extermination" on Native communities. * January 29 ** The 223-mile North Carolina Railroad is completed from Goldsboro through Raleigh and Salisbury to Charlotte. ** Queen Victoria institutes the Victoria Cross as a British military decoration. * February ** The Tintic War breaks out in Utah. ** The National Dress Reform Association is founded in the United States to promote "ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Births
The 19th century began on 1 January 1801 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 (MCM). It was the 9th century of the 2nd millennium. It was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was Abolitionism, abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanded beyond its British homeland for the first time during the 19th century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, France, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Catholic Church, in response to the growing influence and power of modernism, secularism and materialism, formed the First Vatican Council in the late 19th century to deal with such problems an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danyang City
Danyang () is a county-level city located on the southwest (right) bank of the Yangtze River, and is under the administration of Zhenjiang, Jiangsu province, China. It is noted for the production of optical lenses used in sunglasses and eyeglasses. Danyang has a total area of and a population of roughly 988,900 in 2020. Danyang locals speak a dialect of Wu Chinese, and the city is on the linguistic borderline between Wu Chinese and Jianghuai Mandarin. History During the period of the Eastern Jin and four Southern Dynasties (Nan Chao) from 420 to 589 A.D. when China's national capital was in Jiankang (modern Nanjing), Danyang was the hometown of the emperors of the Southern Qi (479-502) and Liang Dynasties (502-557), who were buried in the countryside outside the city. Today 11 of these Southern Dynasties imperial tombs can still be found to the east and northeast of the city. They are notable for their unique stone statues of mythical animals marking the sacred way (圣道, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or serve as a pool of available manpower for regular forces to draw from. When acting independently, militias are generally unable to hold ground against regular forces. Militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. However, militias may also engage in defense activities to protect a community, its territory, property, and laws. For example, naval militias may comprise fishermen and other civilians which are organized and sanctioned by a state to enforce its maritime boundaries. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as profe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Rigang
Qin Rigang (秦日綱, 1821 – 1856), né Qin Richang (秦日昌), was a Hakka military leader of the Taiping Rebellion, known during his military tenure as the King of Yen (燕王). He served under Hong Xiuquan's Taiping Administration and led Taiping forces to many military victories. He was executed by Hong Xiuquan in 1856 because he had killed the family and followers of Shi Dakai during the Tianjing Incident. Chen Yucheng and Li Xiucheng were trained and taught by Qin. Early life Born in the Guiping district of Guangxi, Qin was a miner by trade, but had studied the military arts. He began following Hong Xiuquan in the early days of the God Worshipper movement and was counted among Hong's most trusted friends. Leadership in the Taiping Rebellion Qin was entrusted with key military assignments by Hong Xiuquan and eventually became a marquis of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom and its fourth most senior military officer, behind only Yang Xiuqing, Wei Changhui, and Shi Daka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Guoliang
Zhang Guoliang (; 1810 – April 1860), born in Guangdong, was a Field Marshal for the Qing dynasty. He was born in Gaoyao, Zhaoqing, Guangdong, although Qing stated that he was from Meixian, Guangdong. He was originally a bandit in Guangxi but later joined the Qing Army. He helped to raise the Green Standard Army to 250,000 to fight against the Taiping Rebellion. In the second rout of Army Group Jiangnan in 1860 he was defeated by Li Xiucheng. Zeng Guofan praised Zhang and said he was Jiangnan's "Great Wall of China." Life When the Battle of Nanjing (1853) began, Zhang accepted a SOS order from Nanjing, he and his 15,000 men were the first troops to arrive and save Nanjing. In 1856, Zhang Guoliang led his army in the recovery of Zhenjiang, which had been occupied by Taiping for five years. The Emperor rewarded Zhang with the Imperial yellow jacket and promoted him to First Class Senior General. In April 1860, Zhang was defeated and led his remaining 20,000 soldiers in retreat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhan
Wuhan; is the capital of Hubei, China. With a population of over eleven million, it is the most populous city in Hubei and the List of cities in China by population, eighth-most-populous city in China. It is also one of the nine National central city, national central cities and the second most livable city in China. Wuhan historically served as a busy city port for commerce and trading with some crucial influences on Chinese history. The name "Wuhan" came from the city's historical origin from the conglomeration of Wuchang, Wuhan, Wuchang, Hankou District, Hankou, and Hanyang District, Hanyang, which are collectively known as the "Three Towns of Wuhan" ( zh, s=武汉三镇, labels=no). Wuhan lies in the eastern Jianghan Plain, at the confluence of the Yangtze river and its largest tributary, the Han River (Hubei), Han River, and is known as "Nine Provinces' Thoroughfare" ( zh, labels=no, t= ). Wuhan was the site of the 1911 Wuchang Uprising against the Qing dynasty which Dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Standard Army
The Green Standard Army (; ) was the name of a category of military units under the control of Qing dynasty in China. It was made up mostly of ethnic Han soldiers and operated concurrently with the Manchu-Mongol- Han Eight Banner armies. In areas with a high concentration of Hui people, Muslims served as soldiers in the Green Standard Army. After the Qing consolidated control over China, the Green Standard Army was primarily used as a police force. Despite its name, the Green Standard Army served as a gendarmerie rather than a military force. After the formation of "brave battalions" in response to the mid-19th century rebellions in China, who were mercenaries hired and financed by provincial governors, the Green Standard were relegated for local security only, while the braves became the Qing dynasty's rapid response force. There was an effort starting in the 1860s to modernize Green Standard units to make them similar to the braves, and the Late Qing reforms in the early 1900s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
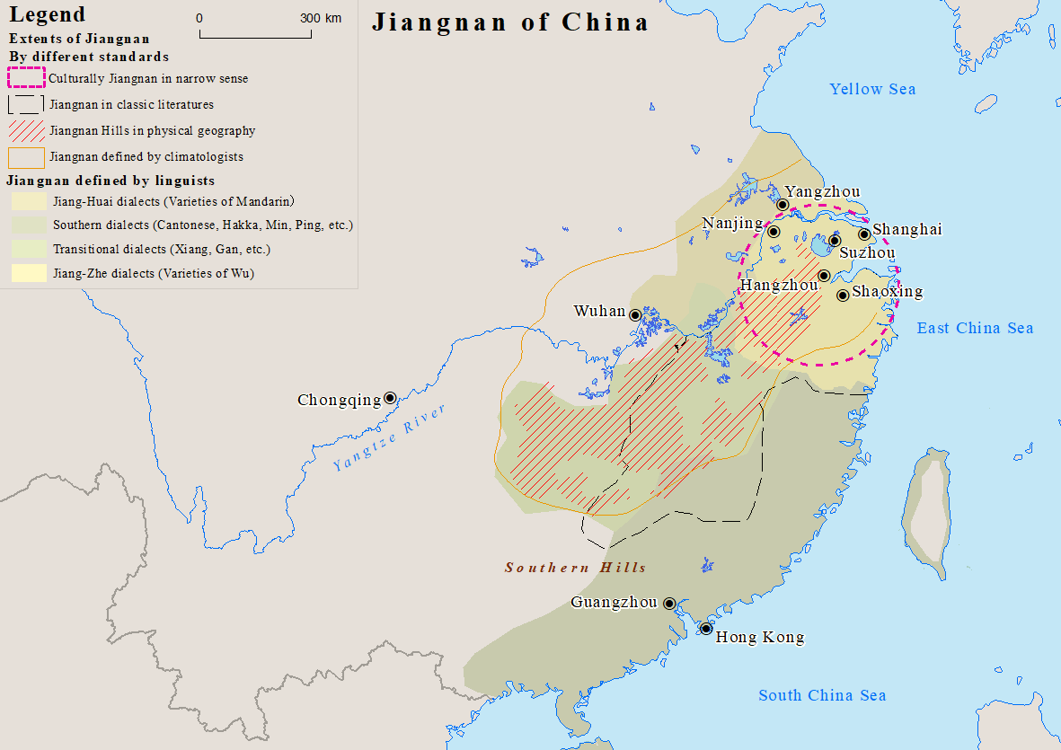
Jiangnan
Jiangnan is a geographic area in China referring to lands immediately to the south of the lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including the southern part of its delta. The region encompasses the city of Shanghai, the southern part of Jiangsu Province, the southeastern part of Anhui Province, the northern part of Jiangxi Province and Zhejiang Province. The most important cities in the area include Anqing, Changzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing, Ningbo, Shaoxing, Suzhou, Wuxi, Wenzhou, Yangzhou and Zhenjiang. Jiangnan has long been regarded as one of the most prosperous regions in China due to its wealth in trade and very high human development. Most people of the region speak Wu Chinese dialects as their native languages. Etymology The name Jiangnan is the pinyin romanization of the Standard Mandarin pronunciation of , meaning " andsSouth of the [Yangtze] River". Although ''jiang'' () is now the common Chinese word for any large river, it was historically used in Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |