|
Green Standard Army
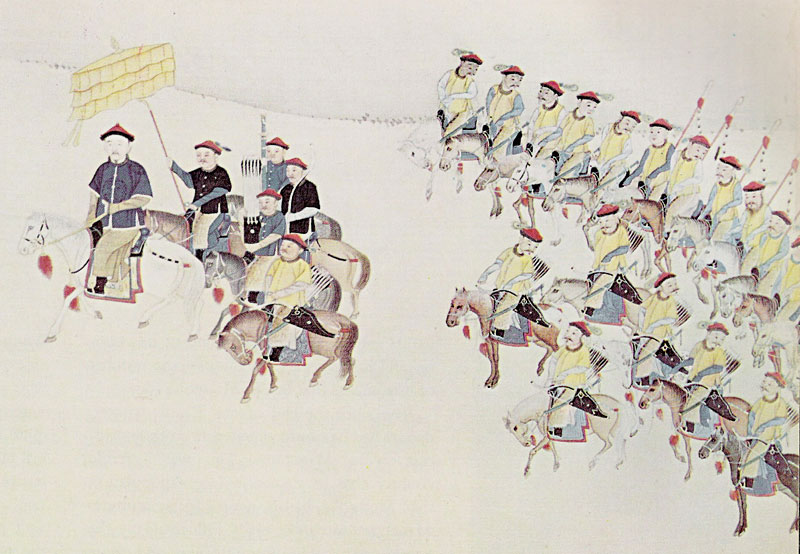
The Green Standard Army (; ) was the name of a category of military units under the control of Qing dynasty in China. It was made up mostly of ethnic Han soldiers and operated concurrently with the Manchu-Mongol- Han Eight Banner armies. In areas with a high concentration of Hui people, Muslims served as soldiers in the Green Standard Army. After the Qing consolidated control over China, the Green Standard Army was primarily used as a police force. Despite its name, the Green Standard Army served as a gendarmerie rather than a military force. After the formation of "brave battalions" in response to the mid-19th century rebellions in China, who were mercenaries hired and financed by provincial governors, the Green Standard were relegated for local security only, while the braves became the Qing dynasty's rapid response force. There was an effort starting in the 1860s to modernize Green Standard units to make them similar to the braves, and the Late Qing reforms in the early 1900s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Chengdu, and its population stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai and Gansu to the north, Shaanxi and Chongqing to the east, Guizhou and Yunnan to the south, and Tibet to the west. During antiquity, Sichuan was home to the kingdoms of Ba and Shu until their incorporation by the Qin. During the Three Kingdoms era (220–280), Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The area was devastated in the 17th century by Zhang Xianzhong's rebellion and the area's subsequent Manchu conquest, but recovered to become one of China's most productive areas by the 19th century. During World War II, Chongqing served as the temporary capital of the Republic of China, and was heavily bombed. It was one of the last mainland areas captured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Yong (Qing Dynasty) (born 1995), Chinese snooker player
{{hndis ...
Zhang Yong may refer to: * Zhang Yong (eunuch) (1465–1529), Chinese eunuch * Jack Yung Chang (Zhang Yong) (1911–1939), Chinese historian of mathematics * Zhang Yong (politician) (born 1953), former director of the China Food and Drug Administration * Zhang Yong (agronomist) (born 1956), Chinese agronomist * Zhang Yong (restaurateur), Chinese billionaire restaurateur, founder of Haidilao * Daniel Zhang or Zhang Yong (born 1972), CEO of Alibaba Group * Zhang Yong (real estate developer), founder of Xinyuan Real Estate * Zhang Yong (snooker player) Zhang Yong (; born 21 July 1995) is a Chinese former professional snooker player. Career Prior to turning professional Zhang featured in Asian Players Tour Championship events from 2012 to 2015, as well as being a semi-finalist in the 2015 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Jinbao
Wang may refer to: Names * Wang (surname) (王), a common Chinese surname * Wāng (汪), a less common Chinese surname * Titles in Chinese nobility * A title in Korean nobility * A title in Mongolian nobility Places * Wang River in Thailand * Wang Township, Minnesota, a township in the United States * Wang, Bavaria, a town in the district of Freising, Bavaria, Germany * Wang, Austria, a town in the district of Scheibbs in Lower Austria * An abbreviation for the town of Wangaratta, Australia * Wang Theatre, in Boston, Massachusetts * Charles B. Wang Center, an Asian American center at Stony Brook University Broadcasting * WWNG, a radio station (1330 AM) licensed to serve Havelock, North Carolina, United States, which held the call sign WANG from 1999 to 2017 * WBKZ, a radio station licensed to Havelock, North Carolina formerly known as WANG-FM * WANG, a radio station using the call sign since 2018 Other * Wang (Tibetan Buddhism), a form of empowerment or initiation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Liangdong
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Zhang may refer to: Chinese culture, etc. * Zhang (surname) (張/张), common Chinese surname ** Zhang (surname 章), a rarer Chinese surname * Zhang County (漳县), of Dingxi, Gansu * Zhang River (漳河), a river flowing mainly in Henan * ''Zhang'' (unit) (丈), a traditional Chinese unit of length equal to 10 ''chi'' (3–3.7 m) * 璋, a type of shaped stone or jade object in ancient Chinese culture thought to hold great value and protective properties; see also Bi (jade) and Cong (jade) Other * Zhang, the proper name of the star Upsilon¹ Hydrae See also * Zang (other) Zang may refer to: * Official abbreviation for Tibet Autonomous Region (藏) * Tibetan people * Zang (bell), Persian musical instrument * Zang (surname) (臧), a Chinese surname * Zang, Iran, a village in Kerman Province, Iran * Persian form of Zan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Fuchen
Wang Fuchen (; d. 1681) was a participant in the Revolt of the Three Feudatories during the Qing dynasty against the Kangxi Emperor. Wang was born in Datong, Shanxi Province, he was born to a poor family and grew up to be a bandit. His original surname was Li, nicknamed Horse-Sparrowhawk (馬鷂子) by the Manchu soldiers. Originally resisting the Manchu conquest of the Ming dynasty, ancient historians left behind records stating that Wang Fuchen was a handsome, tall and strong man with pale face, and thick eyebrows that resembled reclining silkworms. He was famous for his valour in battle and was known to the Manchus as a tough opponent, his presence was sometimes discouraging enough for the Manchu soldiers to retreat. He was highly regarded by Shunzhi Emperor and was won over to the Regent Dorgon. He assisted the former Ming dynasty generals Hong Chengchou and Wu Sangui in suppressing the Ming remnants of the Southern Ming. He followed Wu to Burma to capture and execute Zhu You ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 165420 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, personal name Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. He is considered one of China's greatest emperors. The third son of the Shunzhi Emperor, Kangxi was enthroned at the age of seven while actual power was held for six more years by the four regents nominated by his father. After assuming personal rule, Kangxi's attempt to revoke the fiefdoms of feudal princes sparked the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, which he suppressed. He also forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan and Mongols in the north and northwest to submit to Qing rule, and launched an expedition that incorporated Tibet into the empire. Domestically, he initially welcomed the Jesuits and the propagation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Sangui
Wu Sangui (; 8 June 1612 – 2 October 1678), courtesy name Changbai () or Changbo (), was a Chinese military leader who played a key role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the founding of the Qing dynasty. In Chinese folklore, Wu Sangui is regarded as a disreputable Hanjian, Han Chinese traitor for his defection over to the Manchu people, Manchu invaders, suppression of the Southern Ming resistance and execution of the Zhu Youlang, Yongli Emperor. Wu eventually double-crossed both of his masters, the Ming and the Qing dynasties. In 1644, Wu was a Ming general in charge of garrisoning Shanhai Pass, the strategic choke point between Manchuria and Beijing. After learning that Li Zicheng's rebel army had conquered Beijing and captured his family, including his father Wu Xiang (Ming general), Wu Xiang and concubine Chen Yuanyuan, Wu allowed the Manchu to enter China proper through Shanhai Pass to drive Li from Beijing, where the Manchu then set up the Qing dynasty. For his aid, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
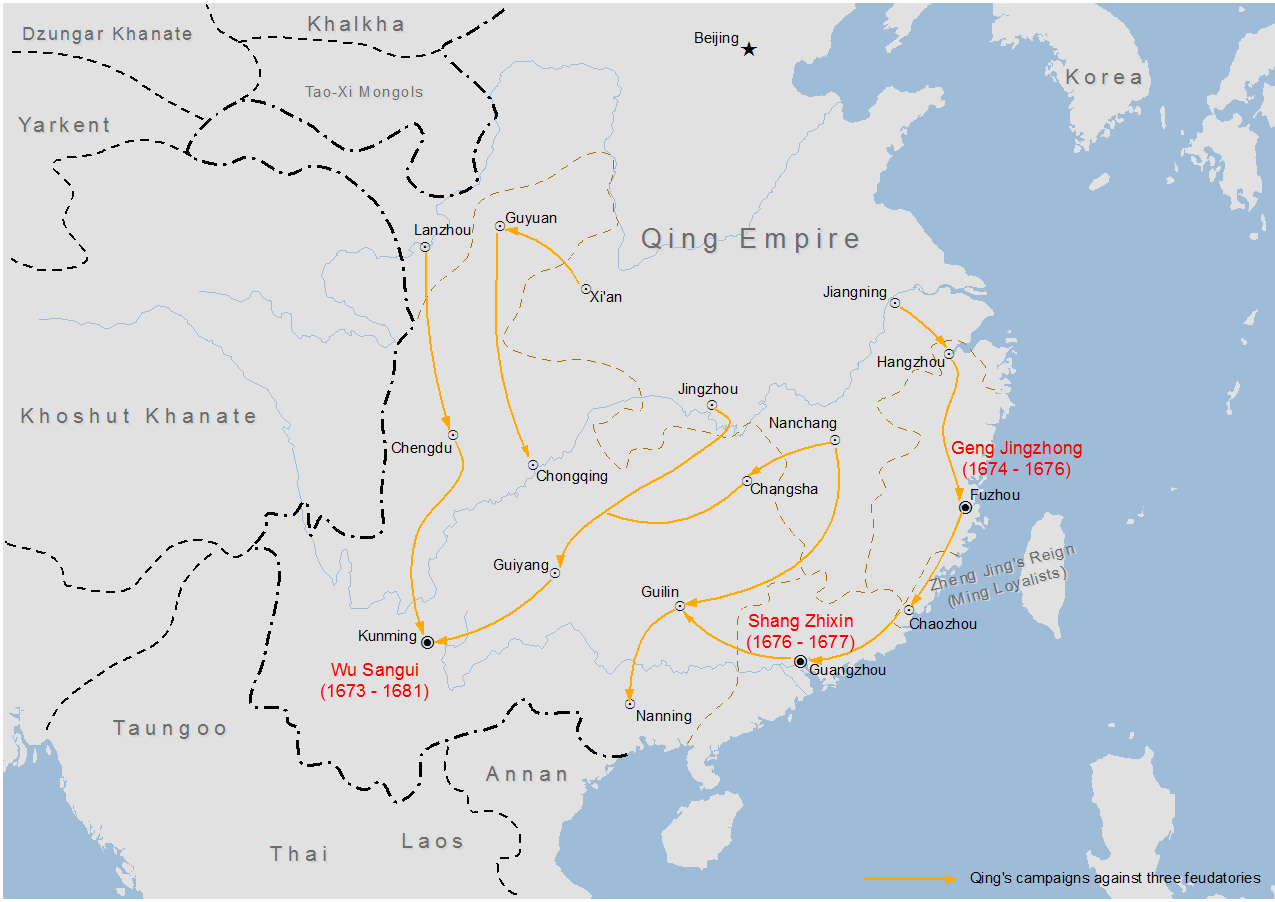
Revolt Of The Three Feudatories
The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, () also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion lasting from 1673 to 1681 in the early Qing dynasty of China, during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722). The revolt was led by Wu Sangui, Shang Zhixin and Geng Jingzhong, the three ethnic Han lords of Yunnan, Guangdong and Fujian provinces whose hereditary titles were given to them for defecting to and helping the Qing dynasty conquer China proper, who rebelled after the Qing central government started abolishing their fiefs. The feudatories were supported by Zheng Jing's Kingdom of Tungning on the island of Taiwan, which sent forces to invade Mainland China. Additionally, minor Han military figures, such as Wang Fuchen, and the Chahar Mongols, also revolted against Qing rule. Due to their history as defectors that helped to topple the Southern Ming dynasty, the Three Feudatories failed to win over the support of the general Han populace and were eventually def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
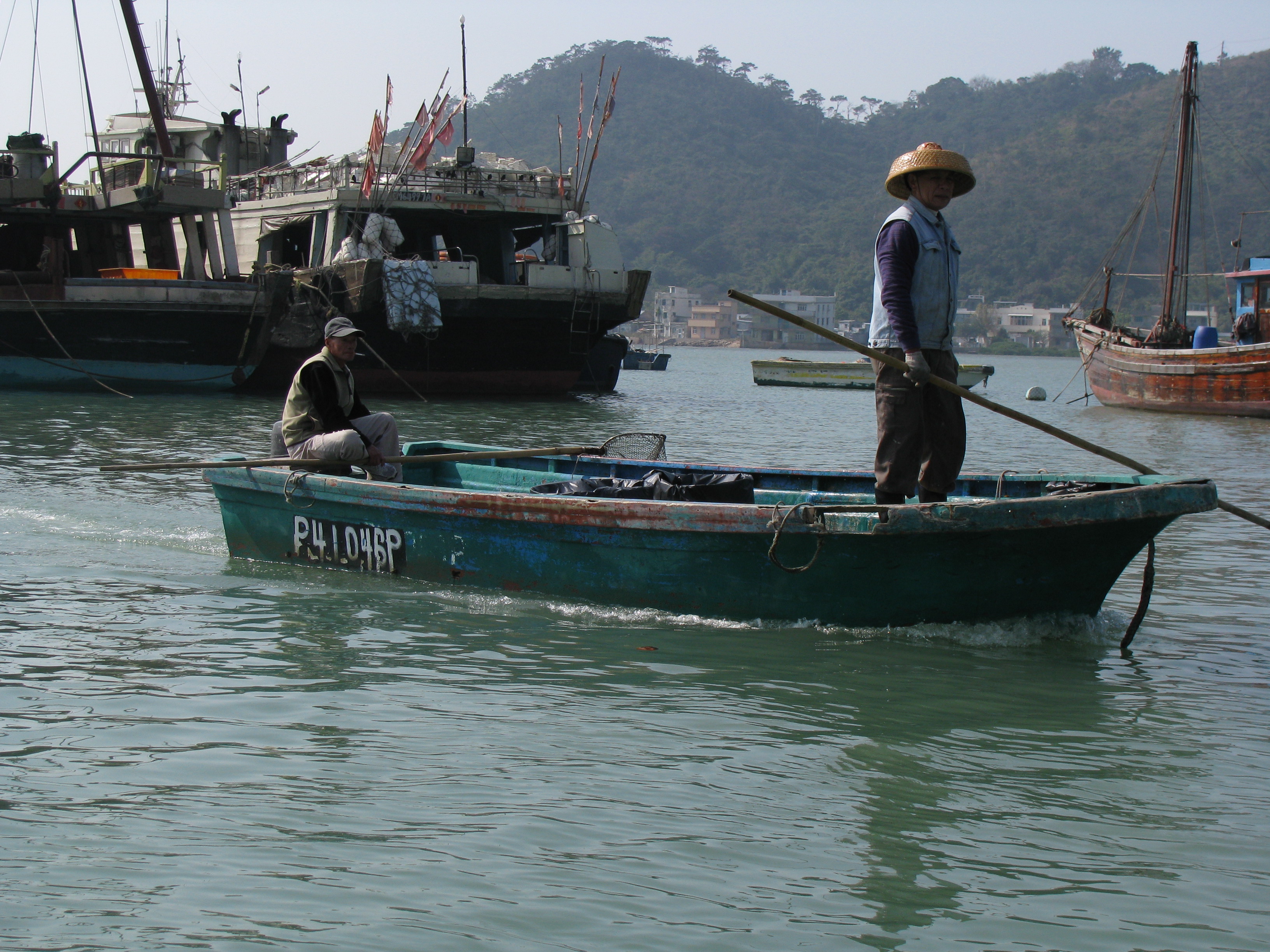
Tanka People
The Boat Dwellers, also known as Shuishangren (; "people living on the water") or Boat People, or the derogatory Tankas, are a sinicised ethnic group in Southern China who traditionally lived on junks in coastal parts of Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, Hainan, Shanghai, Zhejiang and along the Yangtze river, as well as Hong Kong, and Macau. The Boat Dwellers are referred to with other names outside of Guangdong. Though many now live onshore, some from the older generations still live on their boats and pursue their traditional livelihood of fishing. The origins of the Boat Dwellers can be traced back to the native ethnic minorities of southern China known historically as the Baiyue, who may have taken refuge on the sea and gradually assimilated into Han Chinese culture. However, they have preserved many of their native traditions not found in Han culture. A small number of Boat Dwellers also live in parts of Vietnam. There they are called Dan () and are classified as a subgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Clearance
The Great Clearance (), also translated as the Great Evacuation or Great Frontier Shift, was caused by edicts issued in 1661, 1664, and 1679, which required the evacuation of the coastal areas of Guangdong, Fujian, Zhejiang, Jiangnan, and Shandong, in order to fight the Taiwan-based anti-Qing loyalist movement of the erstwhile Ming dynasty (1368–1644). The edict was first issued by the Shunzhi Emperor of the Qing dynasty in 1661, the last year of his rule. With the Shunzhi Emperor's death in the same year, his son, the Kangxi Emperor (1661–1722), succeeded this edict under a regency led by Oboi (1661–1669). The ban on human settlement of those coastal areas was lifted in 1669, and some residents were allowed to return. Yet, in 1679, the edict was issued again. In 1683, after the Qing defeated the Kingdom of Tungning in the Battle of Penghu and took control of Taiwan, the people from the cleared areas according to the edict were allowed to return and to live in the clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |