|
Wuttagoonaspidae
Wuttagoonaspidae is a family of extinct primitive arthrodire placoderm fishes from Early Devonian China and Middle Devonian Australia. It contains two genera, '' Wuttagoonaspis'' and '' Yiminaspis'', some of the more basal members of the order Arthrodira, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ... below: References Placoderm families Early Devonian first appearances Middle Devonian extinctions {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodire
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an Order (biology), order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are covered by a Sclerotic ring, bony ring, which supports the eye, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus ''Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuttagoonaspidae
Wuttagoonaspidae is a family of extinct primitive arthrodire placoderm fishes from Early Devonian China and Middle Devonian Australia. It contains two genera, '' Wuttagoonaspis'' and '' Yiminaspis'', some of the more basal members of the order Arthrodira, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ... below: References Placoderm families Early Devonian first appearances Middle Devonian extinctions {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodira
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are covered by a bony ring, which supports the eye, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus '' Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed '' Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuttagoonaspis Fletcheri
''Wuttagoonaspis'' is an extinct genus of primitive arthrodire placoderm fish from the Middle Devonian of Australia. The box-like skull is up to 18 centimeters in length, and the median dorsal plate averages in length about 10 centimeters. It contains two species: the type species ''Wuttagoonaspis fletcheri'', described by Ritchie in 1973, and ''Wuttagoonaspis milligani'', described by Young and Goujet in 2003. Classification ''Wuttagoonaspis'' belongs to the family Wuttagoonaspidae, and is closely related to '' Yiminaspis''. It is one of the more basal members of the order Arthrodira, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ... below: References Placoderms of Australia Wuttagoonaspidae {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiminaspis
''Yiminaspis'' is an extinct monospecific genus of primitive arthrodire placoderm fish from Emsian-aged marine strata in Yunnan, China. The type species ''Yiminaspis shenme'' was named and described in 2008, and is known from a flattened partial skull and portions of the thoracic armor. Etymology The genus name translates as "Yi People's shield", deriving from the Chinese name ( zh, s=, t=, l=Yi People, an ethnic group in China, Vietnam, and Thailand) and the Greek word ''aspis'' ("a type of round shield"). The specific name is from Chinese ( zh, s=, t=, l=what), as in "what is it?" reference to the peculiar anatomy of this prehistoric fish. Classification ''Yiminaspis'' belongs to the family Wuttagoonaspidae, and is closely related to '' Wuttagoonaspis''. It is one of the more basal members of the order Arthrodira, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emsian
The Emsian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 410.62 ±1.95 million years ago to 393.47 ±0.99 million years ago. It was preceded by the Pragian Stage and followed by the Eifelian Stage. It is named after the Ems river in Germany. The GSSP is located in the Zinzil'ban Gorge in the Kitab State Geological Reserve of Uzbekistan , image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg , image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg , symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem , national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ..., above the contact with the Madmon Formation. In North America the Emsian Stage is represented by Sawkill or Sawkillian time. Biological events During this period, earliest known agoniatitid ammonoid fossils began appearing within this stage after first appearing in previous stage and began to evolutionarily radiate within this stage, in which a new ammonoid or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
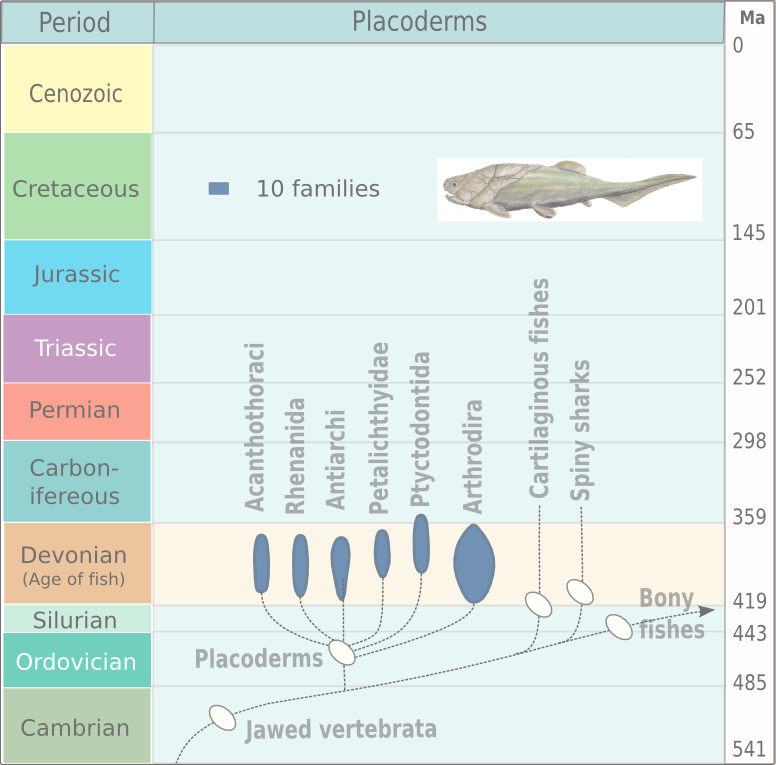
Placoderm Families
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ 'plax'', ''plakos''' plate' and δέρμα 'derma'''skin') are vertebrate animals of the class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates (hence the name), and the rest of the body was scaled or naked depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish (their jaws likely evolved from the first pair of gill arches), as well as the first vertebrates to have true teeth. They were also the first fish clade to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins and the homologous precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, '' Incisoscutum'', ''Materpiscis'' and '' Austroptyctodus'', represent the oldest known examples of live birth. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderm
Placoderms (from Ancient Greek πλάξ [''plax'', ''plakos''] 'Plate (animal anatomy), plate' and δέρμα [''derma''] 'skin') are vertebrate animals of the class (biology), class Placodermi, an extinct group of prehistoric fish known from Paleozoic fossils during the Silurian and the Devonian geological period, periods. While their endoskeletons are mainly cartilaginous, their head and thorax were covered by articulated armour (zoology), armoured plates (hence the name), and the rest of the body was scale (zoology), scaled or naked depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish (their fish jaw, jaws likely Evolution, evolved from the first pair of gill arches), as well as the first vertebrates to have true tooth, teeth. They were also the first fish clade to develop pelvic fins, the second set of paired fins and the homology (biology), homologous precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods. 380-million-year-old fossils of three other genera, ''Incisoscutum'', ''M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |