|
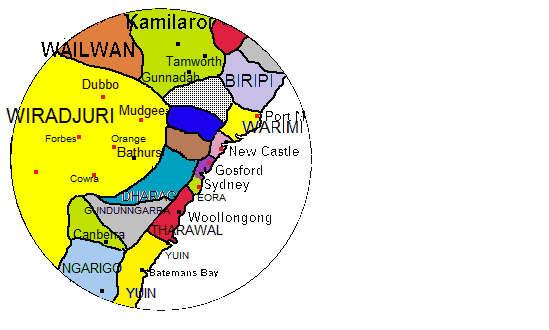
Worimi
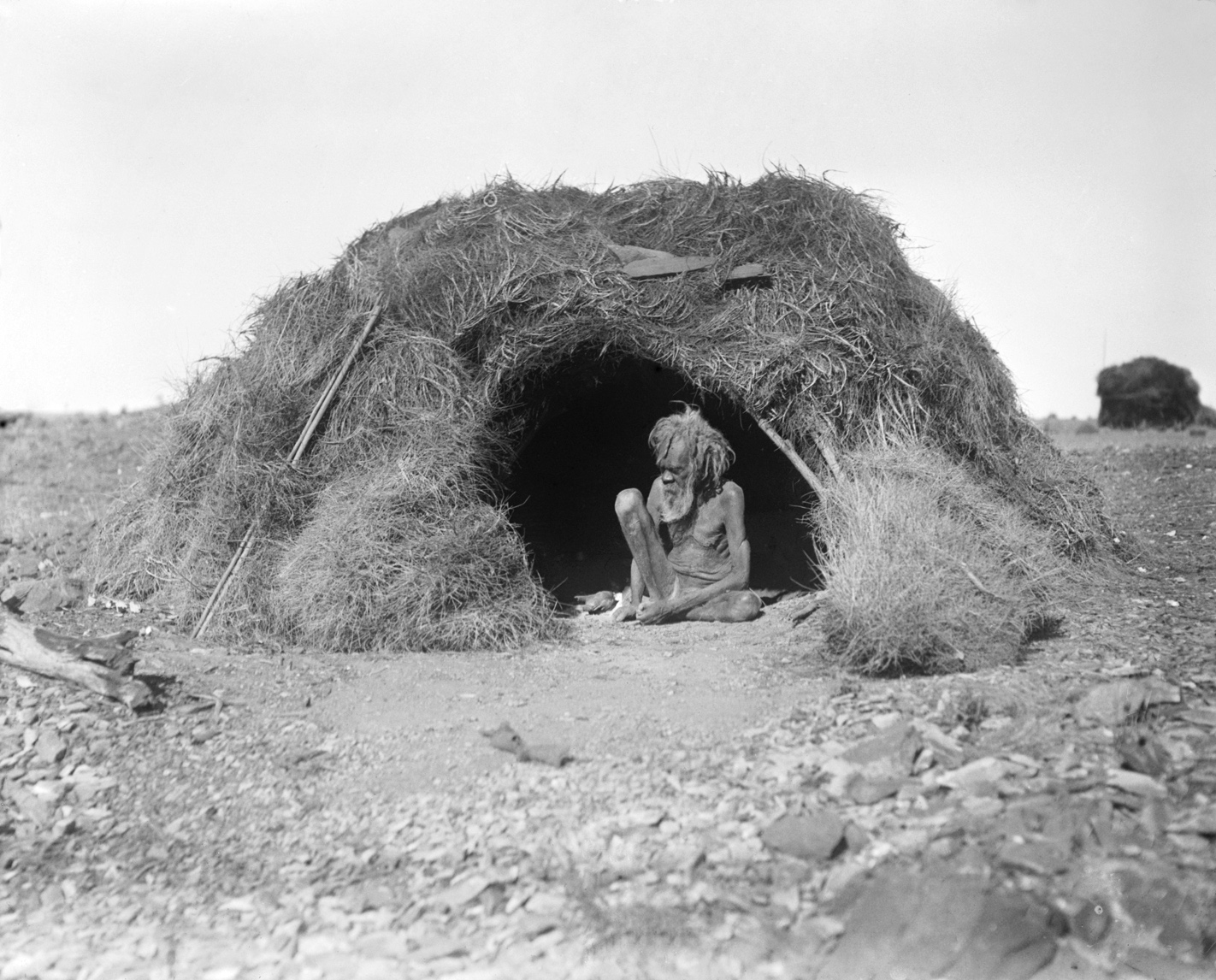
The Worimi (also spelt Warrimay) people are Aboriginal Australians from the eastern Port Stephens and Great Lakes regions of coastal New South Wales, Australia. Before contact with settlers, their people extended from Port Stephens in the south to Forster/ Tuncurry in the north and as far west as Gloucester. Country The Worimi's lands extended over according to Norman Tindale, who specified that the tribal area encompassed the Hunter River to the coastal town of Forster near Cape Hawke. It reached Port Stephens and ran inland as far as roughly Gresford and in proximity of Glendon Brook, Dungog, and the upper Myall Creek. To the south, their territory extended to Maitland. Social organisation The Worimi were divided into four bands: * ''Garuagal'' (the country adjoining Teleghery Creek and along the lower Hunter) * ''Maiangal'' (sea-shore south of Port Stephens, inland to Teleghery Creek) * ''Gamipingal'' (northern side of Port Stephens, left bank of Karuah) * ''Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gathang
The Gathang language, also spelt Gadjang, Kattang, Kutthung, Gadhang, Gadang and previously known as Worimi (also spelt Warrimay), is an Australian Aboriginal language or group of dialects. The three known dialects are Birrbay, Guringay, and Warrimay, which are used by the Worimi, Guringay, and Birrbay peoples. It went extinct during the latter half of the 20th century, but has been revived in the 21st century. History and status After the colonisation of Australia, many of the hundreds of Aboriginal languages fell into disuse. The Worimi people comprised 18 clan groups (''ngurras''), all of whom spoke Gathang. The four ngurras of the Port Stephens area moved to the settlement at Carrington to work at the Australian Agricultural Company, and over the years lost their language and culture as they learnt European ways. Many Worimi people were forced into missions and reserves. In 1887: E.M. Curr published the first word list of the Gathang language, which had been compile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Stephens (New South Wales)
Port Stephens, an open youthful tide-dominated drowned-valley estuary, is a large natural harbour of about in the Hunter and Mid North Coast regions of New South Wales, Australia. Port Stephens lies within the Port Stephens–Great Lakes Marine Park and is situated about north-east of Sydney. The harbour lies wholly within the local government area of Port Stephens; although its northern shoreline forms the boundary between the Port Stephens and MidCoast local government areas. According to the 2006 census, more than people lived within of its long shoreline and more than lived within .Consolidated population figures from the Australian Bureau of Statistics 2006 census Geography Port Stephens is formed through the confluence of the Myall and Karuah rivers, Tilligerry Creek, and the Tasman Sea of the South Pacific Ocean. The lower port has a predominantly marine ecology and the upper port an estuarine ecology. The area to the east of Port Stephens comprises the Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gringai
Gringai otherwise known as ''Guringay'', is the name for one of the Australian Aboriginal people who were recorded as inhabiting an area of the Hunter Valley in eastern New South Wales, north of Sydney. They were united by a common language, strong ties of kinship and survived as skilled hunter–fisher–gatherers in family groups as a clan of the Worimi people. Country The Gringai lived round the Williams River, Barrington tops, Dungog, Barrington and Gloucester area and traded with the Paterson River Aboriginals The centre of their territory is on the land where the modern town of Dungog (perhaps "clear hills" in the Gringai dialect) lies. History Two people of the Gringai are known by that name as a result of their arrest and subsequent trials. ''Wong-ko-bi-kan'' (Jackey) and Charley were both arrested within a year or so of each other in the 1830s. He was judged guilty and sentenced to be transported to Tasmania for manslaughter after spearing John Flynn on 3 April 1834 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forster, New South Wales
Forster is a coastal town in the Mid North Coast, New South Wales, Mid North Coast region of New South Wales, on country of the Worimi, Worimi People, Australia, in the Mid-Coast Council Local government in Australia, LGA, about 308 km north-north-east of Sydney. It is immediately adjacent to its twin, Tuncurry, New South Wales, Tuncurry, which is the smaller of the two towns. Forster is known for its stunning waters and Manning Valley beauty. History Forster is named after William Forster (Australian politician), William Forster, who also was the 4th Premier of New South Wales and who later served as Agent-General in London. The first post office in Forster opened on 1 October 1872, with John Wyllie Breckenridge as postmaster at a salary of £10 a year. The area was well known in the early days for its timber cutting and sawmills. Timber was collected from the lakes and rivers by the logpunts (droghers). A bridge over the Coolongolook River that marks the entrance to W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands. Humans first migrated to Australia (continent), Australia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, and over time formed as many as 500 List of Aboriginal Australian group names, language-based groups. In the past, Aboriginal people lived over large sections of the continental shelf. They were isolated on many of the smaller offshore islands and Tasmania when the land was inundated at the start of the Holocene Interglacial, inter-glacial period, about 11,700 years ago. Despite this, Aboriginal people maintained extensive networks within the continent and certain groups maintained relationships with Torres Strait Islanders and the Makassar people, Makassar people of modern-day Indonesia. Over the millennia, Aboriginal people developed complex trade networks, inter-cultural relationships, law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telegherry River
Telegherry River, a perennial river of the Mid-Coast Council system, is located in the Mid North Coast and Upper Hunter regions of New South Wales, Australia. Course and features Telegherry River rises on the southeastern slopes of the Williams Range within the Great Dividing Range, below The Mountaineer, southwest of Gloucester, and flows generally south southeast and east, before reaching its confluence with the Karuah River north of Dungog. The river descends over its course. See also * Rivers of New South Wales * List of rivers of New South Wales (L–Z) * List of rivers of Australia Rivers are ordered alphabetically, by state. The same river may be found in more than one state as many rivers cross state borders. Longest rivers nationally Longest river by state or territory Although the Murray River forms much of the bor ... References External links * Rivers of New South Wales Mid-Coast Council Rivers of the Hunter Region {{NewSouthWales-river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceania (journal)
''Oceania'' is a triannual peer-reviewed academic journal that was established in 1930. It covers social and cultural anthropology of the peoples of Oceania, including Australia, Melanesia, Polynesia, Micronesia, and Southeast Asia. The journal publishes research papers as well as review articles, correspondence, and shorter comments. Occasionally, a special issue is devoted to a single topic, comprising thematically connected collections of papers prepared by a guest editor. The journal is published by Wiley-Blackwell and the editors-in-chief are Jadran Mimica (University of Sydney) and Sally Babidge (University of Queensland). Past editors include Alfred Radcliffe-Brown, Adolphus Peter Elkin, Raymond Firth Sir Raymond William Firth (25 March 1901 – 22 February 2002) was an ethnologist from New Zealand. As a result of Firth's ethnographic work, actual behaviour of societies (social organization) is separated from the idealized rules of behavio ... and Nancy Williams. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smith, Elder & Co
Smith, Elder & Co., alternatively Smith, Elder, and Co. or Smith, Elder and Co. was a British publishing company which was most noted for the works it published in the 19th century. It was purchased by John Murray in the early 1900s, its archive now kept as part of the John Murray Archive at the National Library of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland. History The firm was founded by George Smith (1789–1846) and Alexander Elder (1790–1876) and successfully continued by George Murray Smith (1824–1901). They are known to have published as early as 1826. They are notable for producing the first edition of the ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB''). The firm achieved its first major success with the publication of Charlotte Brontë's ''Jane Eyre'' in 1847, under the pseudonym of "Currer Bell". Other major authors published by the firm included Robert Browning, George Eliot, Elizabeth Gaskell, Thomas Hardy, Richard Jefferies, George MacDonald, Charles Reade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales Government
The Government of New South Wales, also known as the NSW Government, is the executive state government of New South Wales, Australia. The government comprises 11 portfolios, led by a ministerial department and supported by several agencies. There are also a number of independent agencies that fall under a portfolio but remain at arms-length for political reasons, such as the Independent Commission Against Corruption and Electoral Commission. The state Executive Council, consisting of the governor and senior ministers, exercises the executive authority through the relevant portfolio. The current government is held by the state Labor Party, led by Premier Chris Minns. Minns succeeded Dominic Perrottet from the Liberal Party on 28 March 2023 following the state election. Ministries The following individuals serve as government ministers, appointed by the Governor, on behalf of the Monarch, and at the recommendation of the Premier. The full ministry was announced on 4 April 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and woody fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, banksias are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of species ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doryanthes Excelsa
''Doryanthes excelsa'', commonly known as the gymea lily, is a flowering plant in the family Doryanthaceae that is endemic to coastal areas of New South Wales near Sydney. It has sword-like leaves more than long and it grows a flower spike up to high. The apex of the spike bears a large cluster of bright red flowers, each across. Its common name is derived from ''kai'mia'' (anglicised as ''Gymea'') in the indigenous Dharawal language. The Sydney suburbs of Gymea and Gymea Bay are named after the lily. Description Gymea lilies have a rosette of large numbers of sword-shaped, strap like leaves long and wide. The leaves are bright green, fibrous and glabrous. In winter the flower spike grows from the centre of the rosette until it is up to high, bearing shorter leaves up to long. At the top of the spike, a head of flowers in diameter develops, each flower being bright red, trumpet-shaped and about long. The head is surrounded by reddish-brown bracts, sometimes making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Parry (explorer)
Sir William Edward Parry (19 December 1790 – 8 July 1855) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer best known for his 1819–1820 expedition through the Parry Channel, probably the most successful in the long quest for the Northwest Passage, until it was finally negotiated by Roald Amundsen in 1906. In 1827, Parry attempted one of the earliest expeditions to the North Pole. He reached 82° 45' N, setting a record for human exploration Farthest North that stood for nearly five decades before being surpassed at 83° 20' N by Albert Hastings Markham in 1875. Early life Parry was born in Bath, Somerset, the son of Caleb Hillier Parry and Sarah Rigby. He was educated at King Edward's School. At the age of thirteen he joined the flagship of Admiral Sir William Cornwallis in the Channel fleet as a first-class volunteer, in 1806 became a midshipman, and in 1810 received promotion to the rank of lieutenant in the frigate ''Alexander'', which spent th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |