|
Witchaven Gameplay
''Witchaven'' (usually pronounced ) is a dark fantasy first-person shooter video game developed by Capstone Software and published by Intracorp Entertainment in 1995. Its sword-and-sorcery themed story tasks the knight Grondoval with a quest to seek out and destroy a lair of witches in their titular fortress, fighting hordes of hostile monsters along the way. ''Witchaven'' features action role-playing elements such as leveling, as well as an emphasis on melee combat. Its code was based upon an early version of the nascent Build engine. The game received overall mixed reviews, such as praise for its atmosphere and gory combat, but criticism for some aspects of gameplay. It was followed by a sequel titled '' Witchaven II: Blood Vengeance'' in 1996. Gameplay Although the game is considered a first-person shooter (FPS), the game has several role-playing video game (RPG) elements, including character progression by acquiring experience points (EXP) (gained by defeating enemies and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Kelly (artist)
Ken W. Kelly (May 19, 1946 – June 2, 2022) was an American fantasy artist. Over his 50-year career, he focused in particular on paintings in the sword and sorcery and heroic fantasy subgenres. Biography Kelly was the nephew of Frank Frazetta's wife Eleanor "Ellie" Frazetta ( Kelly; 1935–2009). Early in his career he was able to study the paintings of Frank Frazetta in the latter's studio. In the early 1970s he did a couple of cover paintings for ''Castle of Frankenstein'' magazine. Throughout the 1970s he was one of the foremost cover artists on Warren Publishing's ''Creepy'' and ''Eerie'' magazines. He depicted Conan the Barbarian, Tarzan and the rock acts KISS, Manowar, Sleepy Hollow, Rainbow, and Ace Frehley. His work often portrays exotic, enchanted locales and primal battlefields. He developed the artwork for Coheed and Cambria's album '' Good Apollo, I'm Burning Star IV, Volume Two: No World for Tomorrow'', and a painting of his was used as the cover art for Ala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witchaven Gameplay
''Witchaven'' (usually pronounced ) is a dark fantasy first-person shooter video game developed by Capstone Software and published by Intracorp Entertainment in 1995. Its sword-and-sorcery themed story tasks the knight Grondoval with a quest to seek out and destroy a lair of witches in their titular fortress, fighting hordes of hostile monsters along the way. ''Witchaven'' features action role-playing elements such as leveling, as well as an emphasis on melee combat. Its code was based upon an early version of the nascent Build engine. The game received overall mixed reviews, such as praise for its atmosphere and gory combat, but criticism for some aspects of gameplay. It was followed by a sequel titled '' Witchaven II: Blood Vengeance'' in 1996. Gameplay Although the game is considered a first-person shooter (FPS), the game has several role-playing video game (RPG) elements, including character progression by acquiring experience points (EXP) (gained by defeating enemies and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankh
The ankh or key of life is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol used to represent the word for "life" and, by extension, as a symbol of life itself. The ankh has a T-shape topped by a droplet-shaped loop. It was used in writing as a triliteral sign, representing a sequence of three consonants, ''Ꜥ-n-ḫ''. This sequence was found in several Egyptian words, including the terms for "mirror", "floral bouquet", and "life". The symbol often appeared in Egyptian art as a physical object representing either life or related life-giving substances such as air or water. Commonly depicted in the hands of ancient Egyptian deities, sometimes being given by them to the pharaoh, it represents their power to sustain life and to revive human souls in the afterlife. The ankh was a widespread decorative motif in ancient Egypt, also used decoratively by neighbouring cultures. Copts adapted it into the ''crux ansata'', a shape with a circular rather than droplet loop, and used it as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potion
A potion is a liquid "that contains medicine, poison, or something that is supposed to have magic powers." It derives from the Latin word ''potio'' which refers to a drink or the act of drinking. The term philtre is also used, often specifically to describe a love potion, a potion that is believed to induce feelings of love or attraction in the one who drinks it. Throughout history, there have been several types of potions for a range of purposes. Reasons for taking potions have included curing an illness, Elixir of life, securing immortality, and trying to inspire love. These potions, while often ineffective or poisonous, occasionally had some degree of medicinal benefits depending on what they sought to fix and the type and amount of ingredients used. Common ingredients in historical potions included Lytta vesicatoria, Spanish fly, Solanaceae, nightshade plants, cannabis, and opium. During the 17th to 19th century, it was common in Europe to see peddlers offering potions fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invocation
Invocation is the act of calling upon a deity, spirit, or supernatural force, typically through prayer, ritual, or spoken formula, to seek guidance, assistance, or presence. It is a practice found in numerous religious, spiritual, and esoteric traditions, where it serves to establish a connection between the human and the divine or metaphysical realms. Invocation can be directed toward a singular deity, multiple deities, spirits, or abstract forces, and may involve formal liturgies, spontaneous prayers, chants, or symbolic actions. Unlike evocation, which is generally understood as calling a spirit to appear outside the practitioner, invocation often implies inviting the entity to be present within or to closely align with the practitioner. The purpose of invocation varies across cultural and religious contexts. In many traditions, it is used to request divine intervention, protection, wisdom, or blessings in personal or communal matters. Invocation may also serve to con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scroll
A scroll (from the Old French ''escroe'' or ''escroue''), also known as a roll, is a roll of papyrus, parchment, or paper containing writing. Structure A scroll is usually partitioned into pages, which are sometimes separate sheets of papyrus or parchment glued together at the edges. Scrolls may be marked divisions of a continuous roll of writing material. The scroll is usually unrolled so that one page is exposed at a time, for writing or reading, with the remaining pages rolled and stowed to the left and right of the visible page. Text is written in lines from the top to the bottom of the page. Depending on the language, the letters may be written left to right, right to left, or alternating in direction (boustrophedon). History Scrolls were the first form of editable record keeping texts, used in Eastern Mediterranean ancient Egyptian civilizations. Parchment scrolls were used by the Israelites among others before the codex or bound book with parchment pages was invented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge), is a two-handed polearm that was in prominent use from the 13th to 16th centuries. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It may have a hook or thorn on the back of the axe blade for grappling mounted combatants and protecting allied soldiers, typically musketeers. The halberd was usually long. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from Middle High German ''halm'' (handle) and ''barte'' (battleaxe) joined to form ''helmbarte''. Troops that used the weapon were called halberdiers or halbardiers. The word has also been used to describe a weapon of the early Bronze Age in Western Europe. This consisted of a blade mounted on a pole at a right angle. History The halberd is first mentioned (as ) in a work by 13th-century German poet Konrad von Würzburg. John of Winterthur described it as a new weapon used by the Swiss at the Battle of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longsword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximately . The "longsword" type exists in a morphological continuum with the medieval knightly sword and the Renaissance-era Zweihänder. It was prevalent during the Late Middle Ages, late medieval and Renaissance periods (approximately 1350 to 1550), with early and late use reaching into the 11th and 17th centuries. Names English The longsword has many names in the English language, which, aside from variant spellings, include terms such as "bastard sword" and "hand-and-a-half sword." Of these, "bastard sword" is the oldest, its use being contemporaneous with the weapon's heyday. The French ' and the English "bastard sword" originate in the 15th or 16th century, originally in the general sense of "irregular sword, sword of uncertain orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pike (weapon)
A pike is a long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the early modern warfare, early modern period, and wielded by infantry, foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped muskets. The pike was particularly well known as the primary weapon of Spanish tercios, Swiss mercenary, German Landsknecht units and French sans-culottes. A similar weapon, the sarissa, had been used in classical antiquity, antiquity by Alexander the Great's Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian phalanx infantry. Design The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th-century military writer John Smith (High Sheriff of Kent), Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadsword
The basket-hilted sword is a sword type of the early modern era characterised by a basket-shaped guard that protects the hand. The basket hilt is a development of the quillons added to swords' crossguards since the Late Middle Ages. This variety of sword is also sometimes referred to as the broadsword, though this term may also be applied loosely and imprecisely to other swords. The basket-hilted sword was generally in use as a military sword. A true broadsword possesses a double-edged blade, while similar wide-bladed swords with a single sharpened edge and a thickened back are called backswords. Various forms of basket-hilt were mounted on both broadsword and backsword blades. One of the weapon types in the modern German dueling sport of ("academic fencing") is the basket-hilted . Nomenclature The designation "broadsword" is ambiguous, and can refer to many different types of sword. Though attestations of "broad swords" date from the 11th century, these simply refer to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
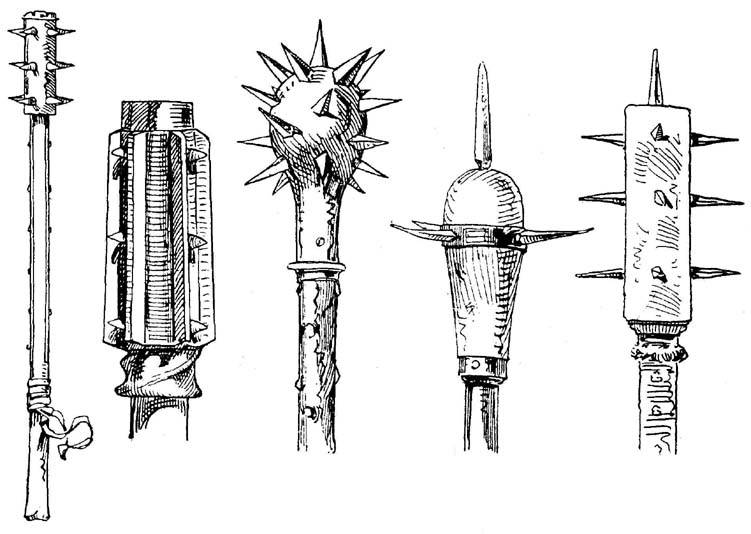
Morning Star (weapon)
A morning star () is any of several medieval club-like weapons consisting of a shaft with an attached ball adorned with one or more spikes. Such weapons provided their wielders with a combination of blunt-force and puncture attack to kill or wound an enemy. History The morning star first came into widespread use around the beginning of the fourteenth century, particularly in Germany where it was known as ''Morgenstern''. The term is often confused with the military flail (''fléau d'armes'' in French and ''Kriegsflegel'' in German), which typically consists of a wooden shaft joined by a length of chain to one or more iron-shod wooden bars. (Heavy sword pommels have also been used as weights.) However, there are few depictions of such a ball-and-chain flail from the period, so the weapon of this type appears to have been uncommon. Design The morning star is a medieval weapon consisting of a spiked head mounted on a shaft, resembling a mace, usually with a long spike exten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hack And Slash
Hack and slash, also known as hack and slay (H&S or HnS) or slash 'em up, refers to a type of gameplay that emphasizes combat with melee-based weapons (such as swords or blades). They may also feature projectile-based weapons as well (such as guns) as secondary weapons. It is a sub-genre of beat 'em up games, which focuses on melee combat, usually with swords. The term "hack and slash" was originally used to describe a play style in tabletop role-playing games, carrying over from there to MUDs, massively multiplayer online role-playing games, and role-playing video games. In arcade and console style action video games, the term has an entirely different usage, specifically referring to action games with a focus on real-time combat with hand-to-hand weapons as opposed to guns or fists. The two types of hack-and-slash games are largely unrelated, though action role-playing games may combine elements of both. Types of hack-and-slash games Action video games In the context of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |