|
WinDVD
WinDVD (owned by Alludo, formerly Corel Corporation, which acquired InterVideo in 2006) is a commercial DVD video player software for Microsoft Windows. Features and functions Features and functions supported by InterVideo WinDVD version 8.0 during video/movie and audio/music playback are: *Supported video formats/codecs: MPEG-1, MPEG-2 (including HD support), MPEG-TS, DVD-Video, MiniDVD, MPEG-4 ASP (like Xvid and DivX, including DivX Pro), H.264/MPEG-4 AVC, VC-1, WMV HD, DVD-VR, DVD+VR, 3GPP and 3GPP2, QuickTime, RealMedia/RealVideo *Supported audio formats/codecs: WAV, MP3, AAC, LPCM, MLP Lossless, Dolby Digital (5.1) and Dolby Digital (2.0), Dolby Digital EX, DTS 2.0 and 5.1, DTS Neo:6, DTS 96/24, DTS-ES Discrete, RealMedia/RealAudio eeds citation/sup> Video playback * TrimensionDNM interpolates frames to give smooth playback * Smooth Reverse Playback smooth reverse/rewind playback without dropping frames * Video Desktop display subpanel to let the movie play ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alludo
Cascade Parent Limited, trade name, doing business as Alludo ( ), is a Canadian software company headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario, specializing in graphics processing. Formerly called the Corel Corporation ( ; from the abbreviation "Cowpland Research Laboratory"), the company is known for producing software titles such as CorelDRAW, and for acquiring AfterShot Pro, PaintShop Pro, Corel Painter, Painter, Corel VideoStudio, Video Studio and WordPerfect. History Corel was founded by Michael Cowpland in 1985 as a research laboratory. Michael Cowpland was CEO of Mitel. Mitel needed writing and creative design programs to enhance the company product line. Corel products were born. Additional products were added. The company had great success early in the Dot-com bubble, high-tech boom of the 1990s and early 2000s with the product CorelDRAW, and became, for a time, the biggest software company in Canada. In 1996, it acquired Novell WordPerfect and started competing with the thought of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InterVideo
InterVideo was a software publisher specializing in multimedia-related programs. InterVideo's products include video capture, video capturing, video editing, DVD authoring, Optical disc authoring, CD/DVD recording, film distribution, and video playback. Its best known product was WinDVD. InterVideo marketed its products to the retail market as well as to original equipment manufacturers. The company was headquartered in Fremont, California. InterVideo HandHeld Business Unit developed multimedia software solutions in the mobile and Embedded system, embedded multimedia market. Their unique iMobi technologies are embedded widely on Smartphones, GPS units, car entertainment solutions and portable entertainment devices. History On 13 August 2005, InterVideo acquired Ulead Systems for approximately $68 million and announced its merger with Ulead on July 9, 2006. On 28 August 2006, Corel Corporation announced that it would acquire InterVideo for about $196 million. Closure On December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD-Video
DVD-Video is a consumer video format used to store digital video on DVDs. DVD-Video was the dominant consumer home video format in most of the world in the 2000s. As of 2024, it competes with the high-definition Blu-ray Disc, while both receive competition as delivery methods by streaming services such as Netflix and Disney+. Discs using the DVD-Video specification require a DVD drive and an MPEG-2 decoder (e.g., a DVD player, or a computer DVD drive with a software DVD player). Commercial DVD movies are encoded using a combination of MPEG-2 compressed video and audio of varying formats (often multi-channel formats as described below). Typically, the data rate for DVD movies ranges from 3 to 9.5 Mbit/s, and the bit rate is usually adaptive. DVD-Video was first available in Japan on October 19, 1996 (with major releases beginning December 20, 1996), followed by a release on March 24, 1997, in the United States. The DVD-Video specification was created by the DVD Forum a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Interpolation
Motion interpolation, motion-compensated frame interpolation (MCFI), or frame generation is a form of video processing in which intermediate film, video or animation frames are synthesized between existing ones by means of interpolation, in an attempt to make animation more fluid, to compensate for display motion blur, and for fake slow motion effects. Hardware applications Devices Motion interpolation is a common, optional feature of various modern video devices such as HDTVs and AV receivers, aimed at increasing perceived framerate or alleviating display motion blur, a common problem on LCD flat-panel displays. Difference from display framerate A display's output refresh rate, input drive signal framerate, and original content framerate, are not always equivalent. In other words, a display capable of or operating at a high framerate does not necessarily mean that it can or must perform motion interpolation. For example, a TV running at 120 Hz and displaying 24 FPS con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprietary Software
Proprietary software is computer software, software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting their freedoms. Proprietary software is a subset of non-free software, a term defined in contrast to free and open-source software; non-commercial licenses such as CC BY-NC are not deemed proprietary, but are non-free. Proprietary software may either be closed-source software or source-available software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s, computers—especially large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than Sales, sold. Service and all software available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuickTime
QuickTime (or QuickTime Player) is an extensible multimedia architecture created by Apple, which supports playing, streaming, encoding, and transcoding a variety of digital media formats. The term ''QuickTime'' also refers to the QuickTime Player front-end media player application, which is built-into macOS, and was formerly available for Windows. QuickTime was created in 1991, when the concept of playing digital video directly on computers was "groundbreaking." QuickTime could embed a number of advanced media types, including panoramic images (called QuickTime VR) and Adobe Flash. Over the 1990s, QuickTime became a dominant standard for digital multimedia, as it was integrated into many websites, applications, and video games, and adopted by professional filmmakers. The QuickTime File Format became the basis for the MPEG-4 standard. During its heyday, QuickTime was notably used to create the innovative ''Myst'' and '' Xplora1'' video games, and to exclusively distribute mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RealAudio
RealAudio, also spelled Real Audio, is a proprietary audio format developed by RealNetworks and first released in April 1995. It uses a variety of audio codecs, ranging from low-bitrate formats that can be used over dialup modems, to high-fidelity formats for music. It can be used as a streaming audio format, that is played at the same time as it is downloaded. In the past, many internet radio stations used RealAudio to stream their programming over the internet in real time. In recent years, however, the format has become less common and has given way to more popular audio formats. RealAudio was heavily used by the BBC websites until 2009, though it was discontinued due to its declining use. BBC World Service, the last of the BBC websites to use RealAudio, discontinued its use in March 2011. File extensions RealAudio files were originally identified by a filename extension of .ra (for Real Audio). In 1997, RealNetworks also began offering a video format called RealVideo. The com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Theater System
DTS, Inc. (originally Digital Theater Systems) is an American company. DTS company makes multichannel audio technologies for film and video. Based in Calabasas, California, the company introduced its DTS technology in 1993 as a competitor to Dolby Laboratories, incorporating DTS in the film ''Jurassic Park'' (1993). The DTS product is used in surround sound formats for both commercial/theatrical and consumer-grade applications. It was known as The Digital Experience until 1995. DTS licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers. DTS, Inc. was acquired by Tessera Technologies Inc. in December 2016 and combined under the newly created Tessera Holding Corporation. The combined company was renamed to Xperi Corporation in February 2017. History DTS was founded by Terry Beard, an audio engineer and Caltech graduate. Beard, speaking to a friend of a friend, was able to get in touch with Steven Spielberg to audition a remastering of Spielberg's film ''Close Encounters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DTS 96/24
DTS or DTs may refer to: Media and entertainment * ''Dictionnaire du théâtre en Suisse'', an encyclopedia * '' Formula 1: Drive to Survive'', a Netflix documentary series Science and technology * Delirium tremens (DTs), the symptoms associated with alcohol withdrawal * DTS (sound system), a group of digital sound technologies and a company of the same name * Distributed temperature sensing, an optoelectronic temperature sensing device * Distributed transmission system, in broadcasting, as a form of single-frequency network * Diplomatic Telecommunications Service, a U.S. Department of State telecommunications network * Digital tomosynthesis, a medical imaging technique Computing * Dispatcher training simulator, a computer system for training operators of electrical power grids * Data Transformation Services, a Microsoft database tool * Digital Temperature Sensor, part of Intel's DTS/PECI * Discoverable Taxonomy Set, part of Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DTS Coherent Acoustics
DTS, Inc. (originally Digital Theater Systems) is an American company. DTS company makes multichannel audio technologies for film and video. Based in Calabasas, California, the company introduced its DTS technology in 1993 as a competitor to Dolby Laboratories, incorporating DTS in the film ''Jurassic Park'' (1993). The DTS product is used in surround sound formats for both commercial/theatrical and consumer-grade applications. It was known as The Digital Experience until 1995. DTS licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers. DTS, Inc. was acquired by Tessera Technologies Inc. in December 2016 and combined under the newly created Tessera Holding Corporation. The combined company was renamed to Xperi Corporation in February 2017. History DTS was founded by Terry Beard, an audio engineer and Caltech graduate. Beard, speaking to a friend of a friend, was able to get in touch with Steven Spielberg to audition a remastering of Spielberg's film '' Close Encou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
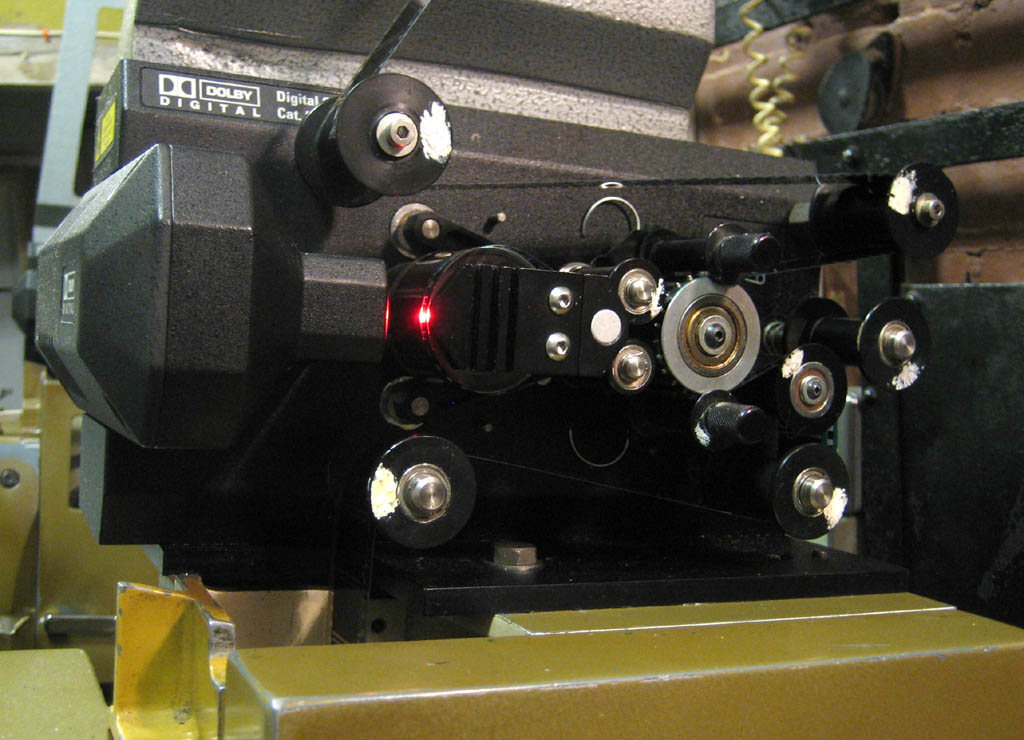
Dolby Digital EX
Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3 (see below), is the name for a family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, it is lossy compression (except for Dolby TrueHD). The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35 mm film prints. It has since also been used for TV broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray discs and game consoles. Dolby AC-3 was the original version of the Dolby Digital codec. The basis of the Dolby AC-3 multi-channel audio coding standard is the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT), a lossy audio compression algorithm. It is a modification of the discrete cosine transform (DCT) algorithm, which was proposed by Nasir Ahmed in 1972 for image compression. The DCT was adapted into the MDCT by J.P. Princen, A.W. Johnson and Alan B. Bradley at the University of Surrey in 1987. Dolby Laboratories adapted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3 (see below), is the name for a family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, it is lossy compression (except for Dolby TrueHD). The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35 mm film prints. It has since also been used for TV broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray discs and game consoles. Dolby AC-3 was the original version of the Dolby Digital codec. The basis of the Dolby AC-3 multi-channel audio coding standard is the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT), a lossy audio compression algorithm. It is a modification of the discrete cosine transform (DCT) algorithm, which was proposed by Nasir Ahmed in 1972 for image compression. The DCT was adapted into the MDCT by J.P. Princen, A.W. Johnson and Alan B. Bradley at the University of Surrey in 1987. Dolby Laboratories adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |