|
Willis Ridge
Willis Ridge () is a narrow-crested ridge extending west–east between Aster Glacier and Sowers Glacier on the east side of Craddock Massif, Sentinel Range. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 2006 after Michael J. Willis, Ohio State University geologist in Antarctica for 7 field seasons, 1997–2006 (currently at the University of Colorado), including research at Siple Dome Siple Dome () is an ice dome approximately 100 km wide and 100 km long, located 130 km east of Siple Coast in Antarctica. Charles Bentley and Robert Thomas established a "strain rosette" on this feature to determine ice movement in ... and the Whillans, Bindschadler and MacAyeal Ice Streams. Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aster Glacier
Aster Glacier () is an Antarctic glacier descending the east slope of Craddock Massif and flowing between Elfring Peak and Willis Ridge to Thomas Glacier in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 2006, after Richard Aster, Professor of Geophysics and Department Head of Geosciences at Colorado State University, whose research in Antarctica includes volcanological studies at the Mount Erebus volcano observatory on Ross Island, glaciological, oceanic, and tectonic seismic source studies, seismic tomography, ice shelf studies, and the coupling of solid Earth geophysics and Antarctic ice sheet evolution. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sowers Glacier
Sowers Glacier () is a glacier that flows from the prominent cirque on the east side of Craddock Massif and continues between Willis Ridge on the north, and Sanchez Peak and Stolnik Peak on the south, to join Thomas Glacier north of Mount Osborne, in the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The glacier was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 2006 after Todd A. Sowers, Environment Institute, Department of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University; United States Antarctic Program (USAP) investigator of climate change and abrupt climate change, using isotopes and atmospheric gases, including greenhouse gases, from the ice core record, 1991–2006. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
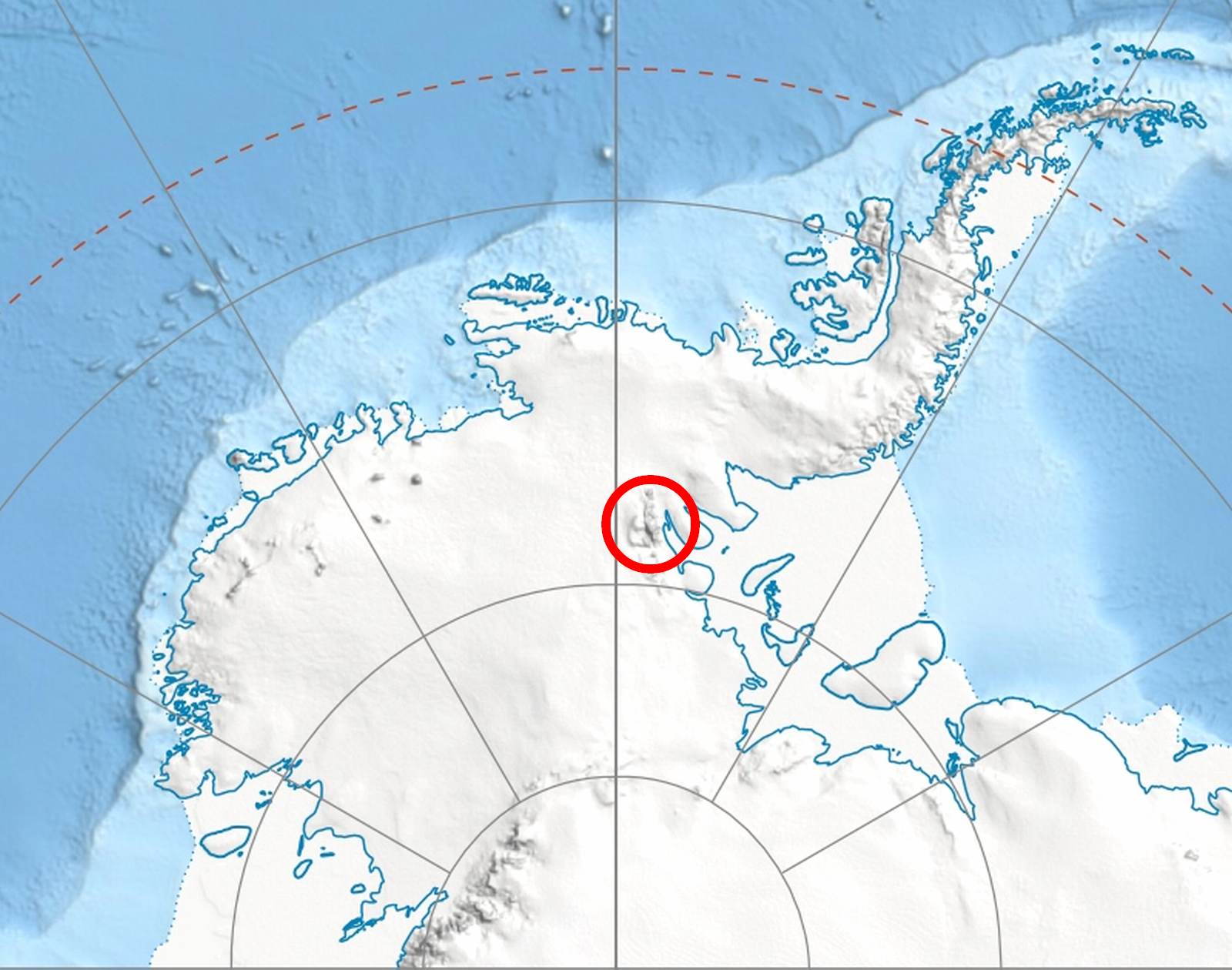
Craddock Massif
Craddock Massif is a mountain massif in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, in the Chilean claim of West Antarctica. Location and highest point Craddock Massif is located at the southeastern side of Vinson Massif, between Hammer Col and Karnare Col linking it to Vinson Massif and the southern Sentinel Range respectively. The highest point of Craddock Massif is Mount Rutford, a sharp peak that rises to . The Craddock Massif also includes (from north to south) Bugueño Pinnacle, Rada Peak and Mount Craddock. Discovery and naming Sentinel Range was first sighted and photographed from the air on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth. The entire range, including Craddock Massif, was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from aerial photography taken by the U.S. Navy, 1958–61. This massif was originally named "Mount Craddock" by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) in 1965, but subsequent maps limited the name to the massif's southernmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Range
The Sentinel Range is a major mountain range situated northward of Minnesota Glacier and forming the northern half of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The range trends NNW-SSE for about and is 24 to 48 km (15 to 30 mi) wide. Many peaks rise over and Vinson Massif (4892 m) in the southern part of the range is the highest elevation on the continent.Sentinel Range. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer. Sentinel Range comprises a main ridge (featuring Vinson Massif in its southern portion) and a number of distinct heights, ridges and mountains on its east side, including (south to north) Owen Ridge, |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio State University
The Ohio State University, commonly called Ohio State or OSU, is a public land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio. A member of the University System of Ohio, it has been ranked by major institutional rankings among the best public universities in the United States. Founded in 1870 as the state's land-grant university and the ninth university in Ohio with the Morrill Act of 1862, Ohio State was originally known as the Ohio Agricultural and Mechanical College and focused on various agricultural and mechanical disciplines, but it developed into a comprehensive university under the direction of then-Governor and later U.S. president Rutherford B. Hayes, and in 1878, the Ohio General Assembly passed a law changing the name to "the Ohio State University" and broadening the scope of the university. Admission standards tightened and became greatly more selective throughout the 2000s and 2010s. Ohio State's political science department and faculty have greatly con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Colorado
The University of Colorado (CU) is a system of public universities in Colorado. It consists of four institutions: University of Colorado Boulder, University of Colorado Colorado Springs, University of Colorado Denver, and the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus. It is governed by the elected, nine-member board of regents. Campuses * The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder) is the flagship university of the University of Colorado System in Boulder, Colorado. Founded in 1876, the university has more than 33,000 undergraduate and graduate students. It offers more than 2,500 courses in more than 150 areas of study through its nine colleges and schools. * The University of Colorado Colorado Springs (UCCS) is the fastest growing of the three campuses with an undergraduate and graduate student population of about 12,000 students. It offers 45 bachelor's, 22 master's, and five doctoral degree programs through its six colleges. The campus is located in central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siple Dome
Siple Dome () is an ice dome approximately 100 km wide and 100 km long, located 130 km east of Siple Coast in Antarctica. Charles Bentley and Robert Thomas established a "strain rosette" on this feature to determine ice movement in 1973–74. They referred to the feature as Siple Dome because of its proximity to Siple Coast. Siple Dome ice core The Siple Dome ice core project (79.468° S 112.086° W) was conducted by the United States National Science Foundation. The deepest ice was recovered in 1999 from 974 m, with an age of 97,600 years. It is best known for the poorly-explained steps in water isotopes during the deglacial, which are unique to this core and may indicate a rapid decrease in the surface elevation of the adjoining ice streams during the deglacial and a record of atmospheric carbon dioxide. The Chief Scientist was Kendrick Taylor. Radar surveys of internal ice structure In the 1990s a team from the University of Washington and St Olaf College su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whillans Ice Stream
Whillans Ice Stream () is a glaciological feature of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, formerly known as Ice Stream B, renamed in 2001 in honor of Ohio State University glaciologist Ian Whillans. Research Whillans Ice Stream is one of about a half-dozen large, fast-moving rivers of ice pouring from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet into the Ross Ice Shelf. The ice stream is the subject of different glaciological studies, one of which is looking at subglacial lakes that researchers believe may be speeding the movement of the ice as they periodically fill and drain. Other researchers, also funded by the National Science Foundation, reported in the June 5, 2008 issue of the journal ''Nature'' that, from seismological and GPS data, they discovered the Whillans Ice Stream releases two bursts of seismic waves every day, each one equivalent to a magnitude 7 earthquake. The data show that the river of ice moves about a half-meter within approximately 30 minutes, remains still for 12 hours, then mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

