|
Westrichus
''Westrichus'' is an extinct acanthodian which lived in the Lower Permian of Germany. It contains two species: the type species, ''Westrichus kraetschmeri'', and ''Westrichus tholeyi'', the latter of which was previously assigned to ''Acanthodes''. Description This animal was very similar to the genus ''Acanthodes'', however it was equipped with an extremely elongated pelvic fin; it started behind the head and ended just before the retracted anal fin. The appearance, compared to that of ''Acanthodes'', was therefore much more massive, however, the head was smaller. It had length up to , and like all acanthodians, ''Westrichus'' had large spines on its fins. The dorsal fin was small and pointed backward, and was located near the larger and elongated anal fin. Classification First described in 2003 on the basis of fossils found in the Meisenheim Formation, ''Westrichus'' is considered a very specialised acanthodian. Like many derived representatives of the group, ''Westrichus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthodes
''Acanthodes'' (from , 'provided with spines') is an extinct genus of acanthodian fish. Species have been found in Europe, North America, and Asia, spanning the Early Carboniferous to the Early Permian, making it one of the youngest known acanthodian genera. Description The largest species of ''Acanthodes'' like ''Acanthodes confusus'' and ''Acanthodes splendidus'' grew to lengths of at least , while some species like ''Acanthodes ultimus'' were much smaller, reaching a total body length of only .Heidtke, U.H.J.Revision der unterpermischen Acanthodier (Acanthodii: Pisces) des südwestdeutschen Saar-Nahe-Beckens evision of the Early Permian acanthodians (Acanthodii : Pisces ) from the southwest german Saar -Nahe Basin ''Mitt. Pollich.'', 2011, no. 95, pp. 15–41. (In German with translation of species descriptions into English) The body was elongate and had a pair of pectoral fins, an unpaired dorsal fin far back on the body, with an unpaired long ventral/pelvic fin and an anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthodidae
Acanthodiformes (alternatively spelled Acanthodida) is an Order (biology), order of "Acanthodii, acanthodians" which lived from the Early Devonian to the Early Permian. Members of the order have been found Cosmopolitan distribution, worldwide in rocks preserving both Freshwater fish, freshwater and Saltwater fish, marine environments, and are distinguished from other acanthodians by the presence of only a single dorsal fin and dorsal fin spine, and in most members a lack of Tooth, teeth and well-developed Gill raker, gill rakers. Some acanthodiforms are presumed to have fed by Filter feeder, filter-feeding, and had large mouths and Branchial arch, gill arches. While they have been suggested to be close relatives of modern Osteichthyes, bony fish due to similarities in their skulls, recent research indicates that, like other acanthodians, they are more likely to be stem-group Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish. Classification The order was first established by Soviet Union, Sovie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asselian
In the geologic timescale, the Asselian is the earliest geochronologic age or lowermost chronostratigraphic stage of the Permian. It is a subdivision of the Cisuralian Epoch or Series. The Asselian lasted between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Gzhelian (the latest or uppermost subdivision in the Carboniferous) and followed by the Sakmarian. Stratigraphy The Asselian Stage was introduced into scientific literature in 1954, when the Russian stratigrapher V.E. Ruzhenchev split it off from the Artinskian. At the time, the Artinskian still encompassed most of the lower Permian – its current definitions are more restricted. The Asselian is named after the Assel River in the southern Ural Mountains of Kazakhstan and Bashkortostan. The base of the Asselian Stage is equivalent to the base of the Cisuralian Series and the Permian System. It is defined as the point in the stratigraphic record where fossils of the conodont '' Streptognathodus isolatus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
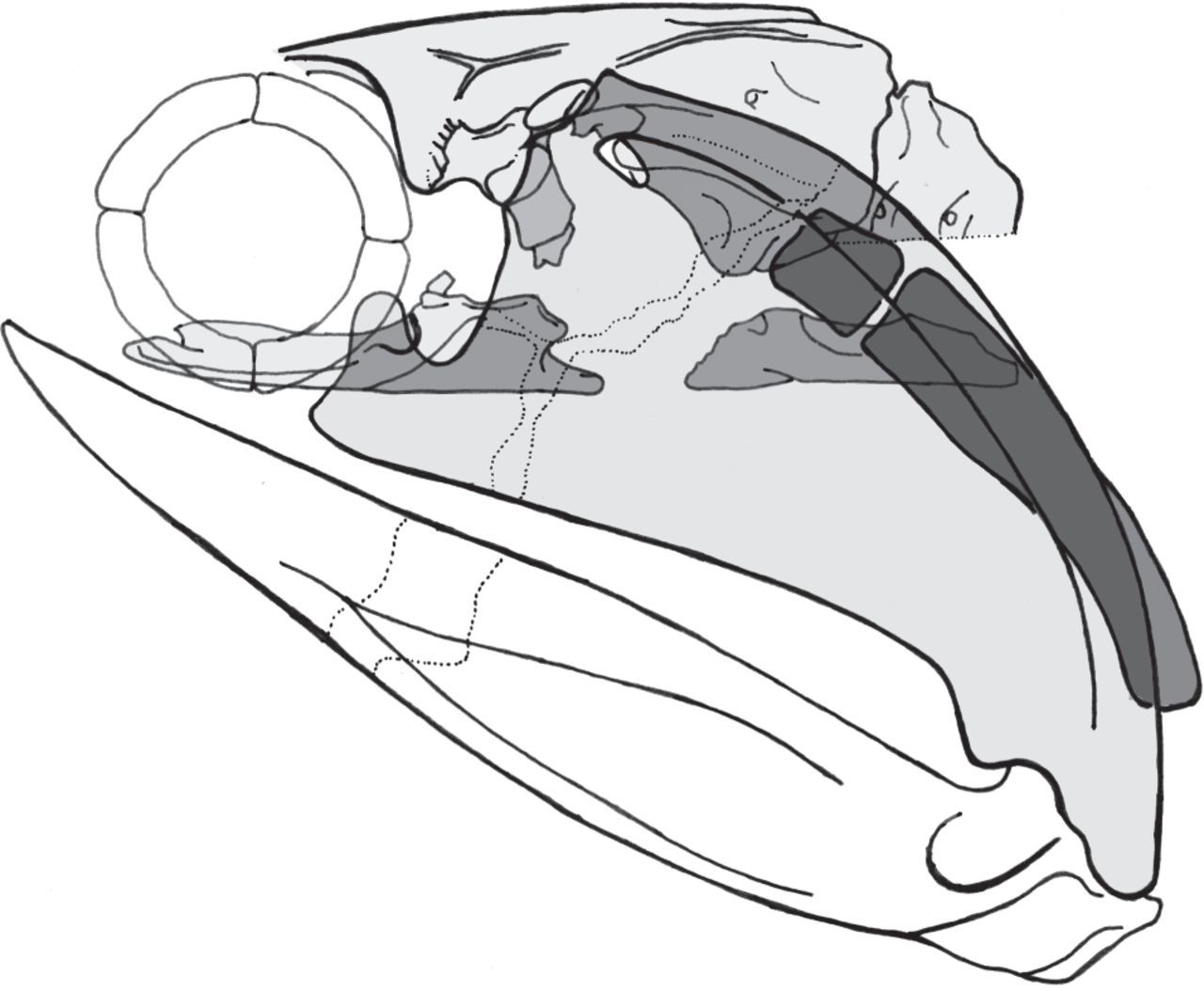
Acanthodii
Acanthodii or acanthodians is an extinct class of gnathostomes (jawed fishes). They are currently considered to represent a paraphyletic grade of various fish lineages basal to extant Chondrichthyes, which includes living sharks, rays, and chimaeras. Acanthodians possess a mosaic of features shared with both osteichthyans (bony fish) and chondrichthyans (cartilaginous fish). In general body shape, they were similar to modern sharks, but their epidermis was covered with tiny rhomboid platelets like the scales of holosteians ( gars, bowfins). The popular name "spiny sharks" is because they were superficially shark-shaped, with a streamlined body, paired fins, a strongly upturned tail, and stout, largely immovable bony spines supporting all the fins except the tail—hence, "spiny sharks". However, acanthodians are not true sharks; their close relation to modern cartilaginous fish can lead them to be considered " stem-sharks". Acanthodians had a cartilaginous skeleton, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of Arthropod, arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic animal, aquatic arthropods including decapoda, decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), ostracoda, seed shrimp, branchiopoda, branchiopods, argulidae, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, Mysida, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the Hexapoda, hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans (oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Cartilaginous Fish Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |