Crustaceans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crustaceans (from
 The body of a crustacean is composed of segments, which are grouped into three regions: the '' cephalon'' or head, the ''pereon'' or
The body of a crustacean is composed of segments, which are grouped into three regions: the '' cephalon'' or head, the ''pereon'' or
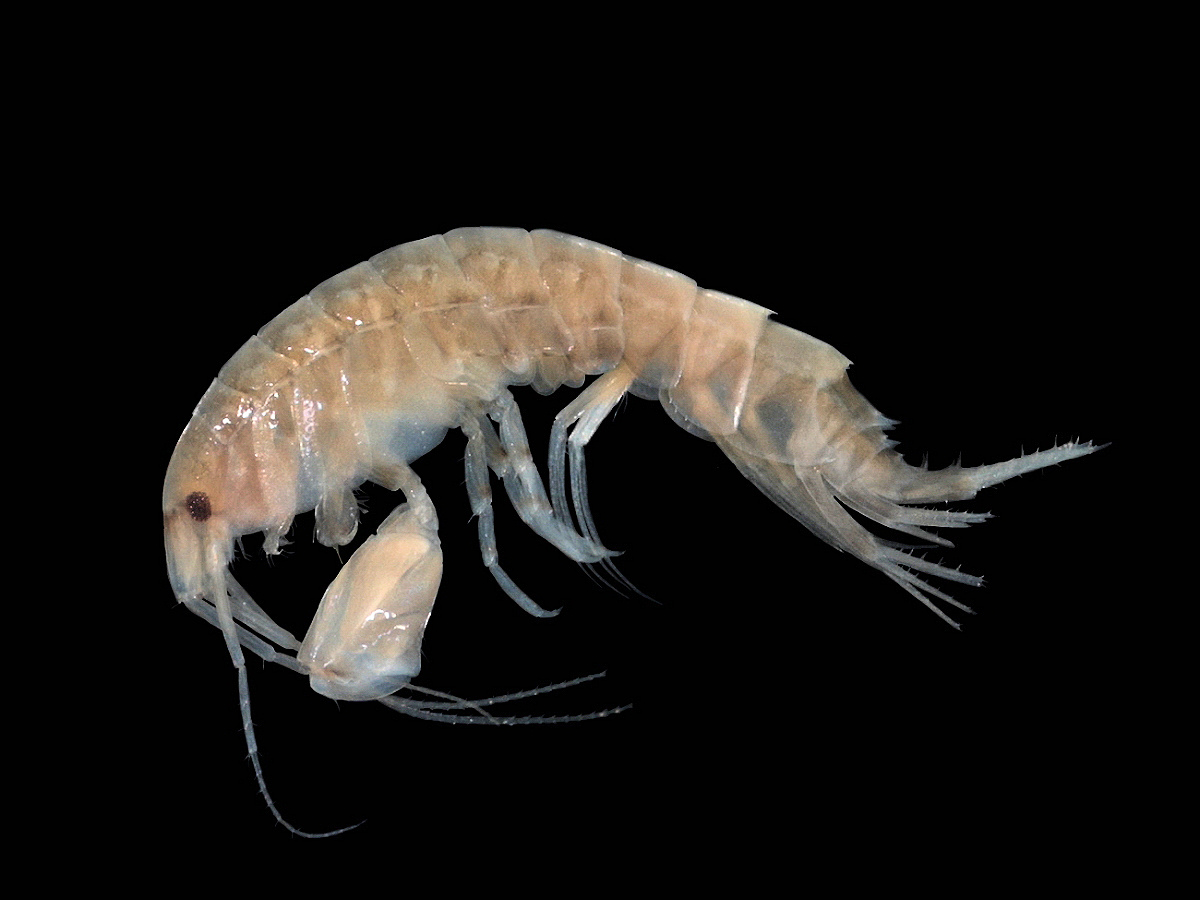 Most crustaceans are aquatic, living in either marine or
Most crustaceans are aquatic, living in either marine or
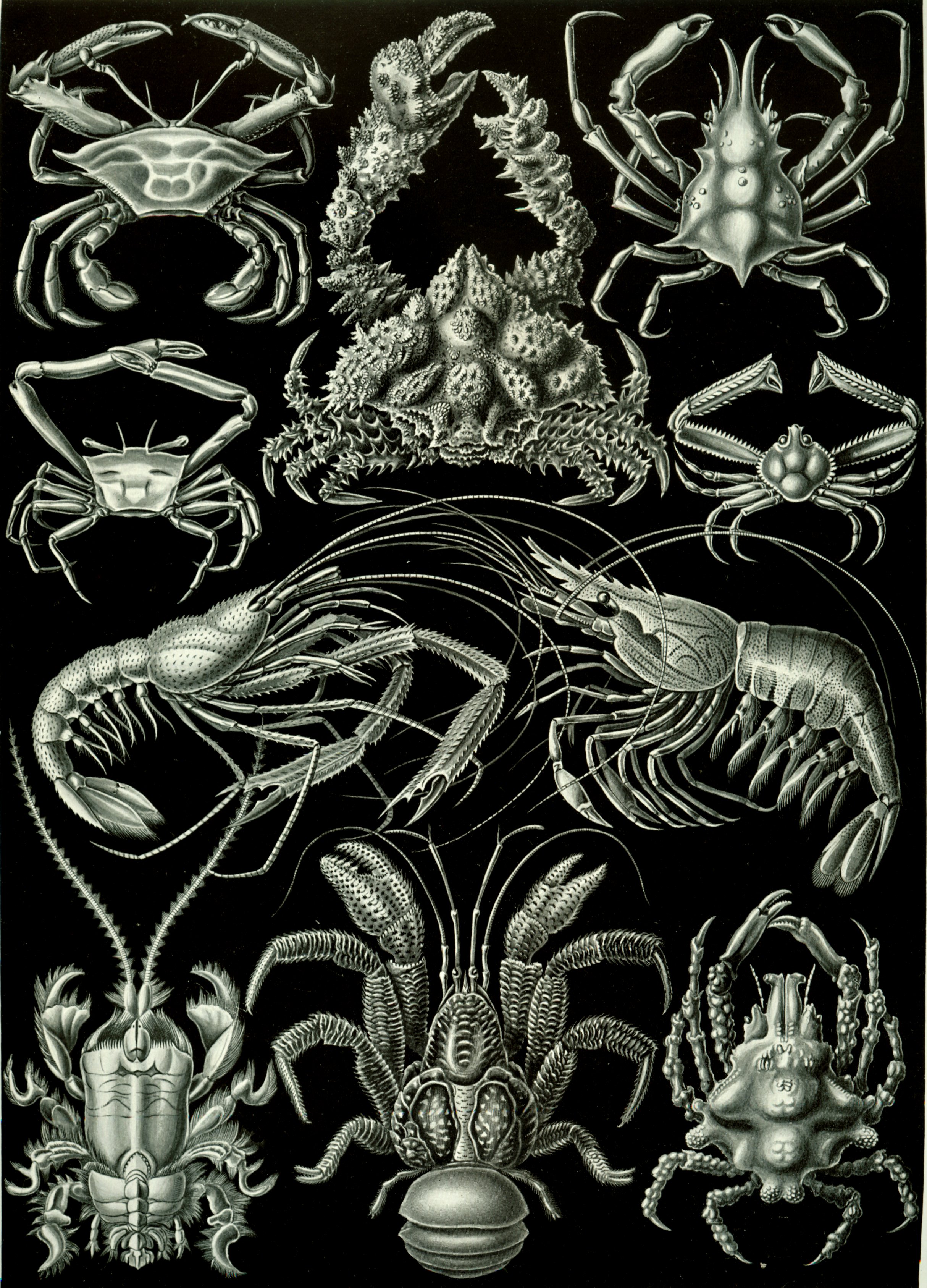


 The name "crustacean" dates from the earliest works to describe the animals, including those of Pierre Belon and Guillaume Rondelet, but the name was not used by some later authors, including
The name "crustacean" dates from the earliest works to describe the animals, including those of Pierre Belon and Guillaume Rondelet, but the name was not used by some later authors, including
 Many crustaceans are consumed by humans, and nearly 10,700,000 tons were harvested in 2007; the vast majority of this output is of decapod crustaceans:
Many crustaceans are consumed by humans, and nearly 10,700,000 tons were harvested in 2007; the vast majority of this output is of decapod crustaceans:
An experimental test of mate choice for red carotenoid coloration in the marine copepod Tigriopus californicus
Crustacea.net, an online resource on the biology of crustaceansCrustacea
:
Crustacea
Tree of Life Web Project
The Crustacean Society
Natural History Collections: Crustacea
Crustaceans (Crustacea) on the shore of SingaporeCrustacea(crabs, lobsters, shrimps, prawns, barnacles)
: Biodiversity Explorer {{Good article Cambrian Series 2 first appearances Extant Cambrian first appearances Paraphyletic groups Pancrustacea
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
animals that constitute one group of arthropods
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
that are traditionally a part of the subphylum
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum.
The taxonomic rank of " subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used th ...
Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s including decapods ( shrimps, prawns, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s, lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopod
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons ...
s, barnacle
Barnacles are arthropods of the subclass (taxonomy), subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea. They are related to crabs and lobsters, with similar Nauplius (larva), nauplius larvae. Barnacles are exclusively marine invertebra ...
s, copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans).
The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, crustaceans have an exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their larval forms, such as the nauplius stage of branchiopods and copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s.
Most crustaceans are free-living aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
s, but some are terrestrial (e.g. woodlice
Woodlice are terrestrial isopods in the suborder Oniscidea. Their name is derived from being often found in old wood, and from louse, a parasitic insect, although woodlice are neither parasitic nor insects.
Woodlice evolved from marine isopods ...
, sandhoppers), some are parasitic (e.g. Rhizocephala, fish lice, tongue worms) and some are sessile (e.g. barnacle
Barnacles are arthropods of the subclass (taxonomy), subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea. They are related to crabs and lobsters, with similar Nauplius (larva), nauplius larvae. Barnacles are exclusively marine invertebra ...
s). The group has an extensive fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
, reaching back to the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
. More than 7.9 million tons of crustaceans per year are harvested by fishery or farming for human consumption, consisting mostly of shrimp and prawns. Krill and copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s are not as widely fished, but may be the animals with the greatest biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
on the planet, and form a vital part of the food chain. The scientific study of crustaceans is known as carcinology (alternatively, ''malacostracology'', ''crustaceology'' or ''crustalogy''), and a scientist who works in carcinology is a carcinologist.
Anatomy
 The body of a crustacean is composed of segments, which are grouped into three regions: the '' cephalon'' or head, the ''pereon'' or
The body of a crustacean is composed of segments, which are grouped into three regions: the '' cephalon'' or head, the ''pereon'' or thorax
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
, and the ''pleon'' or abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the gut, belly, tummy, midriff, tucky, or stomach) is the front part of the torso between the thorax (chest) and pelvis in humans and in other vertebrates. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal ...
. The head and thorax may be fused together to form a cephalothorax, which may be covered by a single large carapace. The crustacean body is protected by the hard exoskeleton
An exoskeleton () . is a skeleton that is on the exterior of an animal in the form of hardened integument, which both supports the body's shape and protects the internal organs, in contrast to an internal endoskeleton (e.g. human skeleton, that ...
, which must be moulted for the animal to grow. The shell around each somite can be divided into a dorsal tergum
A ''tergum'' (Latin for "the back"; : ''terga'', associated adjective tergal) is the dorsal ('upper') portion of an arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton wi ...
, ventral sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
and a lateral pleuron. Various parts of the exoskeleton may be fused together.
Each somite, or body segment can bear a pair of appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s: on the segments of the head, these include two pairs of antennae, the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
s and maxillae; the thoracic segments bear legs, which may be specialised as pereiopods (walking legs) and maxillipeds (feeding legs). Malacostraca and Remipedia (and the hexapods) have abdominal appendages. All other classes of crustaceans have a limbless abdomen, except from a telson and caudal rami which is present in many groups. The abdomen in malacostracans bears pleopods, and ends in a telson, which bears the anus, and is often flanked by uropods to form a tail fan. The number and variety of appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s in different crustaceans may be partly responsible for the group's success.
Crustacean appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s are typically biramous, meaning they are divided into two parts; this includes the second pair of antennae, but not the first, which is usually uniramous, the exception being in the Class Malacostraca where the antennules may be generally biramous or even triramous. It is unclear whether the biramous condition is a derived state which evolved in crustaceans, or whether the second branch of the limb has been lost in all other groups. Trilobites, for instance, also possessed biramous appendages.
The main body cavity is an open circulatory system, where blood is pumped into the haemocoel by a heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
located near the dorsum. Malacostraca have haemocyanin as the oxygen-carrying pigment, while copepods, ostracods, barnacles and branchiopods have haemoglobins. The alimentary canal consists of a straight tube that often has a gizzard-like "gastric mill" for grinding food and a pair of digestive glands that absorb food; this structure goes in a spiral format. Structures that function as kidneys are located near the antennae. A brain exists in the form of ganglia close to the antennae, and a collection of major ganglia is found below the gut.
In many decapods, the first (and sometimes the second) pair of pleopods are specialised in the male for sperm transfer. Many terrestrial crustaceans (such as the Christmas Island red crab) mate seasonally and return to the sea to release the eggs. Others, such as woodlice
Woodlice are terrestrial isopods in the suborder Oniscidea. Their name is derived from being often found in old wood, and from louse, a parasitic insect, although woodlice are neither parasitic nor insects.
Woodlice evolved from marine isopods ...
, lay their eggs on land, albeit in damp conditions. In most decapods, the females retain the eggs until they hatch into free-swimming larvae.
Ecology
 Most crustaceans are aquatic, living in either marine or
Most crustaceans are aquatic, living in either marine or freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
environments, but a few groups have adapted to life on land, such as terrestrial crabs, terrestrial hermit crabs, and woodlice
Woodlice are terrestrial isopods in the suborder Oniscidea. Their name is derived from being often found in old wood, and from louse, a parasitic insect, although woodlice are neither parasitic nor insects.
Woodlice evolved from marine isopods ...
. Marine crustaceans are as ubiquitous in the oceans as insects are on land. Most crustaceans are also motile, moving about independently, although a few taxonomic units are parasitic and live attached to their hosts (including sea lice, fish lice, whale lice, tongue worms, and '' Cymothoa exigua'', all of which may be referred to as "crustacean lice"), and adult barnacles live a sessile life – they are attached headfirst to the substrate and cannot move independently. Some branchiurans are able to withstand rapid changes of salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
and will also switch hosts from marine to non-marine species. Krill are the bottom layer and most important part of the food chain in Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
animal communities. Some crustaceans are significant invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
, such as the Chinese mitten crab, '' Eriocheir sinensis'', and the Asian shore crab, '' Hemigrapsus sanguineus''. Since the opening of the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal (; , ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, Indo-Mediterranean, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest ...
, close to 100 species of crustaceans from the Red Sea and the Indo-Pacific realm have established themselves in the eastern Mediterranean sub-basin, with often significant impact on local ecosystems.
Life cycle


Mating system
Most crustaceans have separate sexes, andreproduce sexually
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex Biological life cycle, life cycle in which a gamete (haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to p ...
. In fact, a recent study explains how the male '' T. californicus'' decide which females to mate with by dietary differences, preferring when the females are algae-fed instead of yeast-fed. A small number are hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
s, including barnacle
Barnacles are arthropods of the subclass (taxonomy), subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea. They are related to crabs and lobsters, with similar Nauplius (larva), nauplius larvae. Barnacles are exclusively marine invertebra ...
s, remipedes, and Cephalocarida. Some may even change sex during the course of their life. Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertiliz ...
is also widespread among crustaceans, where viable eggs are produced by a female without needing fertilisation by a male. This occurs in many branchiopods, some ostracod
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a Class (biology), class of the crustacean, Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant taxon, extant) have been identified,Brandão, S.N.; Antoni ...
s, some isopod
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons ...
s, and certain "higher" crustaceans, such as the '' Marmorkrebs'' crayfish.
Eggs
In many crustaceans, the fertilised eggs are released into the water column, while others have developed a number of mechanisms for holding on to the eggs until they are ready to hatch. Most decapods carry the eggs attached to the pleopods, while peracarids,notostraca
The order Notostraca, containing the single family Triopsidae, is a group of crustaceans known as tadpole shrimp or shield shrimp. The two genera, ''Triops'' and ''Lepidurus'', are considered living fossils, with similar forms having existed since ...
ns, anostracans, and many isopod
Isopoda is an Order (biology), order of crustaceans. Members of this group are called isopods and include both Aquatic animal, aquatic species and Terrestrial animal, terrestrial species such as woodlice. All have rigid, segmented exoskeletons ...
s form a brood pouch from the carapace and thoracic limbs. Female Branchiura do not carry eggs in external ovisacs but attach them in rows to rocks and other objects. Most leptostracans and krill carry the eggs between their thoracic limbs; some copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s carry their eggs in special thin-walled sacs, while others have them attached together in long, tangled strings.
Larvae
Crustaceans exhibit a number of larval forms, of which the earliest and most characteristic is the nauplius. This has three pairs ofappendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s, all emerging from the young animal's head, and a single naupliar eye. In most groups, there are further larval stages, including the zoea (pl. zoeæ or zoeas). This name was given to it when naturalists believed it to be a separate species. It follows the nauplius stage and precedes the post-larva. Zoea larvae swim with their thoracic appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s, as opposed to nauplii, which use cephalic appendages, and megalopa, which use abdominal appendages for swimming. It often has spikes on its carapace, which may assist these small organisms in maintaining directional swimming. In many decapods, due to their accelerated development, the zoea is the first larval stage. In some cases, the zoea stage is followed by the mysis stage, and in others, by the megalopa stage, depending on the crustacean group involved.
Providing camouflage against predators, the otherwise black eyes in several forms of swimming larvae are covered by a thin layer of crystalline isoxanthopterin that gives their eyes the same color as the surrounding water, while tiny holes in the layer allow light to reach the retina. As the larvae mature into adults, the layer migrates to a new position behind the retina where it works as a backscattering mirror that increases the intensity of light passing through the eyes, as seen in many nocturnal animals.
DNA repair
In an effort to understand whetherDNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
processes can protect crustaceans against DNA damage, basic research was conducted to elucidate the repair mechanisms used by '' Penaeus monodon'' (black tiger shrimp). Repair of DNA double-strand breaks was found to be predominantly carried out by accurate homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organi ...
al repair. Another, less accurate process, microhomology-mediated end joining, is also used to repair such breaks. The expression pattern of DNA repair related and DNA damage response genes in the intertidal copepod ''Tigriopus japonicus'' was analyzed after ultraviolet irradiation. This study revealed increased expression of proteins associated with the DNA repair processes of non-homologous end joining, homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organi ...
, base excision repair and DNA mismatch repair.
Classification and phylogeny

 The name "crustacean" dates from the earliest works to describe the animals, including those of Pierre Belon and Guillaume Rondelet, but the name was not used by some later authors, including
The name "crustacean" dates from the earliest works to describe the animals, including those of Pierre Belon and Guillaume Rondelet, but the name was not used by some later authors, including Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
, who included crustaceans among the " Aptera" in his '. The earliest nomenclatural valid work to use the name "Crustacea" was Morten Thrane Brünnich's ' in 1772, although he also included chelicerates in the group.
The subphylum Crustacea comprises almost 67,000 described species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, which is thought to be just to of the total number as most species remain as yet undiscovered. Although most crustaceans are small, their morphology varies greatly and includes both the largest arthropod in the world – the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of – and the smallest, the 100-micrometre
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a uni ...
-long (0.004 in) '' Stygotantulus stocki''. Despite their diversity of form, crustaceans are united by the special larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
l form known as the nauplius.
The exact relationships of the Crustacea to other taxa are not completely settled . Studies based on morphology led to the Pancrustacea hypothesis, in which Crustacea and Hexapoda (insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s and allies) are sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
s. More recent studies using DNA sequences suggest that Crustacea is paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
, with the hexapods nested within a larger Pancrustacea clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
.
The traditional classification of Crustacea based on morphology recognised four to six classes. Bowman and Abele (1982) recognised 652 extant families and 38 orders, organised into six classes: Branchiopoda, Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Maxillopoda, Ostracoda, and Malacostraca. Martin and Davis (2001) updated this classification, retaining the six classes but including 849 extant families in 42 orders. Despite outlining the evidence that Maxillopoda was non-monophyletic, they retained it as one of the six classes, although did suggest that Maxillipoda could be replaced by elevating its subclasses to classes. Since then phylogenetic studies have confirmed the polyphyly of Maxillopoda and the paraphyletic nature of Crustacea with respect to Hexapoda. Recent classifications recognise ten to twelve classes in Crustacea or Pancrustacea, with several former maxillopod subclasses now recognised as classes (e.g. Thecostraca, Tantulocarida, Mystacocarida, Copepoda, Branchiura and Pentastomida).
The following cladogram shows the updated relationships between the different extant groups of the paraphyletic Crustacea in relation to the class Hexapoda.
According to this diagram, the Hexapoda are deep in the Crustacea tree, and any of the Hexapoda is distinctly closer to e.g. a Multicrustacean than an Oligostracan is.
Fossil record
Crustaceans have a rich and extensivefossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
, most of the major groups of crustaceans appear in the fossil record before the end of the Cambrian, namely the Branchiopoda, Maxillopoda (including barnacle
Barnacles are arthropods of the subclass (taxonomy), subclass Cirripedia in the subphylum Crustacean, Crustacea. They are related to crabs and lobsters, with similar Nauplius (larva), nauplius larvae. Barnacles are exclusively marine invertebra ...
s and tongue worms) and Malacostraca; there is some debate as to whether or not Cambrian animals assigned to Ostracoda are truly ostracod
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a Class (biology), class of the crustacean, Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 33,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant taxon, extant) have been identified,Brandão, S.N.; Antoni ...
s, which would otherwise start in the Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
. The only classes to appear later are the Cephalocarida, which have no fossil record, and the Remipedia, which were first described from the fossil '' Tesnusocaris goldichi'', but do not appear until the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
. Most of the early crustaceans are rare, but fossil crustaceans become abundant from the Carboniferous period onwards.
Within the Malacostraca, no fossils are known for krill, while both Hoplocarida and Phyllopoda contain important groups that are now extinct as well as extant members (Hoplocarida: mantis shrimp are extant, while Aeschronectida are extinct; Phyllopoda: Canadaspidida are extinct, while Leptostraca are extant). Cumacea and Isopoda are both known from the Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, as are the first true mantis shrimp. In the Decapoda, prawns and polychelids appear in the Triassic, and shrimp and crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s appear in the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
. The fossil burrow '' Ophiomorpha'' is attributed to ghost shrimps, whereas the fossil burrow ''Camborygma'' is attributed to crayfishes. The Permian–Triassic deposits of Nurra preserve the oldest (Permian: Roadian) fluvial burrows ascribed to ghost shrimps (Decapoda: Axiidea, Gebiidea) and crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidea, Parastacidea), respectively.
However, the great radiation of crustaceans occurred in the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
, particularly in crabs, and may have been driven by the adaptive radiation of their main predators, bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
. The first true lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s also appear in the Cretaceous.
Consumption by humans
 Many crustaceans are consumed by humans, and nearly 10,700,000 tons were harvested in 2007; the vast majority of this output is of decapod crustaceans:
Many crustaceans are consumed by humans, and nearly 10,700,000 tons were harvested in 2007; the vast majority of this output is of decapod crustaceans: crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
s, lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
s, shrimp, crawfish, and prawns. Over 60% by weight of all crustaceans caught for consumption are shrimp and prawns, and nearly 80% is produced in Asia, with China alone producing nearly half the world's total. Non-decapod crustaceans are not widely consumed, with only 118,000 tons of krill being caught, despite krill having one of the greatest biomasses on the planet.
See also
* Pain in crustaceansReferences
Sources
* *Powers, M., Hill, G., Weaver, R., & Goymann, W. (2020). An experimental test of mate choice for red carotenoid coloration in the marine copepod Tigriopus californicus. Ethology., 126(3), 344–352An experimental test of mate choice for red carotenoid coloration in the marine copepod Tigriopus californicus
External links
*Crustacea.net, an online resource on the biology of crustaceans
:
Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are par ...
Crustacea
Tree of Life Web Project
The Crustacean Society
Natural History Collections: Crustacea
University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under th ...
Crustaceans (Crustacea) on the shore of Singapore
: Biodiversity Explorer {{Good article Cambrian Series 2 first appearances Extant Cambrian first appearances Paraphyletic groups Pancrustacea