|
Weston Price
Weston Andrew Valleau Price (September 6, 1870 – January 23, 1948) was a Canadian dentist known primarily for his theories on the relationship between nutrition, dental health, and physical health. He founded the research institute National Dental Association, which became the research section of the American Dental Association, and was the NDA's chairman from 1914 to 1928. Price initially did dental research on the relationship between endodontic therapy and pulpless teeth and broader systemic disease, known as focal infection theory, a theory which resulted in many extractions of tonsils and teeth. Focal infection theory fell out of favor in the 1930s and was pushed to the margins of dentistry by the 1950s. By 1930, Price had shifted his interest to nutrition. In 1939, he published ''Nutrition and Physical Degeneration'',Price, Weston A. Nutrition and Physical Degeneration A Comparison of Primitive and Modern Diets and Their Effects'' 1939. Paul B. Hoeber, Inc; Medical Book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newburgh, Ontario
Newburgh is an unincorporated community in Ontario, Canada. It is recognized as a designated place by Statistics Canada. Demographics In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Newburgh had a population of 695 living in 278 of its 297 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of 729. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021. See also *List of communities in Ontario *List of designated places in Ontario A designated place is a type of geographic unit used by Statistics Canada to disseminate census data. It is usually "a small community that does not meet the criteria used to define incorporated municipalities or Statistics Canada population ce ... References {{coord, 44.325776, N, 76.877355, W, display=title Designated places in Ontario Former villages in Ontario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is geographically divided among the Swiss Plateau, the Swiss Alps, Alps and the Jura Mountains, Jura; the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, whereas most of the country's Demographics of Switzerland, 9 million people are concentrated on the plateau, which hosts List of cities in Switzerland, its largest cities and economic centres, including Zurich, Geneva, and Lausanne. Switzerland is a federal republic composed of Cantons of Switzerland, 26 cantons, with federal authorities based in Bern. It has four main linguistic and cultural regions: German, French, Italian and Romansh language, Romansh. Although most Swiss are German-speaking, national identity is fairly cohesive, being rooted in a common historical background, shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lötschental
The Lötschental () is the largest valley on the northern side of the Rhône valley in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. It lies in the Bernese Alps, with the running down the length of the valley from its source within the Langgletscher (lit.: Long Glacier). Geography The valley extends about from the Lötschenlücke (3178 m) at the top of the Langgletscher to the mouth of the valley at Steg/Gampel (630 m). It is surrounded by 3,000 meter high mountains, including the Bietschhorn (3,934 m), the Hockenhorn (3,293 m), the Wilerhorn (3,307 m) and the Petersgrat (3,205 m). The Jungfrau-Aletsch Protected Area is the most glaciated area in the Swiss Alps, and was declared a Natural World Heritage Site by decision of UNESCO on December 13, 2001, along with southern and eastern parts of the Lötschental. The main villages of the Lötschental are Wiler and Kippel, with 538 and 383 inhabitants respectively. Other villages in the valley include Ferden a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation, where the researcher participates in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these in their local contexts. It had its origin in social and cultural anthropology in the early twentieth century, but has, since then, spread to other social science disciplines, notably sociology. Ethnographers mainly use Qualitative research, qualitative methods, though they may also include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. They are a chemically diverse class of compounds. Dietary supplements containing all eight are referred to as a vitamin B complex. Individual B vitamins are referred to by B-number or by chemical name, such as B1 for thiamine, B2 for riboflavin, and B3 for niacin, while some are more commonly recognized by name than by number, such as pantothenic acid (B5), biotin (B7), and folate (B9). B vitamins are present in protein-rich foods, such as fish, poultry, meat, dairy products, and eggs; they are also found in leafy green vegetables, beans, and peas. Fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals, baked products, and infant formulas, may contain B vitamins. Each B vitamin is either a cofactor (generally a coenzyme) for key metabolic processes or is a precursor needed to make one. List of B vitamins Note: Other substances once thought to be vitamin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
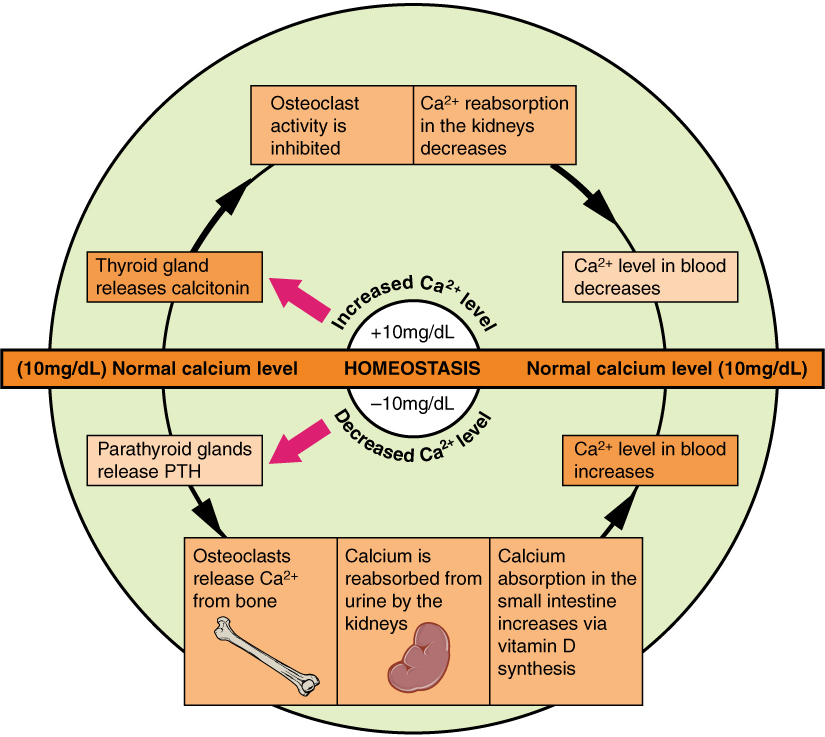
Calcium Metabolism
Calcium metabolism is the movement and regulation of calcium ions (Ca2+) ''in'' (via the gut) and ''out'' (via the gut and kidneys) of the body, and ''between'' body compartments: the blood plasma, the extracellular and intracellular fluids, and bone. Bone acts as a calcium storage center for deposits and withdrawals as needed by the blood via continual bone remodeling. An important aspect of calcium metabolism is plasma calcium homeostasis, the regulation of calcium ions in the blood plasma within narrow limits. The level of the calcium in plasma is regulated by the hormones parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin. PTH is released by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands when the plasma calcium level falls below the normal range in order to raise it; calcitonin is released by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland when the plasma level of calcium is above the normal range in order to lower it. Body compartment content Calcium is the most abundant mineral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
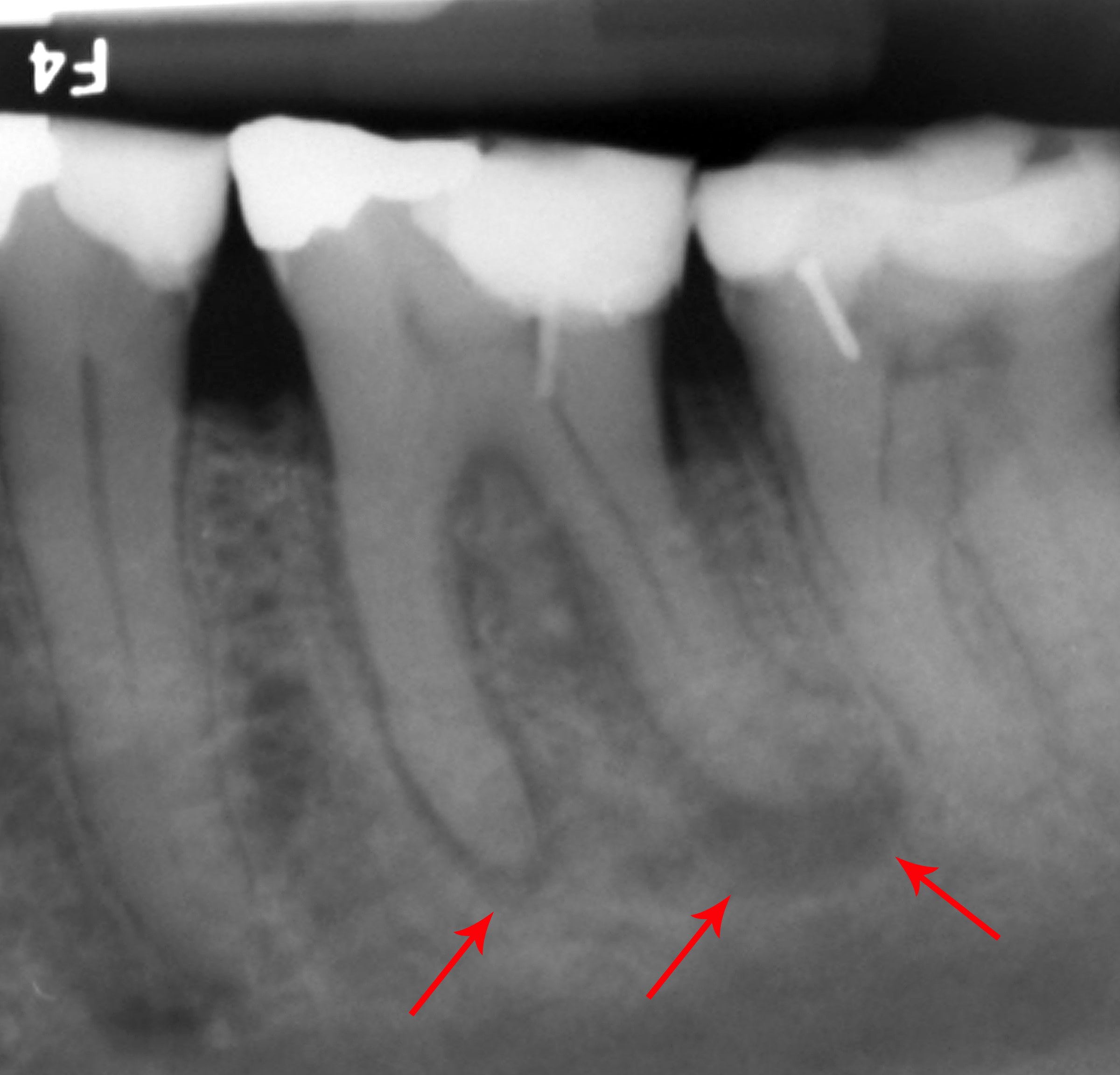
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as caries,The word 'caries' is a mass noun, and is not a plural of 'carie'.'' is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The resulting cavities may be a number of different colors, from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty eating. Complications may include periodontal disease, inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or dental abscess, abscess formation. Tooth regeneration is an ongoing Stem-cell therapy, stem cell–based field of study that aims to find methods to reverse the effects of decay; current methods are based on easing symptoms. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth (Tooth enamel, enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Experiment
A scientific control is an experiment or observation designed to minimize the effects of variables other than the independent variable (i.e. confounding variables). This increases the reliability of the results, often through a comparison between control measurements and the other measurements. Scientific controls are a part of the scientific method. Controlled experiments Controls eliminate alternate explanations of experimental results, especially experimental errors and experimenter bias. Many controls are specific to the type of experiment being performed, as in the molecular markers used in SDS-PAGE experiments, and may simply have the purpose of ensuring that the equipment is working properly. The selection and use of proper controls to ensure that experimental results are valid (for example, absence of confounding variables) can be very difficult. Control measurements may also be used for other purposes: for example, a measurement of a microphone's background noise in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Studies
Animal studies is a recently recognised field in which animals are studied in a variety of cross-disciplinary ways. Scholars who engage in animal studies may be formally trained in a number of diverse fields, including art history, anthropology, biology, film studies, geography, history, psychology, literary studies, museology, philosophy, communication, and sociology. They engage with questions about notions of "animality," "animalization," or "becoming animal," to understand human-made representations of and cultural ideas about "the animal" and what it is to be human by employing various theoretical perspectives. Using these perspectives, those who engage in animal studies seek to understand both human-animal relations now and in the past as defined by our knowledge of them. Because the field is still developing, scholars and others have some freedom to define their own criteria about what issues may structure the field. History Animal studies became popular in the 1970s as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum ( pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |