|
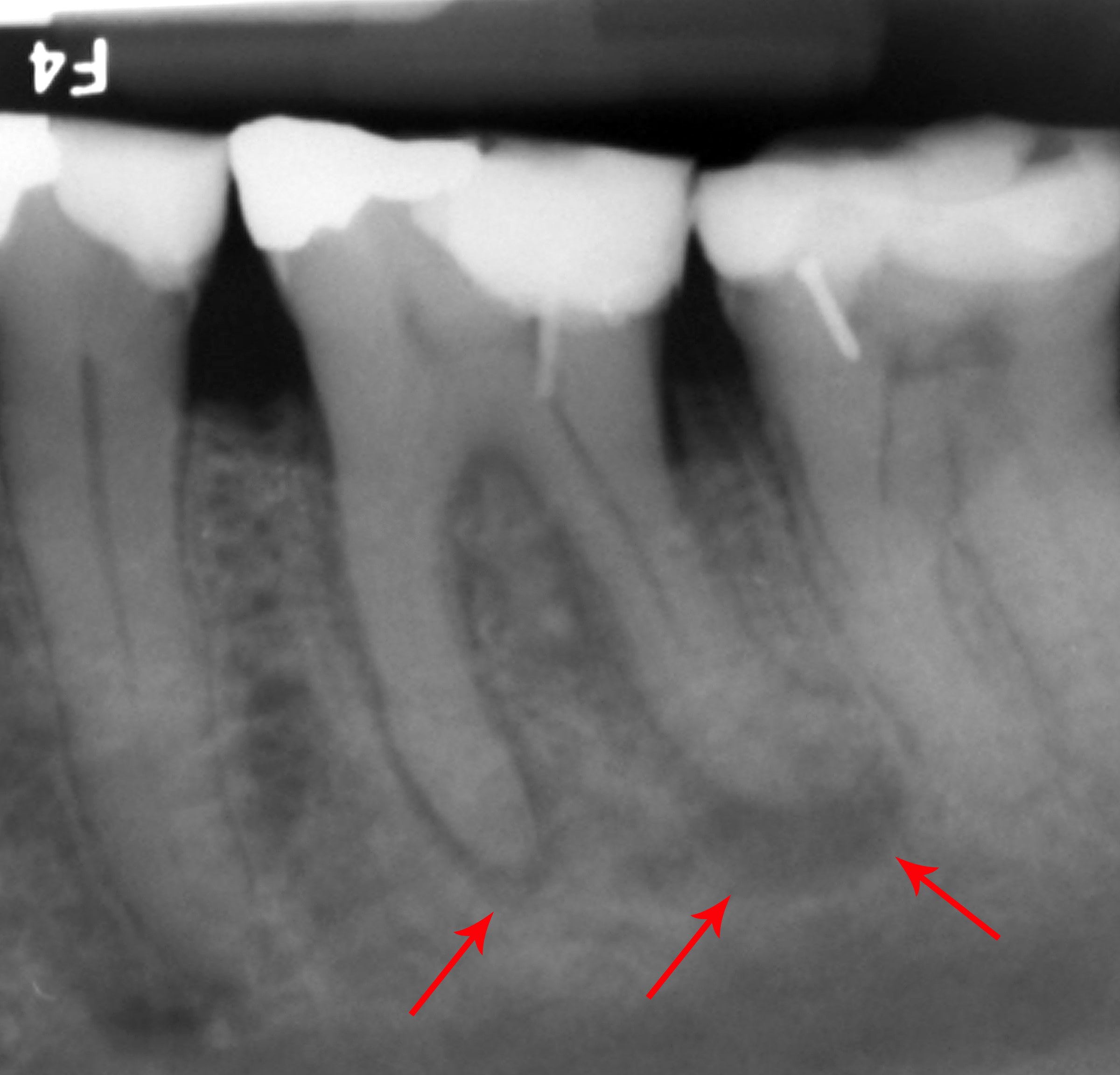
Dental Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum ( pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery (OMFS) is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the Human mouth, mouth, Human head, head and neck, and jaws, as well as facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery. Specialty An oral and maxillofacial surgeon is a specialist surgery, surgeon who treats the entire Craniofacial, craniomaxillofacial complex: Anatomy, anatomical area of the Human mouth, mouth, jaws, face, and Human skull, skull, head and neck as well as associated structures. Depending upon the national jurisdiction, oral and maxillofacial surgery may require a degree in medicine, dentistry or both. United States In the U.S., oral and maxillofacial surgeons, whether possessing a single or dual degree, may further specialise after residency, undergoing additional one or two year sub-specialty oral and maxillofacial surgery fellowship training in the following areas: *Cosmetic surgery#Cosmetic surgery, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
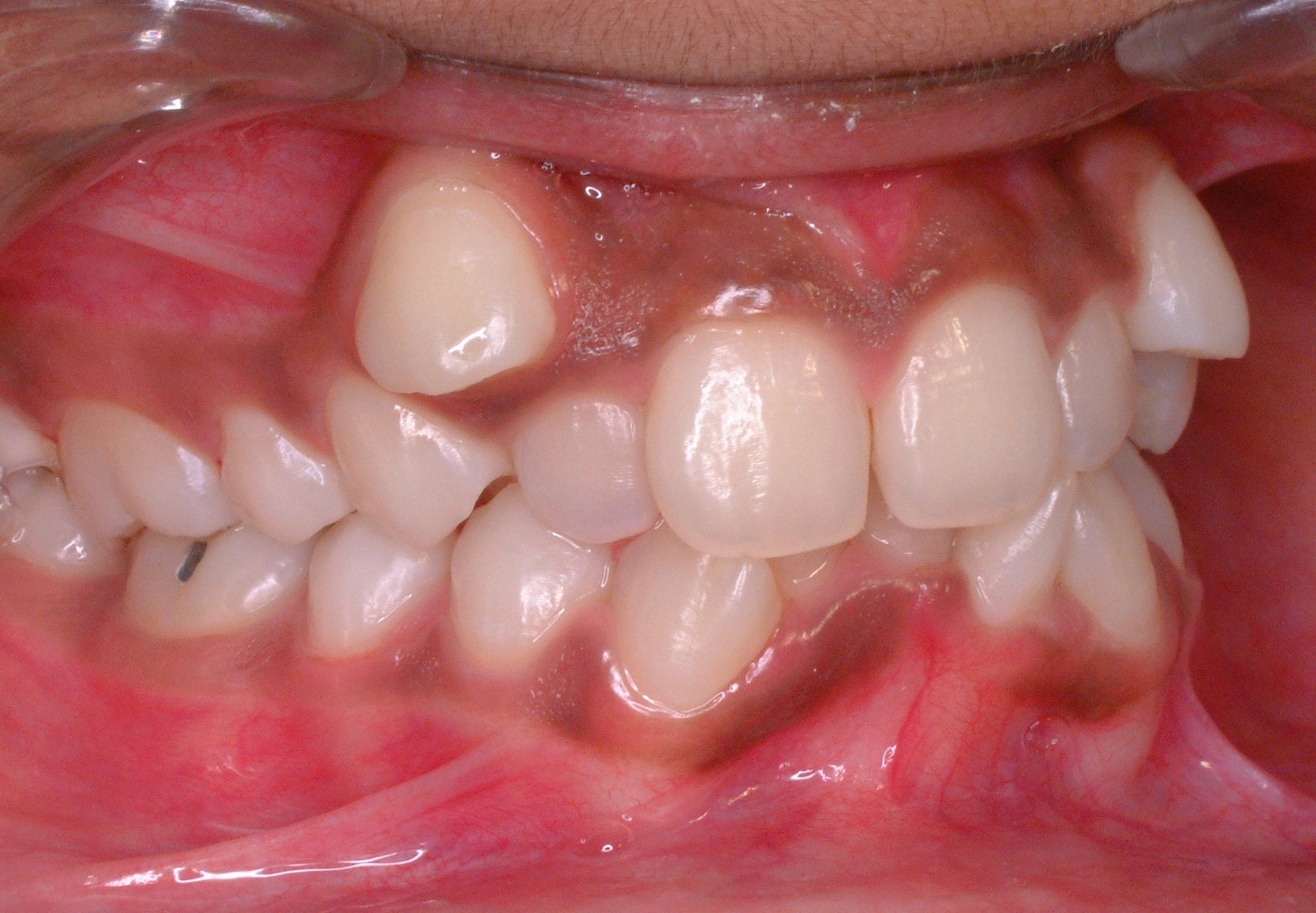
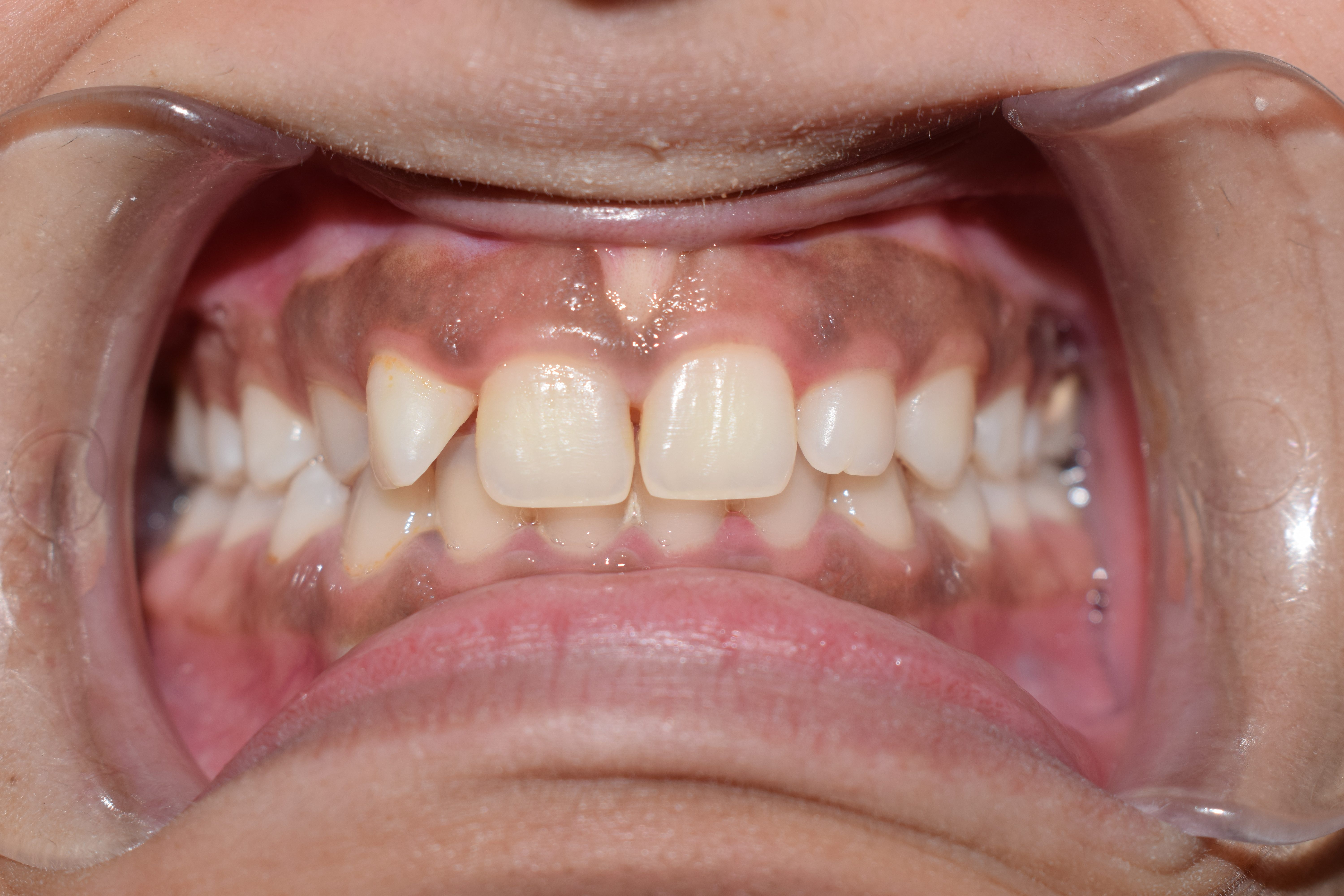
Teeth Crowding
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855–1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word derives . The malocclusion classification is based on the relationship of the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar and the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. If this molar relationship exists, then the teeth can align into normal occlusion. According to Angle, malocclusion is any deviation of the occlusion from the ideal. However, assessment for malocclusion should also take into account aesthetics and the impact on functionality. If these aspects are acceptable to the patient despite meeting the formal definition of malocclusion, then treatment may not be necessary. It is estimated that nearly 30% of the population have malocclusions that are ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products for oral ulcers. It is combined with antipyrine to form A/B ear drops. In the US, products containing benzocaine for oral application are contraindicated in children younger than two years old. In the European Union, the contraindication applies to children under 12 years of age. It was first synthesised in 1890 in Germany and approved for medical use in 1902. Medical uses Benzocaine is indicated to treat a variety of pain-related conditions. It may be used for: * Local anesthesia of oral and pharyngeal mucous membranes (sore throat, cold sores, mouth ulcers, toothache, sore gums, denture irritation)AHFS Drug Information 2007. McEvoy GK, ed. Benzocaine. Bethesda, MD: American Society of Health- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical Anesthetic
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams, ointments, aerosols, sprays, lotions, and jellies. Examples include benzocaine, butamben, dibucaine, lidocaine, oxybuprocaine, pramoxine, proxymetacaine (proparacaine), and tetracaine (also named amethocaine). Usage Topical anesthetics are used to relieve pain and itching caused by conditions such as sunburn or other minor burns, insect bites or stings, poison ivy, poison oak, poison sumac, and minor cuts and scratches. Topical anesthetics are used in ophthalmology and optometry to numb the surface of the eye (the outermost layers of the cornea and conjunctiva) to: * Perform a contact/applanation tonometry. * Perform a Schirmer's test (The Schirmer's test is sometimes used with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articaine
Articaine is a dental amide-type local anesthetic. It is the most widely used local anesthetic in a number of European countriesOertel R, Ebert U, Rahn R, Kirch W. Clinical pharmacokinetics of articaine. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 Dec;33(6):418. and is available in many countries. It is the only local anaesthetic to contain a thiophene ring, meaning it can be described as 'thiophenic'; this conveys lipid solubility. History This drug was synthesized by pharmacologist and chemist Robert Rippel. Muschaweck received a "O. Schmiedeberg" medal by the German Society for Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology for his work in 2002. It was brought to the German market in 1976 by Hoechst AG, a life-sciences German company (now Sanofi-Aventis), under the brand name Ultracain. This drug was also referred to as "carticaine" until 1984. In 1983 it was brought into the North American market, to Canada, under the name Ultracaine for dental use, manufactured in Germany and distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding. If injected intravenously, it may cause cerebral effects such as confusion, changes in vision, numbness, tingling, and vomiting. It can cause low blood pressure and an irregular heart rate. There are concerns that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage. It appears to be generally safe for use in pregnancy. A lower dose may be required in those with liver problems. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Alveolar Nerve Anaesthesia
Inferior alveolar nerve block (abbreviated to IANB, and also termed inferior alveolar nerve anesthesia or inferior dental block) is a nerve block technique which induces anesthesia (numbness) in the areas of the mouth and face innervated by one of the inferior alveolar nerves which are paired on the left and right side. These areas are the skin and mucous membranes of the lower lip, the skin of the chin, the lower teeth and the labial gingiva of the anterior teeth, all unilaterally to the midline of the side on which the block is administered. However, depending on technique, the long buccal nerve may not be anesthetized by an IANB and therefore an area of buccal gingiva adjacent to the lower posterior teeth will retain normal sensation unless that nerve is anesthetized separately, via a (long) buccal nerve block. The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, the third division of the trigeminal nerve. This procedure attempts to anaesthetise the inferior alveol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gums
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle function) also can be induced. Classification LAs are of 2 types: *Clinical LAs: ** amino amide LAs ** amino ester LAs *Synthetic LAs **Cocaine derivatives Synthetic cocaine-derived LAs differ from cocaine because they have a much lower abuse potential and do not cause hypertension vasoconstriction (with few exceptions). The suffix "-caine" at the ends of these medication names is derived from the word "cocaine", because cocaine was formerly used as a local anesthetic. Examples Short Duration of Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy 050326-N-0357S-021 Cmdr
US or Us most often refers to: * Us (pronoun), ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * Us (Brother Ali album), ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * Us (Empress Of album), ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * Us (Mull Historical Society album), ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * Us (Peter Gabriel album), ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * Us (EP), ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * Us (James Bay song), "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * Us (Jennifer Lopez song), "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * Us (Regina Spektor song), "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * Us (Gracie Abrams song), "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from ''Fantasea (mixtape), Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consent
Consent occurs when one person voluntarily agrees to the proposal or desires of another. It is a term of common speech, with specific definitions used in such fields as the law, medicine, research, and sexual consent. Consent as understood in specific contexts may differ from its everyday meaning. For example, a person with a mental disorder, a low mental age, or under the legal age of sexual consent may willingly engage in a sexual act that still fails to meet the legal threshold for consent as defined by applicable law. United Nations agencies and initiatives in sex education programs believe that teaching the topic of consent as part of a comprehensive sexuality education is beneficial. Types of consent include implied consent, express consent, informed consent and unanimous consent. Types * An express consent is one that is unmistakably stated, rather than implied. It may be given in writing, e.g. contract, by speech (orally), or non-verbally, e.g. by a clear gestu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |