|
Westerwood Golf Course - Geograph
Westerwood is an area in the north-east of Cumbernauld in North Lanarkshire, Scotland. Historically it was the site of a Roman Fort of which a video reconstruction has been produced. In the past two decades, new housing developments have been built around the Westerwood Hotel and Golf Course. The golf course, which was designed by Seve Ballesteros and Dave Thomas, is located on the north side of the town, close to Cumbernauld Airport. Westerwood Community Council was set up for local residents and a committee has been appointed. Neighbouring villages which are outside of Cumbernauld include Dullatur to the north-west and Castlecary to the east. Roman Heritage Historically, Westerwood is the site of a Roman Fort on the Antonine Wall. Its neighbouring forts were Croy Hill to the west and Castlecary to the east. At Tollpark, is one of the best preserved continuous sections of the whole Wall, between the forts of Castlecary and Westerwood. There may have been a signal tower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumbernauld Airport From The Air (geograph 4998255)
Cumbernauld (; gd, Comar nan Allt, meeting of the streams) is a large town in the historic county of Dunbartonshire and council area of North Lanarkshire, Scotland. It is the tenth most-populous locality in Scotland and the most populated town in North Lanarkshire, positioned in the centre of Scotland's Central Belt. Geographically, Cumbernauld sits between east and west, being on the Scottish watershed between the Forth and the Clyde; however, it is culturally more weighted towards Glasgow and the New Town's planners aimed to fill 80% of its houses from Scotland's largest city to reduce housing pressure there. Traces of Roman occupation are still visible, for example at Westerwood and, less conspicuously, north of the M80 where the legionaries surfaced the Via Flavii, later called the "Auld Cley Road". This is acknowledged in Cumbernauld Community Park, also site of Scotland's only visible open-air Roman altar, in the shadow of the imposing Carrickstone Water Tower. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areas Of Cumbernauld
Area is the quantity that expresses the extent of a region on the plane or on a curved surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while ''surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. It is the two-dimensional analogue of the length of a curve (a one-dimensional concept) or the volume of a solid (a three-dimensional concept). The area of a shape can be measured by comparing the shape to squares of a fixed size. In the International System of Units (SI), the standard unit of area is the square metre (written as m2), which is the area of a square whose sides are one metre long. A shape with an area of three square metres would have the same area as three such squares ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvanus (mythology)
Silvanus (; meaning "of the woods" in Latin) was a Roman tutelary deity of woods and uncultivated lands. As protector of the forest (''sylvestris deus''), he especially presided over plantations and delighted in trees growing wild.Tibullus II.5.27, 30.Lucan. ''Pharsalia'' III.402.Pliny the Elder. ''Naturalis historia'' XII.2. He is also described as a god watching over the fields and husbandmen, protecting in particular the boundaries of fields.Horace. '' Epodes'' II.21-22. The similarly named Etruscan deity Selvans may be a borrowing of Silvanus, or not even related in origin.Peter F. Dorcey, ''The Cult of Silvanus: A Study in Roman Folk Religion'' (Brill, 1992), pp. 10–1online noting earlier efforts to press an Etruscan etymology on Silvanus. Silvanus is described as the divinity protecting the flocks of cattle, warding off wolves, and promoting their fertility.Virgil. ''Aeneid'' VIII.600-1.Cato the Elder. ''De Re Rustica'' 83 Dolabella, a rural engineer of whom only a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phallus
A phallus is a penis (especially when erect), an object that resembles a penis, or a mimetic image of an erect penis. In art history a figure with an erect penis is described as ithyphallic. Any object that symbolically—or, more precisely, iconically—resembles a penis may also be referred to as a phallus; however, such objects are more often referred to as being phallic (as in "phallic symbol"). Such symbols often represent fertility and cultural implications that are associated with the male sexual organ, as well as the male orgasm. Etymology The term is a loanword from Latin ''phallus'', itself borrowed from Greek (''phallos''), which is ultimately a derivation from the Proto-Indo-European root *''bʰel''- "to inflate, swell". Compare with Old Norse (and modern Icelandic) ''boli'' " bull", Old English ''bulluc'' " bullock", Greek " whale". Archaeology The Hohle phallus, a 28,000-year-old siltstone phallus discovered in the Hohle Fels cave and reassembled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunterian Museum
The Hunterian is a complex of museums located in and operated by the University of Glasgow in Glasgow, Scotland. It is the oldest museum in Scotland. It covers the Hunterian Museum, the Hunterian Art Gallery, the Mackintosh House, the Zoology Museum and the Anatomy Museum, which are all located in various buildings on the main campus of the university in the west end of Glasgow. History In 1783, William Hunter, a Scottish anatomist and physician who studied at the University of Glasgow, died in London. His will stipulated that his substantial and varied collections should be donated to the University of Glasgow. Hunter, writing to Dr William Cullen, stated that they were "to be well and carefully packed up and safely conveyed to Glasgow and delivered to the Principal and Faculty of the College of Glasgow to whom I give and bequeath the same to be kept and preserved by them and their successors for ever... in such sort, way, manner and form as ... shall seem most fit and most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Macdonald (archaeologist)
Sir George Macdonald (30 January 1862 – 9 August 1940) was a British archaeologist and numismatist who studied the Antonine Wall. Life Macdonald was born in Elgin on 30 January 1862. His father, James Macdonald, was a schoolmaster at Elgin Academy and his mother was Margaret Raff. His father moved from Elgin Academy to Ayr Academy during his early youth. Macdonald was educated at Ayr Academy where his father had become rector. He studied in Germany and France, then at the University of Edinburgh and Balliol College, Oxford, graduating Master of Arts in 1887. He then took up a post teaching Classics at Kelvinside Academy. In 1892 he began lecturing in Greek at Glasgow University as Gilbert Murray's assistant. At this time he lived at 21 Lilybank Gardens in Glasgow. Macdonald was involved in archaeological excavations from 1902, when he excavated Bar Hill Fort with Alexander Park. One of his obituaries says "scholarship is not incompatible with administrative ability". He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
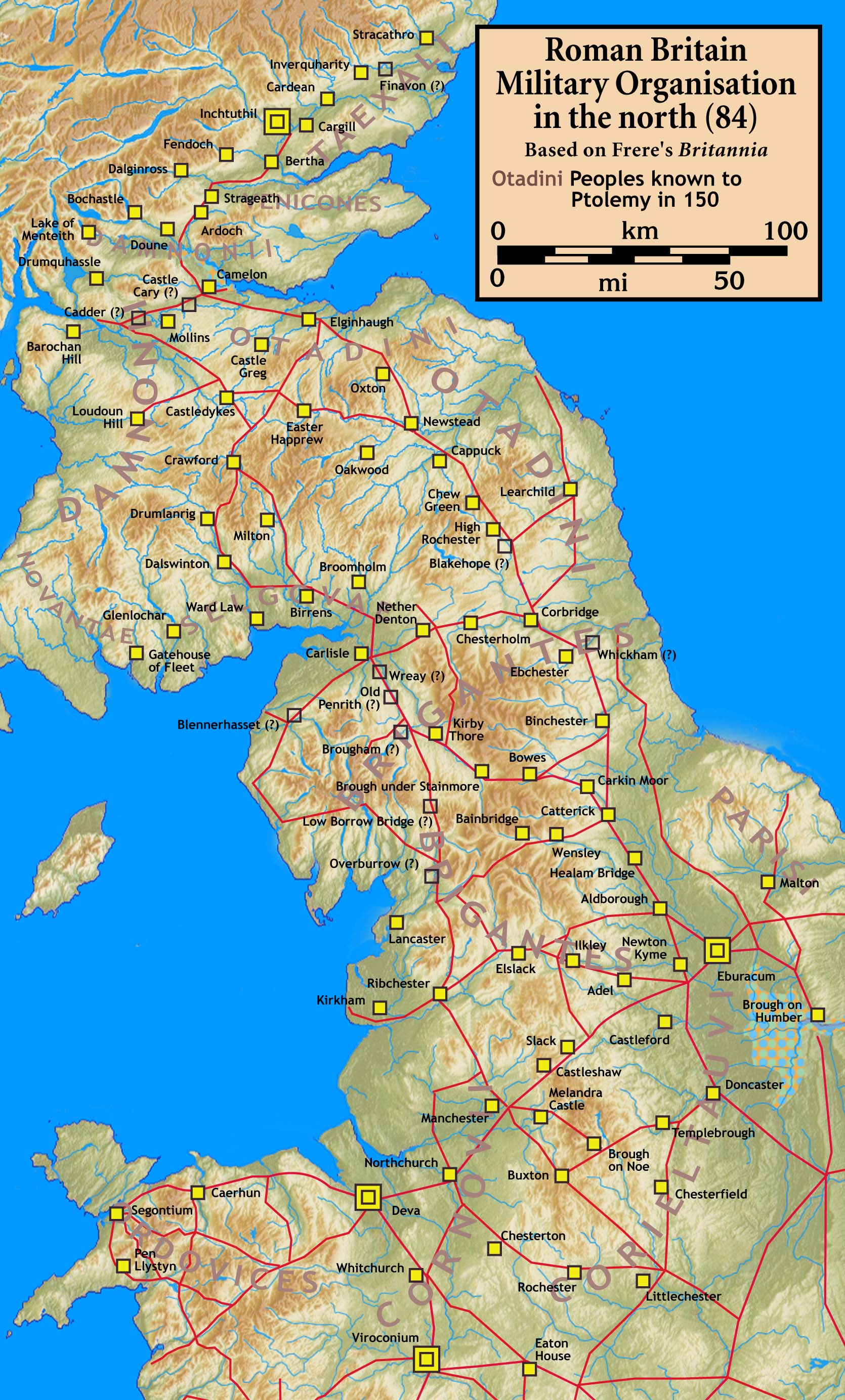
Blatobulgium
Blatobulgium was a Roman fort, located at the modern-day site known as Birrens, in Dumfriesshire, Scotland. Name Blatobulgium is recorded in the Antonine Itinerary. The name derives from the Brittonic roots ''*blāto-'' 'bloom, blossom' or ''*blāto-'' (from earlier ''*mlāto-''), 'flour' and ''*bolgo-'', 'bag, bulge'. The name may mean 'flowery hillock' or 'flowery hollow'. However, as there are granaries at the fort, Blatobulgium may be a nickname meaning ' Flour Sacks'. History The fort formed the northern terminus of the Roman-era Watling Street (using an extended definition of this road), or more simply Route 2 of the Antonine Itinerary. It was located in the territory of the Selgovae. Birrens was first occupied in the Flavian Flavian may refer to: * A member of the Flavian dynasty of Roman emperors, during the late 1st century AD, or their works * Flavian Zeija, a Ugandan lawyer, academic and judge. Principal Judge of Uganda, since December 2019. * A person named Flav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kissing Gate
A kissing gate is a gate that allows people, but not livestock, to pass through. The normal construction is a half-round, rectangular, trapezoidal or V-shaped part-enclosure with the free end of a hinged gate trapped between its arms. When the gate is touching an arm it must be pulled or pushed to pass through. The gate may need to be pushed to give access to the small enclosure, and when in the enclosure the person pulls the gate past the bulk of the enclosure to exit. Some examples have latches. Most are installed self-closing, to the side away from the pasture (livestock field), by hinge geometry, a spring or weight. The gate may be made large enough to fit wheelchairs and the like. Alternatively, to allow pushchairs, wheelchairs, bicycles, and other things too large to pass through, a conventional gate with a less consistent swing-back or default animal-proof mechanism may be nearby, or an additional latch may allow it to open more fully. The name comes from the gate mere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croy Hill
Croy Hill was a Roman fort, fortlet, and probable temporary camp on the Antonine Wall, near Croy, to the north east of the village in Scotland. Two communication platforms known as ‘expansions’ can be seen to the west of the fortlet. Alexander Park excavated the site in 1890-1891. Sir George Macdonald wrote about his excavation of the site which occurred in 1920, 1931, and 1935. At Croy Hill, the ditch in front of the rampart was not excavated by the Romans. It is likely that hard basalt and dolerite of the hill was virtually impossible to shape with Roman tools. This is the only place along the Wall where the ditch wasn't dug. There is a bath house just outside one fort. A video reconstruction of the site has been produced. At Croy Hill three religious objects have been found: one, as fragments of a relief of Jupiter Dolichenus; a second, an altar dedicated to Nymphs; and a third, identified as an altar to Mars. Other artefacts found include a bronze arm purse, a storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall, known to the Romans as ''Vallum Antonini'', was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twenty years after Hadrian's Wall to the south, and intended to supersede it, while it was garrisoned it was the northernmost frontier barrier of the Roman Empire. It spanned approximately and was about high and wide. Lidar scans have been carried out to establish the length of the wall and the Roman distance units used. Security was bolstered by a deep ditch on the northern side. It is thought that there was a wooden palisade on top of the turf. The barrier was the second of two "great walls" created by the Romans in Great Britain in the second century AD. Its ruins are less evident than those of the better-known and longer Hadrian's Wall to the south, primarily because the turf and wood wall has largely weathered away, unlike its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)