Blatobulgium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Blatobulgium was a
Blatobulgium was a


 Blatobulgium was a
Blatobulgium was a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
fort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
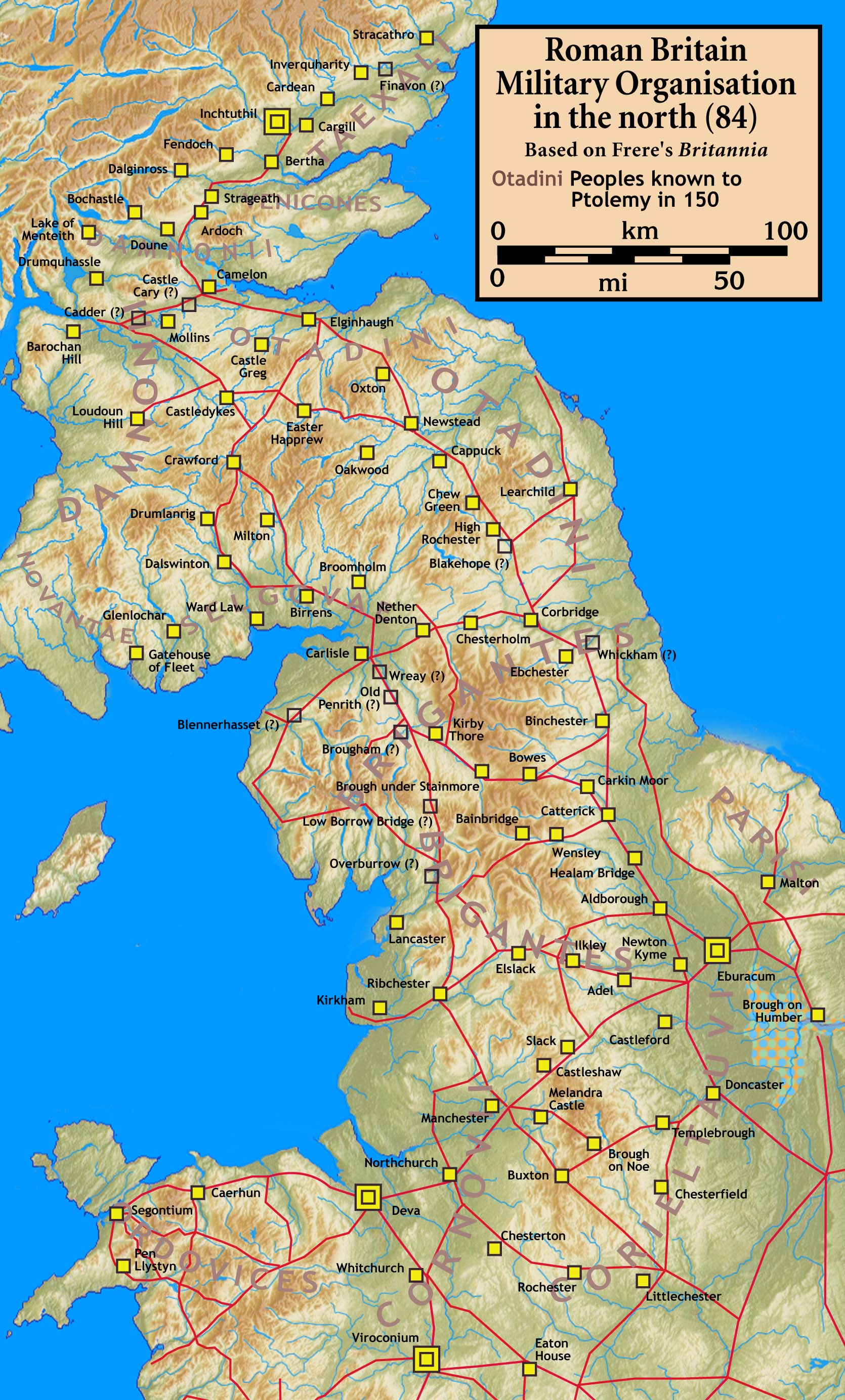
, located at the modern-day site known as Birrens, in Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries () is a Counties of Scotland, historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the hi ...
, Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
. It protected the main western road to Scotland.
It was one of the "outpost forts" outside the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
when the frontier was on Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Ru ...
and was located about 11 miles from the Castra Exploratorum fort (Netherby, Cumbria).
Name
Blatobulgium is recorded in theAntonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary (, "Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is an , a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly in part from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes t ...
. The name derives from the Brittonic roots ''*blāto-'' 'bloom, blossom' or ''*blāto-'' (from earlier ''*mlāto-''), 'flour' and ''*bolgo-'', 'bag, bulge'. The name may mean 'flowery hillock' or 'flowery hollow'. However, as there are granaries at the fort, Blatobulgium may be a nickname meaning ' Flour Sacks'.
History
There are several camps near Birrens at least one of which was first occupied in the Flavian period from 79 AD onwards probably during theAgricola
Agricola, the Latin word for farmer, may also refer to:
People Cognomen or given name
:''In chronological order''
* Gnaeus Julius Agricola (40–93), Roman governor of Britannia (AD 77–85)
* Sextus Calpurnius Agricola, Roman governor of the m ...
n campaigns, when its internal buildings were presumably of timber. Under Hadrian when the frontier was established on Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Ru ...
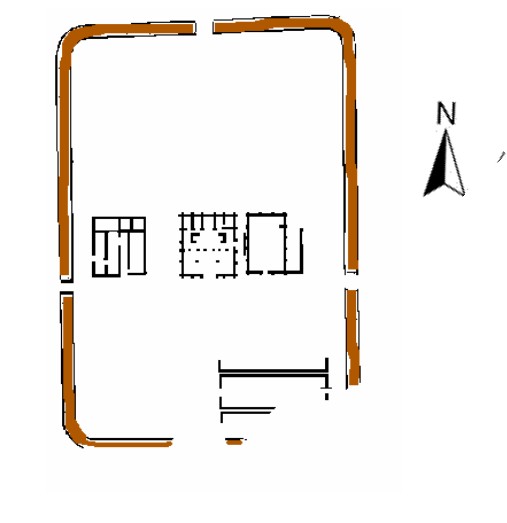
soon after 122, a new fort was constructed as an outpost fort on the site of a late 1st century fortlet with central timber buildings and a large western annexe. The visible fort and its internal buildings date from the Antonine period around 142 after the reconquest of the Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
when the earlier fort was rebuilt and enlarged to protect the western road to the Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall () was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twenty years after Hadrian's Wall to the south ...
and to accommodate a nominally 1,000-strong ''milliaria equitata'' garrison of the 1st Cohort Nerviana Germanorum, a mixed unit of cavalry and infantry of the auxiliary army. It was destroyed perhaps by enemy action around 155 and the replacement stone buildings, although of much poorer quality, in the second Antonine period dating to 159 onwards were for the new garrison of the 2nd Cohort of Tungrians, likewise ''milliaria equitata''. From about 163 it was again an outpost of Hadrian's Wall and was finally abandoned by about 184.
The later fort formed the northern terminus of the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
-era Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England, running from Dover and London in the southeast, via St Albans to Wroxeter. The road crosses the River Thames at London and was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the M ...
(using an extended definition of this road), or more simply Route 2 of the Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary (, "Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is an , a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly in part from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes t ...
. It was located in the territory of the Selgovae.
Finds
There have been more inscribed and sculptured stones found at Birrens than anywhere else in Scotland. An altar stone dedicated to the Celtic goddess Ricagambeda was found at Birrens.References
History of Dumfriesshire Roman auxiliary forts in Scotland Scheduled monuments in Dumfries and Galloway {{Scotland-stub